Abstract
Purpose
The fibular axis (FA) and anterior tibial cortex (ATC) are good determinants of the sagittal mechanical axis (MA) of lower legs during total knee arthroplasty (TKA).When compared with healthy subjects, a significant medial tibial torsion has been reported in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis; this should affect the alignment of lower legs. The purpose of this study was to clarify the effect of the medial torsion on relationship between sagittal MA and intraoperative references (FA and ATC).
Methods
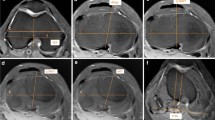
Fifty knees of 50 patients with medial knee osteoarthritis who underwent primary TKA were included in this study. Using preoperative computed tomographic data, the tibial torsion angle was measured in the axial plane. The angle between FA and MA, and the angle between ATC and MA were also measured in the sagittal plane.
Results
The tibial torsion angle was 7.9° ± 7.2° (range −11.3° to −24.3°). The angle between MA and FA was −1.8° ± 0.8° (range −0.1° to −4.3°), and the angle between MA and ATC was 4.6° ± 0.5° (range 3.1° to 5.5°). The population variance was significantly larger for the angle between MA and FA than that between MA and ATC (P = 0.0160). There was a significant positive correlation between the tibial torsion angle and the angle between MA and FA (R 2 = 0.5111, P < 0.0001).
Conclusion
The angle between FA and MA in the sagittal plane increased in patients with large medial tibial torsion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2005) Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:172–176
Akagi M, Oh M, Nonaka T, Tsujimoto H, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2004) An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:213–219
Chauhan SK, Clark GW, Lloyd S, Scott RG, Breidahl W, Sikorski JM (2004) Computer-assisted total knee replacement. A controlled cadaver study using a multi-parameter quantitative CT assessment of alignment (the Perth CT Protocol). J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:818–823
Han HS, Chang CB, Seong SC, Lee S, Lee MC (2008) Evaluation of anatomic references for tibial sagittal alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:373–377
Han HS, Kang SB, Jo CH, Kim SH, Lee JH (2010) The accuracy of intramedullary tibial guide of sagittal alignment of PCL-substituting total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18(10):1334–1338
Jojima H, Whiteside LA, Ogata K (2004) Effect of tibial slope or posterior cruciate ligament release on knee kinematics. Clin Orthop Relat Res 426:194–198
Kansara D, Markel DC (2006) The effect of posterior tibial slope on range of motion after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 21:809–813
Kellgren JK, Lawrenc JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 16:494–501
Lombardi AV Jr, Berend KR, Aziz-Jacobo J, Davis MB (2008) Balancing the flexion gap: relationship between tibial slope and posterior cruciate ligament release and correlation with range of motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Suppl 4):121–132
Longstaff LM, Sloan K, Stamp N, Scaddan M, Beaver R (2009) Good alignment after total knee arthroplasty leads to faster rehabilitation and better function. J Arthroplast 24:570–578
Malviya A, Lingard EA, Weir DJ, Deehan DJ (2009) Predicting range of movement after knee replacement: the importance of posterior condylar offset and tibial slope. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 17:491–498
Matziolis G, Krocker D, Weiss U, Tohtz S, Perka C (2007) A prospective, randomized study of computer-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty. Three-dimensional evaluation of implant alignment and rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:236–243
Nagamine R, Miyanishi K, Miura H, Urabe K, Matsuda S, Iwamoto Y (2003) Medial torsion of the tibia in Japanese patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 408:218–224
Puloski SK, McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB (2001) Tibial post wear in posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty. An unrecognized source of polyethylene debris. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A:390–397
Sikorski JM (2008) Alignment in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:1121–1127
Tamari K, Briffa NK, Tinley P, Aoyagi K (2007) Variations in torsion of the lower limb in Japanese and Caucasians with and without knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 34:145–150
Waelchli B, Romero J (2001) Dislocation of the polyethylene inlay due to anterior tibial slope in revision total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 9:296–298
Whiteside LA, Amador DD (1988) The effect of posterior tibial slope on knee stability after Ortholoc total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 3(Suppl):S51–S57
Yagi T (1994) Tibial torsion in patients with medial-type osteoarthritic knees. Clin Orthop Relat Res 302:52–56
Yoo JH, Chang CB, Shin KS, Seong SC, Kim TK (2008) Anatomical references to assess the posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of 5 anatomical axes. J Arthroplast 23:586–592
Yoshioka Y, Siu DW, Scudamore RA, Cooke TD (1989) Tibial anatomy and functional axes. J Orthop Res 7:132–137
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, A., Aizawa, T., Aki, T. et al. Effect of medial tibial torsion on the sagittal alignment of lower legs in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis. Surg Radiol Anat 35, 205–210 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1011-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1011-2