Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of neurointerventional procedures in acute stroke patients performed by a team of vascular interventional radiologists in close cooperation with diagnostic neuroradiologists and stroke neurologists and to compare the results with those of previous reports from centres with specialised interventional neuroradiologists.
Material and Methods
A total of 39 patients with acute ischemic stroke due to large-vessel occlusion not responding to or not eligible for intravenous thrombolysis were treated with either intra-arterial thrombolysis or mechanical thrombectomy (Penumbra System or solitaire FR thrombectomy system, respectively) and included in our prospective study. Outcomes were measured using the modified Rankin scale after 90 days, and recanalization was assessed by thrombolysis using the myocardial infarction score.
Results
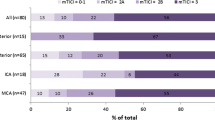
Mean patient age was 68.3 ± 14.2 years; the average National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score at hospital admission was 17.2 (SD = 6.2 [n = 38]). Successful recanalization was achieved in 74.4 % of patients. Median time from clinical onset to recanalization was 5 h 11 min. Procedure-related complications occurred in 5 % of patients, and 7.5 % had a symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage. Of the patients, 22.5 % died within the first 90 postprocedural days, 5 % of these from cerebral causes. Patients who were successfully recanalized had a clinical better outcome at follow-up than those in whom treatment failed. Of the patients, 35.9 % had an mRS score ≤2 after 90 days.
Conclusion
Our results are in line with those in the published literature and show that a treatment strategy with general interventional radiologists performing neurointerventional procedures in acute stroke patients with large vessel occlusions can be achieved to the benefit of patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M et al (2006) Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet 367:1747–1757
Ellekjaer H, Holmen J, Indredavik B et al (1997) Epidemiology of stroke in Innherred, Norway, 1994 to 1996. Incidence and 30-day case-fatality rate. Stroke 28(11):2180–2184
Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M et al (2009) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 119(3):e21–e181
Hatano S (1976) Experience from a multicentre stroke register: a preliminary report. Bull World Health Org 54(5):541–553
Thrift AG, Dewey HM, Macdonell RA et al (2001) Incidence of the major stroke subtypes: initial findings from the North East Melbourne stroke incidence study (NEMESIS). Stroke 32(8):1732–1738
Kolominsky-Rabas PL, Sarti C, Heuschmann PU et al (1998) A prospective community-based study of stroke in Germany—The Erlangen Stroke Project (ESPro): incidence and case fatality at 1, 3, and 12 months. Stroke 29(12):2501–2506
The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group (1995) Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Medicine 333(24):1581–1587
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al (1995) Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274(13):1017–1025
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C et al (1998) Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet 352(9136):1245–1251
Clark WM, Wissman S, Albers GW et al (1999) Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (Alteplase) for ischemic stroke 3 to 5 hours after symptom onset. The ATLANTIS Study: a randomized controlled trial. Alteplase thrombolysis for acute noninterventional therapy in ischemic stroke. JAMA 282(21):2019–2026
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Davalos A et al (2007) Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in the Safe implementation of thrombolysis in stroke-monitoring study (SITS-MOST): an observational study. Lancet 369(9558):275–282
Wolpert SM, Bruckmann H, Greenlee R et al (1993) Neuroradiologic evaluation of patients with acute stroke treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. The rt-PA Acute Stroke Study Group. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:3–13
Saqqur M, Uchino K, Demchuk AM et al (2007) Site of arterial occlusion identified by transcranial Doppler predicts the response to intravenous thrombolysis for stroke. Stroke 38(3):948–954
Nogueira RG, Liebeskind DS, Sung G et al (2009) Predictors of good clinical outcomes, mortality, and successful revascularization in patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing thrombectomy: pooled analysis of the mechanical embolus removal in cerebral ischemia (MERCI) and multi MERCI trials. Stroke 40(12):3777–3783
