Abstract
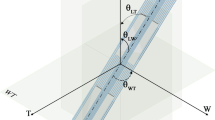
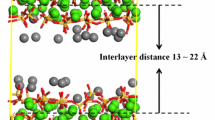
New insights into the dynamical properties of water in hydroxyapatite (HAP) nanopores, a model system for the fluid flow within nanosize spaces inside the collagen-apatite structure of bone, were obtained from molecular dynamics simulations of liquid water confined between two parallel HAP surfaces of different sizes (20 Å ≤ H ≤ 240 Å). Calculations were conducted using a core-shell interatomic potential for HAP together with the extended simple point charge model for water. This force field gives an activation energy for water diffusion within HAP nanopores that is in excellent agreement with available experimental data. The dynamical properties of water within the HAP nanopores were quantified in terms of the second-order water diffusion tensor. Results indicate that water diffuses anisotropically within the HAP nanopores, with the solvent molecules moving parallel to the surface twice as fast as the perpendicular direction. This unusual dynamic behaviour is linked to the strong polarizing effect of calcium ions, and the synergic interactions between the water molecules in the first hydration layer of HAP with the calcium, hydroxyl, and phosphate ions, which facilitates the flow of water molecules in the directions parallel to the HAP surface.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalrahman T, Scheiner S, Hellmich C (2015) Is trabecular bone permeability governed by molecular ordering-induced fluid viscosity gain? Arguments from re-evaluation of experimental data in the framework of homogenization theory. J Theor Biol 365:433–444
Almora-Barrios N, Austen KF, de Leeuw NH (2009) Density functional theory study of the binding of glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline to the hydroxyapatite (0001) and (0110) surfaces. Langmuir 25(9):5018–5025
Berendsen H, Grigera J, Straatsma T (1987) The missing term in effective pair potentials. J Phys Chem 91(24):6269–6271
Berendsen HJ, Postma JP, van Gunsteren WF, Hermans J (1981) Interaction models for water in relation to protein hydration. In: Pullman B (ed) Intermolecular forces. Springer, pp 331–342
Bhide SY, Berkowitz ML (2005) Structure and dynamics of water at the interface with phospholipid bilayers. J Chem Phys 123(22):224702
Boţan A, Rotenberg B, Marry V, Turq P, Noetinger B (2011) Hydrodynamics in clay nanopores. J Phys Chem C 115:16109–16115
Bolis V, Busco C, Martra G, Bertinetti L, Sakhno Y, Ugliengo P, Chiatti F, Corno M, Roveri N (2012) Coordination chemistry of ca sites at the surface of nanosized hydroxyapatite: interaction with H\(_2\)O and CO. Philos T R Soc A 370(1963):1313–1336
Bourg IC, Steefel CI (2012) Molecular dynamics simulations of water structure and diffusion in silica nanopores. J Phys Chem C 116(21):11556–11564
Chandra A (2000) Effects of ion atmosphere on hydrogen-bond dynamics in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Phys Rev Lett 85:768–771
Chandra A (2002) Structure and dynamics of hydrogen bonds in liquid water and aqueous solutions. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 69:49–69
Chiatti F, Corno M, Sakhno Y, Martra G, Ugliengo P (2013) Revealing hydroxyapatite nanoparticle surface structure by CO adsorption: a combined B3LYP and infrared study. J Phys Chem C 117(48):25526–25534
Cleveland G, Chang D, Hazlewood C, Rorschach H (1976) Nuclear magnetic resonance measurement of skeletal muscle: anisotrophy of the diffusion coefficient of the intracellular water. Biophys J 16(9):1043–1053
Corno M, Rimola A, Bolis V, Ugliengo P (2010) Hydroxyapatite as a key biomaterial: quantum-mechanical simulation of its surfaces in interaction with biomolecules. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12(24):6309–6329
Cummings P, Wang B, Evans D, Fraser K (1991) Nonequilibrium molecular dynamics calculation of self-diffusion in a non-Newtonian fluid subject to a Couette strain field. J Chem Phys 94(3):2149–2158
Di Tommaso D, Ruiz-Agudo E, de Leeuw NH, Putnis A, Putnis CV (2014) Modelling the effects of salt solutions on the hydration of calcium ions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:7772–7785
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh ewald method. J Chem Phys 103(19):8577–8593
