Abstract
Background
Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) represents a novel molecular target in non-small-cell-lung cancer (NSCLC). IGF1R and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation are essential to mediate tumor cell survival, proliferation, and invasion. This study investigates the prognostic role of IGF1R and EGFR in surgically resected NSCLC.
Materials and methods
IGF1R and EGFR copy number gain (CNG) were tested by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and protein expression by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in 125 stage I–II–IIIA NSCLC patients.
Results
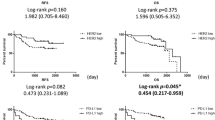
Fourty-six tumors (40.3 %) were IGF1R FISH-positive (FISH+), and 76 (67.2 %) were EGFR FISH+. Tumors with concomitant IGF1R/EGFR FISH+ were observed in 34 cases (30.1 %). IGF1R and EGFR FISH+ were associated with SCC histology (p = 0.01 and p = 0.04, respectively). IGF1R and EGFR protein over-expression (IHC+) were detected in 45 (36.0 %) and 69 (55.2 %) cases, respectively. Tumors with concomitant IGF1R/EGFR IHC+ were detected in 31 (24.8 %) patients. IGF1R/EGFR FISH+ and IGF1R/EGFR IHC+ were significantly associated (χ2 = 4.02, p = 0.04). Patients with IGF1R/EGFR FISH+ and IGF1R/EGFR IHC+ were associated with shorter disease-free survival (DFS) (p = 0.05 and p = 0.05, respectively). Patients with concomitant IGF1R/EGFR FISH+/IHC+ had a worse DFS and overall survival (p = 0.005 and p = 0.01, respectively). The multivariate model confirmed that IGF1R/EGFR FISH+/IHC+ (hazard ratio (HR), 4.08; p = 0.01) and tumor stage (II–III vs I) (HR, 4.77; p = 0.003) were significantly associated with worse DFS.
Conclusions
IGF1R/EGFR FISH+ correlates with IGF1R/EGFR IHC+. IGF1R/EGFR FISH+/IHC+ is an independent negative prognostic factor for DFS in early NSCLC. These features may have important implications for future anti-IGF1R therapeutic approaches.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maxwell PD (2001) Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol 2:533–543
Jemal A, Thomas A, Murray T et al (2002) Cancer statistics 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2:23–47
Dufourny B, Alblas J, van Teeffelen HA et al (1997) Mitogenic signalling of insulin-like growth factor I in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and is independent of mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 272:31163–31171
Khandwala HM, McCutcheon IE, Flyvbjerg A et al (2000) The effects of insulin-like growth factors on tumorigenesis and neoplastic growth. Endocr Rev 21:215–244
Baserga R, Hongo A, Rubini M et al (1997) The IGF-I receptor in cell growth, transformation and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1332:F105–F126
Blakesley VA, Stannard BS, Kalebic T et al (1997) Role of the IGF-I receptor in mutagenesis and tumour promotion. J Endocrinol 152:339–344
LeRoith D, Roberts CT Jr (2003) The insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett 195(2):127–137
Haluska P, Shaw HM, Batzel GN et al (2007) Phase I dose escalation study of the anti insulin-like growth factor-I receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in patients with refractory solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 13:5834–5840
Kurzrock R, Patnaik A, Aisner J et al (2010) A phase I study of weekly R1507, a human monoclonal antibody insulin-like growth factor-I receptor antagonist, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 16(8):2458–2465
Tolcher AW, Sarantopoulos J, Patnaik A et al (2009) Phase I, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of AMG 479, a fully human monoclonal antibody to insulin-like growth factor receptor 1. J Clin Oncol 27(34):5800–5807
Karp DD, Paz-Ares LG, Novello S et al (2009) Phase II study of the anti-insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor antibody CP-751,871 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in previously untreated, locally advanced, or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:2516–2522
Morgillo F, Woo JK, Kim ES et al (2006) Heterodimerization of insulin-like growth factor receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor and induction of survivin expression counteract the antitumor action of erlotinib. Cancer Res 66:10100–10111
Jones HE, Goddard L, Gee JM et al (2004) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signalling and acquired resistance to gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) in human breast and prostate cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer 11:793–814
Knowlden JM, Jones HE, Barrow D et al (2008) Insulin receptor substrate-1 involvement in epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling: implication for gefitinib (‘Iressa’) response and resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111:79–91
Chakravarti A, Loeffler JS, Dyson NJ (2002) Insulin-like growth factor receptor I mediates resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy in primary human glioblastoma cells through continued activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling. Cancer Res 62:200–207
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA et al (2004) Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science 305:1163–1167
Rocha RL, Hilsenbeck SG, Jackson et al (1997) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and insulin receptor substrate-1 in breast cancer: correlation with clinical parameters and disease-free survival. Clin Cancer Res 3:103–109
Turner BC, Haffty BG, Narayanan L et al (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor overexpression mediates cellular radioresistance and local breast cancer recurrence after lumpectomy and radiation. Cancer Res 57:3079–3083
