Abstract
Purpose
Contrast-enhanced MRI is the mainstay for detecting pathology in the skull base foramina and nerve canals, through demonstration of abnormal enhancement. When MRI is contraindicated, or unable to differentiate tumor from non-neoplastic pathology, high-resolution skull base CT is indicated to assess for nerve canal or foramen widening, which is currently determined subjectively. The purpose of this study is to provide objective CT criteria that may help distinguish between normal asymmetry and pathologic nerve canal or foramen widening.
Methods
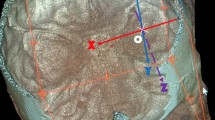
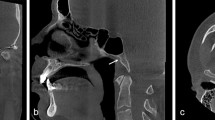
Temporal bone CTs of 50 consecutive adults without facial or trigeminal nerve pathology were retrospectively reviewed. Short axis measurements were obtained in the axial plane for three segments of the facial nerve canal (labyrinthine, tympanic, and mastoid), foramen ovale, pterygoid canal and foramen rotundum on both sides in each subject. Descriptive statistics were obtained, and left–right asymmetry was calculated.
Results
Nerve canal/foramen size was normally distributed across subjects, with a minimal amount of left–right asymmetry. The upper limits of the 95 % confidence interval for absolute left–right asymmetry were: 0.25, 0.21, and 0.15 mm for the labyrinthine, tympanic, and mastoid segments of the facial nerve canal, respectively; 0.62 mm for foramen ovale; 0.36 mm for pterygoid canal; 0.38 mm for foramen rotundum.
Conclusion
Relative asymmetry is more important than absolute size for determining nerve canal/foramen abnormality. These normative data may be useful adjuncts to subjective assessments of nerve canal/foramen size when using skull base CT to identify tumor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blandino A, Gaeta M, Minutoli F, Pandolfo I (2000) CT and MR findings in neoplastic perineural spread along the vidian nerve. Eur Radiol 10:521–526
Curtin HD, Williams R, Johnson J (1985) CT of perineural tumor extension: pterygopalatine fossa. AJR Am J Roentgenol 144:163–169
Dawidowsky K, Branica S, Batelja L, Dawidowsky B, Kovać-Bilić L, Simunić-Veselić A (2011) Anatomical study of the facial nerve canal in comparison to the site of the lesion in Bell’s palsy. Coll Antropol 35:61–65
Gebarski SS, Telian SA, Niparko JK (1992) Enhancement along the normal facial nerve in the facial canal: MR imaging and anatomic correlation. Radiology 183:391–394
Ginsberg LE, Pruett SW, Chen MY, Elster AD (1994) Skull-base foramina of the middle cranial fossa: reassessment of normal variation with high-resolution CT. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:283–291
Gupta R, Bartling SH, Basu SK, Ross WR, Becker H, Pfoh A, Brady T, Curtin HD (2004) Experimental flat-panel high-spatial-resolution volume CT of the temporal bone. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1417–1424
Gupta R, Cheung AC, Bartling SH, Lisauskas J, Grasruk M, Leidecker C, Schmidt B, Flohr T, Brady TJ (2008) Flat-panel volume CT: fundamental principles, technology, and applications. Radiographics 28:2009–2022
Hanna E, Vural E, Prokopakis E, Carrau R, Snyderman C, Weissman J (2007) The sensitivity and specificity of high-resolution imaging in evaluating perineural spread of adenoid cystic carcinoma to the skull base. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:541–545
Kalender WA, Kyriakou Y (2007) Flat-detector computed tomography (FD-CT). Eur Radiol 17:2767–2779
Kalender WA (2003) The use of flat-panel detectors for CT imaging. Radiologe 43:379–387
Kim H, Chung I (1996) High-resolution CT of the pterygopalatine fossa and its communications. Neuroradiology 38:S120–S126
Kinoshita T, Ishii K, Okitsu T, Okudera T, Ogawa T (2001) Facial nerve palsy: evaluation by contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Clin Radiol 56:926–932
Martin N, Sterkers O, Mompoint D, Nahum H (1992) Facial nerve neuromas: MR imaging. Report of four cases. Neuroradiology 34:62–67
Omami G, Hewaidi G, Mathew R (2011) The neglected anatomical and clinical aspects of pterygoid canal: CT scan study. Surg Radiol Anat 33:697–702
Osunwoke E, Mbadugha C, Orish C (2010) A morphometric study of foramen ovale and foramen spinosum of the human sphenoid bone in the southern Nigerian population. J Appl Biosci 26:1631–1635
Rusu MC (2011) Doubled foramen rotundum and maxillary nerve fenestration. Surg Radiol Anat 33:723–726
Shellock FG, Spinazzi A (2008) MRI safety update 2008: part 1, MRI contrast agents and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191:1129–1139
Shellock FG, Spinazzi A (2008) MRI safety update 2008: part 2, screening patients for MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191:1140–1149
Wiggins RH, Harnsberger HR, Salzman KL, Shelton C, Kertesz TR, Glastonbury CM (2006) The many faces of facial nerve schwannoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:694–699
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sepahdari, A.R., Mong, S. Skull base CT: normative values for size and symmetry of the facial nerve canal, foramen ovale, pterygoid canal, and foramen rotundum. Surg Radiol Anat 35, 19–24 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1001-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1001-4