Abstract
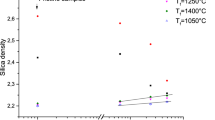
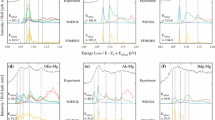
Structural modifications induced by shock-wave compression up to 40 GPa in anorthite glass are investigated by Raman spectroscopy. In the first investigation, densification increases with increasing shock pressure. A maximum densification of 2.2% is obtained for a shock pressure of 24 GPa. This densification is attributed to a decrease of the average ring size, favoring three-membered rings. The densification is much lower than in silica glass subject to shock at similar pressures (11%), because the T-O-T bond angle decrease is impeded in anorthite glass. For higher shock pressures, the decrease of the recovered densification is attributed to partial annealing of the samples due to high after-shock residual temperatures. The study of the annealing process of the most densified glass by in-situ high temperature Raman spectroscopy confirms that relaxation of the three-membered rings occurs above about 900 K.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 July 1998 / Revised and accepted: 27 January 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynard, B., Okuno, M., Shimada, Y. et al. A Raman spectroscopic study of shock-wave densification of anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8) glass. Phys Chem Min 26, 432–436 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050205
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050205