Bose A, Henkes H, Alfke K et al (2008) The penumbra system: a mechanical device for the treatment of acute stroke due to thromboembolism. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(7):1409–1413
Cohen JE, Gomori JM, Leker RR et al (2012) Recanalization with stent-based mechanical thrombectomy in anterior circulation major ischemic stroke. J Clin Neurosci 19(1):39–43
IMS Study Investigators (2004) Combined intravenous and intra-arterial recanalization for acute ischemic stroke: the Interventional Management of Stroke Study. Stroke 35(4):904–911
Machi P, Costalat V, Lobotesis K et al (2012) Solitaire FR thrombectomy system: immediate results in 56 consecutive acute ischemic stroke patients. J Neurointerv Surg 4(1):62–66
Hirsch JA, Yoo AJ, Nogueira RG et al (2009) Case volumes of intra-arterial and intravenous treatment of ischemic stroke in the USA. J Neurointerv Surg 1:27–31
Penumbra Pivotal Stroke Trial Investigators (2009) The penumbra pivotal stroke trial: safety and effectiveness of a new generation of mechanical devices for clot removal in intracranial large vessel occlusive disease. Stroke 40(8):2761–2768
Castano C, Dorado L, Guerrero C et al (2010) Mechanical thrombectomy with the solitaire AB device in large artery occlusions of the anterior circulation. Stroke 41:1836–1840
The IMS Study Investigators (2004) Combined intravenous and intra-arterial recanalization for acute ischemic stroke: the Interventional Management of Stroke Study. Stroke 35:904–911
Roth C, Papanagiotou P, Behnke S et al (2010) Stent-assisted mechanical recanalization for treatment of acute intracerebral artery occlusions. Stroke 41(11):2559–2567
TIMI Study Group (1985) The thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) trial. Phase I findings. N Engl J Med 312(14):932–936
Khatri P, Neff J, Broderick JP et al (2005) Revascularization end points in stroke interventional trials: recanalization versus reperfusion in IMS—I. Stroke 36:2400–2403
Brott T, Adams HP, Olinger CP et al (1989) Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: a clinical examination scale. 20:864–870
Van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC et al (1988) Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19:604–607
Heck VH (2012) Do no harm: the rush to abbreviated training of stroke interventionalists is premature and ill advised. J Neurointerv Surg 4:3–6
Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L et al (1999) Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke. The PROACT II study: a randomized controlled trial. Prolyse in acute cerebral thromboembolism. JAMA 282(21):2003–2011
Tarr R, Hsu D, Kulcsar Z et al (2010) The POST trial: initial post-market experience of the penumbra system: revascularization of large vessel occlusion in acute ischemic stroke in the United States and Europe. J Neurointerv Surg 2(4):341–344
Möhlenbruch M, Seifert M, Okulla T, et al. (2011) Mechanical thrombectomy compared to local-intraarterial thrombolysis in carotid T and middle cerebral artery occlusions: a single center experience. Clin Neuroradiol 22(2):141–147
Kulcsár Z, Bonvin C, Pereira VM et al (2010) Penumbra system: a novel mechanical thrombectomy device for large-vessel occlusions in acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(4):628–633
Smith WS, Sung G, Starkman S et al (2005) Safety and efficacy of mechanical embolectomy in acute ischemic stroke: results of the MERCI trial. Stroke 36:1432–1438
Mpotsaris A, Bussmeyer M, Loehr C et al (2012) Mechanical thrombectomy in severe acute stroke: preliminary results of the solitaire stent. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83(1):117–118
Taschner CA, Treier M, Schumacher M et al (2011) Mechanical thrombectomy with the penumbra recanalization device in acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroradiol 38:47–52
Belisle JG, McCollom VE, Tytle TL et al (2009) Intraarterial therapy for acute ischemic strokes. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20(3):327–333
Conflict of interest
Jan Petter Larsen reports board membership for Lundbeck Pharma and receiving payment for lectures from Lundbeck Pharma. Martin W. Kurz reports receiving payment for lectures from Boehringer Ingelheim and Pfizer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fjetland, L., Roy, S., Kurz, K.D. et al. Endovascular Acute Stroke Treatment Performed by Vascular Interventional Radiologists: Is It Safe and Efficacious?. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35, 1029–1035 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-012-0438-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-012-0438-5