Fechete R, Demco D, Eliav U, Blümich B, Navon G (2005) Self-diffusion anisotropy of water in sheep achilles tendon. NMR Biomed 18(8):577–586
Fernández-Seara MA, Wehrli SL, Wehrli FW (2002) Diffusion of exchangeable water in cortical bone studied by nuclear magnetic resonance. Biophys J 82(1):522–529
Han KN, Bernardi S, Wang L, Searles DJ (2015) Water diffusion in zeolite membranes: molecular dynamics studies on effects of water loading and thermostat. J Membr Sci 495:322–333
von Hansen Y, Gekle S, Netz RR (2013) Anomalous anisotropic diffusion dynamics of hydration water at lipid membranes. Phys Rev Lett 111(11):118103
Hellmich C, Katti D (2015) Multiscale mechanics of biological, bioinspired, and biomedical materials. MRS Bull 40(04):309–313
Hernandez SER, Streeter I, de Leeuw NH (2015) The effect of water on the binding of glycosaminoglycan saccharides to hydroxyapatite surfaces: a molecular dynamics study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(34):22377–22388
Hille B (2001) Ion channels of excitable membranes, vol 507. Sinauer, Sunderland
Holmboe M, Bourg IC (2014) Molecular dynamics simulations of water and sodium diffusion in smectite interlayer nanopores as a function of pore size and temperature. J Phys Chem C 118:1001–1013
Holmes J, Davies D, Meath W, Beebe R (1964) Gas adsorption and surface structure of bone mineral. Biochem 3(12):2019–2024
Holz M, Heil SR, Sacco A (2000) Temperature-dependent self-diffusion coefficients of water and six selected molecular liquids for calibration in accurate 1H NMR PFG measurements. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2:4740–4742
Kandori K, Fudo A, Ishikawa T (2000a) Adsorption of myoglobin onto various synthetic hydroxyapatite particles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2(9):2015–2020
Kandori K, Mukai M, Yasukawa A, Ishikawa T (2000b) Competitive and cooperative adsorptions of bovine serum albumin and lysozyme to synthetic calcium hydroxyapatites. Langmuir 16(5):2301–2305
Katti KS, Pradhan SM, Katti DR (2010) Mechanics of collagen in the human bone: role of collagen-hydroxyapatite interactions. In: MRS Proceedings, vol 1274. Cambridge Univ Press, pp 1274–QQ06–03
Kirkpatrick R, Kalinichev A, Wang J (2005) Molecular dynamics modelling of hydrated mineral interlayers and surfaces: structure and dynamics. Mineral Mag 69(3):289–308. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/minsoc/mag/2005/00000069/00000003/art00005
Kubicki J (ed) (2016) Molecular modeling of geochemical reactions: an introduction. Wiley, Chichester
Kubo R (1957) Statistical-mechanical theory of irreversible processes. I. General theory and simple applications to magnetic and conduction problems. J Phys Soc Jpn 12(6):570–586
de Leeuw NH (2004a) A computer modelling study of the uptake and segregation of fluoride ions at the hydrated hydroxyapatite (0001) surface: introducing a Ca\(_{10}\)(PO\(_4)_6\)(OH)\(_2\) potential model. Phys Chem Chem Phys 6(8):1860–1866
de Leeuw NH (2004b) Resisting the onset of hydroxyapatite dissolution through the incorporation of fluoride. J Phys Chem B 108(6):1809–1811
de Leeuw NH, Parker S (1998) Molecular-dynamics simulation of MgO surfaces in liquid water using a shell-model potential for water. Phys Rev B 58(20):13901
Lemaire T, Pham T, Capiez-Lernout E, de Leeuw N, Naili S (2015a) Water in hydroxyapatite nanopores: possible implications for interstitial bone fluid flow. J Biomech 48(12):3066–3071
Lemaire T, Pham TT, de Leeuw N, Naili S (2015b) Bone water at the nanoscale: a molecular dynamics study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 18(sup1):1982–1983
Liu P, Harder E, Berne B (2004) On the calculation of diffusion coefficients in confined fluids and interfaces with an application to the liquid–vapor interface of water. J Phys Chem B 108:6595–6602
Lukasheva NV, Tolmachev DA (2015) Cellulose nanofibrils and mechanism of their mineralization in biomimetic synthesis of hydroxyapatite/native bacterial cellulose nanocomposites: molecular dynamics simulations. Langmuir 32(1):125–134
Mkhonto D, de Leeuw NH (2002) A computer modelling study of the effect of water on the surface structure and morphology of fluorapatite: introducing a Ca\(_{10}\)(PO\(_4) 6\)F\(_2\) potential model. J Mater Chem 12:2633–2642
