Abstract
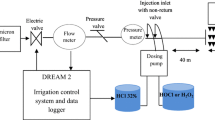
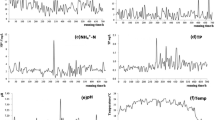
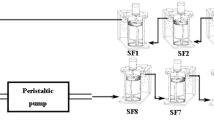
Drip irrigation systems are prone to changes in flow rate (FR) and increasing coefficients of variation (CV) when fed with treated wastewater, due to fouling inside the drippers. A model system was designed to measure the FR and fouling accumulation in laterals and drippers under different treatment conditions. A novel approach was taken to compare the different maintenance treatments. A comparison of chlorination and acidification strategies showed that daily chlorination and periodic acidification may prolong proper functioning of the drippers by maintaining a normal FR [(up to ±7 %) of nominal FR] and CV (<7 %) index in correlation with low fouling accumulation in the pipeline (<0.01 mg deposit/cm 2pipe ). Current recommendations for the frequency of conventional treatments were found to be insufficient. Chemical analyses of the fouling inside the dripper and accumulated on the pipe wall showed that biofilm can survive inside the dripper under harsh environmental conditions, even when the pipeline stays clean. These results shed light on biofilm growth and survival mechanisms inside the dripper and may pave the way to developing new treatments or improving dripper design.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MJ, Geldreich EE (1977) Distribution line sediments and bacterial regrowth. In: Proceedings of the water quality technical conference, Kansas City, MO. American Water Works Association, Denver, CO
Capra A, Scicolone B (2007) Recycling of poor quality urban wastewater by drip irrigation systems. J Clean Prod 15:1529–1534
Cararo DC, Botrel TA, Hills DJ, Leverenz HL (2006) Analysis of clogging drip emitters during wastewater irrigation. Appl Eng Agric 22:251–257
Comte S, Guibaud G, Baudu M (2006) Biosorption properties of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) resulting from activated sludge according to their type: soluble or bound. Process Biochem 41:815–823
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322
De Beer D, Srinivasan R, Stewart PS (1994) Direct measurement of chlorine penetration into biofilms during disinfection. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4339–4344
Denkhaus E, Meisen S, Telgheder U, Wingender J (2007) Chemical and physical methods for characterisation of biofilms. Microchim Acta 158:1–27
Dosoretz CG, Tarchitzky J, Katz I, Kenig E, Chen Y (2010) Fouling in microirrigation systems applying treated wastewater effluents. In: Levy G, Fine P, Bar-Tal A (eds) Treated wastewater in agriculture: use and impacts on the soil environments and crops, chapter 10. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, pp 328–350
Duran-Ros M, Puigbargues J, Arbat G, Barragan J, Cartagena F (2009) Effect of filter, emitter and location on clogging when using effluents. Agric Water Manag 96:67–79
FAO (2012) Food and agriculture organization of the United Nations. AQUASTAT. https://www.fao.org/nr/water/main/index.stm
Flemming HC (2002) Biofouling in water systems—cases, causes and countermeasures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:629–640
Flemming HC, Schaule G, Griebe T, Schmitt J, Tamachkiarowa A (1997) Biofouling—the Achilles heel of membrane processes. Desalination 113:215–225
ISO (International Standard Organization) (2004) Agricultural irrigation equipment—emitters and emitting pipes—specification and test methods. ISO 9261:2004(E)
Li T, Bai R, Liu J (2008) Distribution and composition of extracellular polymeric substances in membrane-aerated biofilm. J Biotechnol 135:52–57
Li JS, Chen L, Li YF (2009) Comparison of clogging in drip emitters during application of sewage effluent and groundwater. Trans ASABE 52:1203–1211
Li JS, Chen L, Li YF, Yin JF, Zhang H (2010) Effects of chlorination schemes on clogging in drip emitters during applications of sewage effluent. Appl Eng Agric 26:565–578
Li GB, Li YK, Xu TW, Liu YZ, Jin H, Yang PL, Yan DZ, Ren SM, Tian ZF (2011a) Effects of average velocity on the growth and surface topography of biofilms attached to the reclaimed wastewater drip irrigation system laterals. Irrig Sci 30:103–113
Li YK, Liu YZ, Li GB, Xu TW, Liu HS, Ren SM, Yan DZ, Yang PL (2011b) Surface topographic characteristics of suspended particulates in reclaimed wastewater and effects on clogging in labyrinth drip irrigation emitters. Irrig Sci 30:43–56
Liang Z, Li W, Yang S, Du P (2010) Extraction and structural characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), pellets in autotrophic nitrifying biofilm and activated sludge. Chemosphere 81:626–632
Nakayama FS, Bucks DA (1991) Water quality in drip/trickle irrigation: a review. Irrig Sci 12:187–192
Nakayama FS, Boman BJ, Pitts DJ (2007) Maintenance. In: Lamm FR, Ayars JE, Nakayama FS (eds) Microirrigation for crop production: design, operation and management. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 389–430
Or D, Phutane S, Dechesne A (2007) Extracellular polymeric substances affecting pore-scale hydrologic conditions for bacterial activity in unsaturated soils. Vadose Zone J 6:298–305
Pei Y, Li Y, Liu Y, Zhou B, Shi Z, Jiang Y (2014) Eight emitters clogging characteristics and its suitability under on-site reclaimed water drip irrigation. Irrig Sci 32:141–157
Puig-Bargués J, Arbat G, Barragán J, Ramírez de Cartagena F (2005) Hydraulic performance of drip irrigation subunits using WWTP effluents. Agric Water Manag 77:249–262
Ravina I, Paz E, Sofer Z, Marcu A, Shisha A, Sagi G (1992) Control of emitter clogging in drip irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Irrig Sci 13:129–139
Ridgway HF, Olson BH (1981) Scanning electron microscope evidence for bacterial colonization of a drinking-water distribution system. Appl Environ Microbiol 41:274–287
Rimon A (2010) Biological and chemical fouling in irrigation system: effects on performance. Master’s Thesis, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel
Tarchitzky J, Rimon A, Kenig E, Dosoretz CG, Chen Y (2013) Biological and chemical fouling in drip irrigation systems utilizing treated wastewater. Irrig Sci 31:1277–1288
Trooien TP, Hills DJ, Lamm FR (2002) Drip irrigation with biological effluent. In: Proceedings of the Irrigation Association International Irrigation Technical Conference, 24–26 Oct 2002, New Orleans, LA. http://www.oznet.ksu.edu/sdi/Reports/2002/DIBioEff.pdf
Zhang X, Bishop PL (2003) Biodegradability of biofilm extracellular polymeric substances. Chemosphere 50:63–69
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the BMBF-Germany and the MOST-Israel: “On-line detection, treatment, and reduction of biofilm and chemical scaling in irrigation systems utilizing treated wastewater (TWW)” project and also wish to thank the Chief Scientist of the Israeli Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development for the financial support of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, S., Dosoretz, C., Chen, Y. et al. Fouling formation and chemical control in drip irrigation systems using treated wastewater. Irrig Sci 32, 459–469 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-014-0442-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-014-0442-4