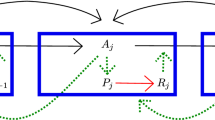
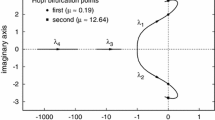
Abstract
Transport models of growth hormones can be used to reproduce the hormone accumulations that occur in plant organs. Mostly, these accumulation patterns are calculated using time step methods, even though only the resulting steady state patterns of the model are of interest. We examine the steady state solutions of the hormone transport model of Smith et al. (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(5):1301–1306, 2006) for a one-dimensional row of plant cells. We search for the steady state solutions as a function of three of the model parameters by using numerical continuation methods and bifurcation analysis. These methods are more adequate for solving steady state problems than time step methods. We discuss a trivial solution where the concentrations of hormones are equal in all cells and examine its stability region. We identify two generic bifurcation scenarios through which the trivial solution loses its stability. The trivial solution becomes either a steady state pattern with regular spaced peaks or a pattern where the concentration is periodic in time.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allgower E, Georg K (1994) Numerical path following. Springer, Berlin
Bayer EM, Smith RS, Mandel T, Nakayama N, Sauer M, Prusinkiewcz P, Kuhlemeier C (2009) Integration of transport-based models for phyllotaxis and midvein formation. Genes Dev 23:373–384
Benková E, Michniewicz M, Sauer M, Teichmann T, Seifertová D, Jürgens G, Friml J (2003) Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell 115:591–602
Bilsborough G, Runions A, Barkoulas M, Jenkins H, Hasson A, Galinha C, Laufs P, Hay A, Prusinkiewicz P, Tsiantis M (2011) Model for the regulation of arabidopsis thaliana leaf margin development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:3424–3429
Champneys AR, Sandstede B (2007) Numerical computation of coherent structures. In: Krauskopf B, Osinga HM, Galan-Vioque J (eds) Numerical continuation methods for dynamical systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 331–358
Clewley R, Sherwood W, LaMar M, Guckenheimer J (2007) Pydstool, a software environment for dynamical systems modeling. http://pydstool.sourceforge.net
De Smet I, Tetsumura T, De Rybel B, Frey N, Laplaze L, Casimiro I, Swarup R, Naudts M, Vanneste S, Audenaert D, Inzé D, Bennet M, Beeckman T (2007) Auxin-dependent regulation of lateral root positioning in the basal meristem of arabidopsis. Development 134:681–690
Dhondt S, Van Haerenborgh D, Van Cauwenbergh C, Merks R, Philips W, Beemster G, Inzé D (2011) Quantitative analysis of venation patterns of arabidopsis leaves by supervised image analysis. Plant J 69:553–563
Doedel E, Champneys A, Fairgrieve T, Kuznetsov Y, Sandstede B, Wang X (1997) Continuation and bifurcation software for ordinary differential equations (with homcont). Available by anonymous ftp from ftp cs concordia ca, directory pub/doedel/auto
Draelants D, Vanroose W, Broeckhove J, Beemster GTS (2012) Influence of an exogenous model parameter on the steady states in an auxin transport model. Proceedings PMA (to appear)
Grieneisen VA, Xu J, Marée AFM, Hogeweg P, Scheres B (2007) Auxin transport is sufficient to generate a maximum and gradient guiding root growth. Nature 449:1008–1013
Hairer E, Nørsett S, Wanner G (2009) Solving ordinary differential equations I: nonstiff problems. Springer, Berlin
Hoyle RB (2006) Pattern formation: an introduction to methods. University Press, Cambridge
Jönsson H, Heisler M, Shapiro B, Meyerowitz E, Mjolsness E (2006) An auxin-driven polarized transport model for phyllotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(5):1633–1638
Kelley CT (1995) Iterative methods for linear and nonlinear equations, Society for Industrial Mathematics
Krauskopf B, Osinga H, Galán-Vioque J (2007) Numerical continuation methods for dynamical systems: path following and boundary value problems. Springer, Berlin
Merks RMH, Van de Peer Y, Inzé D, Beemster GTS (2007) Canalization without flux sensors: a traveling-wave hypothesis. Trends Plant Sci 12:384–390
Muday GK, DeLong A (2001) Polar auxin transport: controlling where and how much. Trends Plant Sci 6:535–542
Palme K, Gälweiler L (1999) Pin-pointing the molecular basis of auxin transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2(5):375–381
Péret B, Swarup K, Ferguson A, Seth M, Yang Y, Dhondt S, James N, Casimiro I, Perry P, Syed A, Yang H, Reemer J, Venison E, Howell C, Perez-Amador MA, Yun J, Alonso J, Beemster GTS, Laplaze L, Murphy A, Bennett MJ, Nielsen E, Swarup R (2012) AUX/LAX genes encode a family of auxin influx transporters that perform distinct function during Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell (submitted)
Reinhardt D, Pesce E, Stieger P, Mandel T, Baltensperger K, Bennett M, Traas J, Friml J, Kuhlemeier C (2003) Regulation of phyllotaxis by polar auxin transport. Nature 426(6964):255–260
Salinger A, Burroughs E, Pawlowski R, Phipps E, Romero L (2005) Bifurcation tracking algorithms and software for large scale applications. Int J Bifurc Chaos Appl Sci Eng 15(3):1015–1032
Scarpella E, Marcos D, Friml J, Berleth T (2006) Control of leaf vascular patterning by polar auxin transport. Genes Dev 20:1015–1027
Seydel R (1994) Practical bifurcation and stability analysis: from equilibrium to chaos, vol 5. Springer, Berlin
Shirakawa M, Ueda H, Shimada T, Nishiyama C, Hara-Nishimura I (2009) Vacuolar SNAREs function in the formation of the leaf vascular network by regulating auxin distribution. Plant Cell Physiol 50(7):1319–1328
Smith R, Guyomarc’h S, Mandel T, Reinhardt D, Kuhlemeier C, Prusinkiewicz P (2006) A plausible model of phyllotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(5):1301–1306
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge fruitful discussions with Dirk De Vos and Przemyslaw Klosiewicz. DD acknowledges financial support from the Department of Mathematics and Computer Science of the University of Antwerp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is part of the Geconcerteerde Onderzoeksactie (G.O.A.) research grant “A System Biology Approach of Leaf Morphogenesis” granted by the research council of the University of Antwerp.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Draelants, D., Broeckhove, J., Beemster, G.T.S. et al. Numerical bifurcation analysis of the pattern formation in a cell based auxin transport model. J. Math. Biol. 67, 1279–1305 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-012-0588-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-012-0588-8
Keywords
- Bifurcation analysis
- Pattern formation
- Parameter dependence
- Auxin transport model
- Stability
- Periodic solution pattern