Fidler MJ, Basu S, Buckingham L et al (2012) Utility of insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 expression in gefitinib-treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 32(5):1705–1710
Cappuzzo F, Toschi L, Tallini G et al (2006) Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR-1) is significantly associated with longer survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib. Ann Oncol 17:1120–1127
Cappuzzo F, Tallini G, Finocchiaro G et al (2010) Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) expression and survival in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Ann Oncol 21:562–567
Makoto N, Hidetaka U, Soichi O et al (2011) Clinical significance of IGF1R expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clinical Lung cancer 13(2):136–142
Dziadziuszko R, Merrick DT, Witta SE et al (2010) Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF1R) gene copy number is associated with survival in operable non–small-cell lung cancer: a comparison between IGF1R fluorescent in situ hybridization, protein expression, and mRNA expression. J Clin Oncol 28(13):2174–2180
Ludovini V, Bellezza G, Pistola L et al (2009) High coexpression of both insulin-like growth factor receptor-1(IGFR-1) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is associated with shorter disease-free survival in resected non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol 20:842–849
Beasley MB, Brambilla E, Travis WD (2005) The 2004 World Health Organization. Classification of lung tumors. Semin Roentgenol 40(2):90–97
Mountain CF (1997) Revisions in the international system for staging lung cancer. Chest 111:1710–1717
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ, Tanoue LT (2009) The new lung cancer stagging system. Chest 136:260–271
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA Jr et al (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J Clin Oncol 21:3798–3807
Varella-Garcia M, Diebold J, Eberhard DA et al (2009) EGFR fluorescence in situ hybridisation assay: guidelines for application to non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Pathol 62(11):970–977
Selvaggi G, Novello S, Torri V et al (2004) Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression correlates with a poor prognosis in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 15(1):28–32
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S, May S (2008) Applied survival analysis: regression modelling of time to event data. Wiley-Interscience, New York, NY
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1985) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Cox DR (1972) Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc B 34:187–220
Huang F, Greer A, Hurlburt W et al (2009) The mechanisms of differential sensitivity to an insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibitor (BMS-536924) and rationale for combining with EGFR/HER2 inhibitors. Cancer Res 69:161–170
Gualberto A, Dolled-Filhart M, Gustavson M et al (2010) Molecular analysis of non–small cell lung cancer identifies subsets with different sensitivity to insulin-like growth factor I receptor inhibition. Clin Cancer Res 16(18):4654–4665
Jassem J, Langer C, Karp D, Mok T, Benner R et al (2010) Randomized, open label, phase III trial of figitumumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin versus paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol 28:539a
Gualberto A, Pollak M (2009) Emerging role of insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitors in oncology:early clinical trial results and future directions. Oncogene 28:3009–3021
Frystyk J (2007) Utility of free IGF-1 measurements. Pituitary 10:181–187
Merrick DT, Dziadziuszko R, Szostakiewicz B et al. (2007) High insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) expression is associated with poor survival in surgically treated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients (pts). J Clin Oncol 25:18 s (Abstr 7550)
Lee YC, Jeon HJ, Kim JH et al (2008) Clinical significance of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression in stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: immunohistochemical analysis. Korean J Intern Med 23:116–120
Bianconi F, Baldelli E, Ludovini V, Crinò L, Flacco A, Valigi P (2012) Computational model of EGFR and IGF1R pathways in lung cancer: a systems biology approach for translational oncology. Biotechnol Adv 30(1):142–153
Van den Berg HW, Claffie D, Boylan M, McKillen J, Lynch M, McKibben B (1996) Expression of receptors for epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I by ZR-75-1 human breast cancer cell variants is inversely related: the effect of steroid hormones on insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression. Br J Cancer 73:477–481
Cunningham MP, Essapen S, Thomas H et al (2006) Coexpression of the IGF-IR, EGFR and HER-2 is common in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Oncol 28:329–335
Nguyen KS, Kobayashi S, Costa DB (2009) Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Clin Lung Cancer 10:281–289
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the technical assistance of the Cytogenetics Core of the University of Colorado Cancer Center for all FISH analyses. The authors thank the patients who participated in this study. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC) to A.F. and from Umbria Association Against Cancer (AUCC) for IHC reagents.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ludovini, V., Flacco, A., Bianconi, F. et al. Concomitant high gene copy number and protein overexpression of IGF1R and EGFR negatively affect disease-free survival of surgically resected non-small-cell-lung cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 71, 671–680 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-2056-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-2056-y