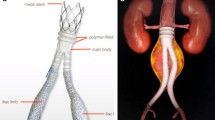
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate medium-term outcomes following endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms (EVAR) with unfavourable neck anatomy using stent grafts with a 36 mm or larger proximal diameter.
Materials and Methods
A retrospective review of 27 patients who underwent elective EVAR between 2006 and 2008 using a stent graft with a 36 mm or larger proximal diameter was carried out. All patients had computed tomography angiography (CTA) for procedure planning, and detailed assessment of the aneurysm neck was performed using a three-dimensional CTA workstation. Patients were followed up with CTA at 3 and 12 months and annual duplex thereafter.
Results
The median aneurysm diameter was 7 cm, and the median aneurysm neck diameter was 31 mm. Cook Zenith stent grafts were used in all patients, with a proximal diameter of 36 mm (n = 25) and 40 mm (n = 2). Primary and assisted primary technical success rates were 74 and 93 %, respectively. The follow-up period ranged from 62 to 84 months, with a median of 72 months. 15 patients died during follow-up. Two patients died from aortic rupture, and the remaining patients died from cardiac disease (n = 4), chest sepsis (n = 6), cancer (n = 2) and renal failure (n = 1). Complications included type I endoleak (n = 5), limb occlusion (n = 2), limb stenosis (n = 2), limb kinking (n = 1), dissection of an artery (n = 1), occlusion of a femorofemoral cross-over graft (n = 1) and poor attachment of a distal limb (n = 1).
Conclusions
EVAR using stent grafts in the presence of an unfavourable neck has a high risk of complications. Medium-term survival in this group is low but mainly due to patient co-morbidities.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbruzzese TA, Kwolek CJ, Brewster DC, Chung TK, Kang J, Conrad MF et al (2008) Outcomes following endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR): an anatomic and device-specific analysis. J Vasc Surg 48(1):19–28
AbuRahma AF, Campbell J, Stone PA, Nanjundappa A, Jain A, Dean LS et al (2009) The correlation of aortic neck length to early and late outcomes in endovascular aneurysm repair patients. J Vasc Surg 50(4):738–748
Mohan IV, Laheij RJ, Harris PL (2001) Risk factors for endoleak and the evidence for stent-graft oversizing in patients undergoing endovascular aneurysm repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 21(4):344–349
Zayed HA, Bell RE, Clough RE, Thomas S, Sabharwal T, Reidy JF et al (2009) Results of endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms with an unfavorable proximal neck using large stent-grafts. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32(6):1161–1164
Fairman RM, Velazquez OC, Carpenter JP, Woo E, Baum RA, Golden MA et al (2004) Midterm pivotal trial results of the talent low profile system for repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm: analysis of complicated versus uncomplicated aortic necks. J Vasc Surg 40(6):1074–1082
Torsello G, Troisi N, Donas KP, Austermann M (2011) Evaluation of the Endurant stent graft under instructions for use vs off-label conditions for endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg 54(2):300–306
Greenhalgh RM, Brown LC, Powell JT, Thompson SG, Epstein D (2010) Endovascular repair of aortic aneurysm in patients physically ineligible for open repair. N Engl J Med 362(20):1872–1880
Greenhalgh RM, Brown LC, Powell JT, Thompson SG, Epstein D, Sculpher MJ (2010) Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med 362(20):1863–1871
Jim J, Rubin BG, Geraghty PJ, Criado FJ, Fajardo A, Sanchez LA (2010) A 5-year comparison of EVAR for large and small aortic necks. J Endovasc Ther 17(5):575–584
Aburahma AF, Campbell JE, Mousa AY, Hass SM, Stone PA, Jain A et al (2011) Clinical outcomes for hostile versus favorable aortic neck anatomy in endovascular aortic aneurysm repair using modular devices. J Vasc Surg 54(1):13–21
Stather PW, Sayers RD, Cheah A, Wild JB, Bown MJ, Choke E (2012) Outcomes of endovascular aneurysm repair in patients with hostile neck anatomy. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 44(6):556–561
Antoniou GA, Georgiadis GS, Antoniou SA, Kuhan G, Murray D (2013) A meta-analysis of outcomes of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair in patients with hostile and friendly neck anatomy. J Vasc Surg 57(2):527–538
Litwinski RA, Donayre CE, Chow SL, Song TK, Kopchok G, Walot I et al (2006) The role of aortic neck dilation and elongation in the etiology of stent graft migration after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair with a passive fixation device. J Vasc Surg 44(6):1176–1181
Stanley BM, Semmens JB, Mai Q, Goodman MA, Hartley DE, Wilkinson C et al (2001) Evaluation of patient selection guidelines for endoluminal AAA repair with the Zenith Stent-Graft: the Australasian experience. J Endovasc Ther 8(5):457–464
Conway AM, Modarai B, Taylor PR, Carrell TW, Waltham M, Salter R et al (2012) Stent-graft limb deployment in the external iliac artery increases the risk of limb occlusion following endovascular AAA repair. J Endovasc Ther 19(1):79–85
Georgakarakos E, Argyriou C, Schoretsanitis N, Ioannou CV, Kontopodis N, Morgan R, et al (2014) Geometrical factors influencing the hemodynamic behavior of the AAA stent grafts: essentials for the clinician. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37(6):1420–1429
Buck DB, van Herwaarden JA, Schermerhorn ML, Moll FL (2014) Endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Nat Rev Cardiol 11(5):250
Acknowledgments
None.
Conflict of interest
Prakash Saha, John Hughes, Ashish S Patel, Tomasso Donati, Morad Sallam, Sanjay D Patel, Rachel E Bell, Konstantinos Katsanos, Bijan Modarai, and Hany A Zayed have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, P., Hughes, J., Patel, A.S. et al. Medium-Term Outcomes Following Endovascular Repair of Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms with an Unfavourable Proximal Neck. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38, 840–845 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-1038-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-1038-3