Nair AK, Gautieri A, Buehler MJ (2014) Role of intrafibrillar collagen mineralization in defining the compressive properties of nascent bone. Biomacromolecules 15(7):2494–2500
Nguyen TX, Bhatia SK (2012) Some anomalies in the self-diffusion of water in disordered carbons. J Phys Chem C 116(5):3667–3676
Nie GX, Wang Y, Huang JP (2016) Shape effect of nanochannels on water mobility. Front Phys 11(6):1–8
Oddou C, Lemaire T, Pierre J, David B (2011) Hydrodynamics in porous media with applications to tissue engineering. In: Vafai K (ed) Porous media: applications in biological systems and biotechnology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 75–119
Parvaneh L, Donadio D, Sulpizi M (2016) Molecular mechanism of crystal growth inhibition at the calcium oxalate/water interfaces. J Phys Chem C 120(8):4410–4417
Pham TT, Lemaire T, Capiez-Lernout E, Lewerenz M, To QD, Christie JK, Di Tommaso D, de Leeuw NH, Naili S (2015) Properties of water confined in hydroxyapatite nanopores as derived from molecular dynamics simulations. Theor Chem Acc 134(5):1–14
Planchais A, Devautour-Vinot S, Salles F, Ragon F, Devic T, Serre C, Maurin G (2014) A joint experimental/computational exploration of the dynamics of confined water/zr-based mofs systems. J Phys Chem C 118(26):14441–14448
Prakash M, Subramanian V (2011) Structure, stability and spectral signatures of monoprotic carborane acid–water clusters (CBWn, where n \(=\) 1–6). Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(48):21479–21486
Prakash M, Subramanian V, Gadre SR (2009) Stepwise hydration of protonated carbonic acid: a theoretical study. J Phys Chem A 113(44):12260–12275
Prakash M, Jobic H, Ramsahye NA, Nouar F, Damasceno Borges D, Serre C, Maurin G (2015) Diffusion of H\(_2\), CO\(_2\), and their mixtures in the porous Zirconium based metal-organic framework MIL-140A(Zr): Combination of quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements and molecular dynamics simulations. J Phys Chem C 119(42):23978–23989
Qin Z, Gautieri A, Nair AK, Inbar H, Buehler MJ (2012) Thickness of hydroxyapatite nanocrystal controls mechanical properties of the collagen–hydroxyapatite interface. Langmuir 28(4):1982–1992
Qiu T, Huang JP (2015) Unprecedentedly rapid transport of single-file rolling water molecules. Front Phys 10:1–8
Rimola A, Corno M, Garza J, Ugliengo P (2012) Ab initio modelling of protein–biomaterial interactions: influence of amino acid polar side chains on adsorption at hydroxyapatite surfaces. Philos T R Soc A 370(1963):1478–1498
Rohanizadeh R, Trécant-Viana M, Daculsi G (1999) Ultrastructural study of apatite precipitation in implanted calcium phosphate ceramic: influence of the implantation site. Calcif Tissue Int 64(5):430–436
Sakhno Y, Bertinetti L, Iafisco M, Tampieri A, Roveri N, Martra G (2010) Surface hydration and cationic sites of nanohydroxyapatites with amorphous or crystalline surfaces: a comparative study. J Phys Chem C 114(39):16640–16648
Salles F, Bourrelly S, Jobic H, Devic T, Guillerm V, Llewellyn P, Serre C, Ferey G, Maurin G (2011) Molecular insight into the adsorption and diffusion of water in the versatile hydrophilic/hydrophobic flexible MIL-53(Cr) MOF. J Phys Chem C 115(21):10764–10776
Sansalone V, Naili S, Lemaire T (2012) Nanostructure and effective elastic properties of bone fibril. Bioinspir Biomim Nanobiomater 1(3):154–165
Sansalone V, Kaiser J, Naili S, Lemaire T (2013) Interstitial fluid flow within bone canaliculi and electro-chemo-mechanical features of the canalicular milieu. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 12(3):533–553
Sendner C, Horinek D, Bocquet L, Netz RR (2009) Interfacial water at hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces: slip, viscosity, and diffusion. Langmuir 25(18):10768–10781
Srivastava R, Singh JK, Cummings PT (2012) Effect of electric field on water confined in graphite and mica pores. J Phys Chem C 116(33):17594–17603
Su J, Guo H (2011) Effect of nanotube-length on the transport properties of single-file water molecules: transition from bidirectional to unidirectional. J Chem Phys 134(24):244513
Sudarsanan KT, Young R (1969) Significant precision in crystal structural details. Holly Springs hydroxyapatite. Acta Crystallogr Sect B 25(8):1534–1543
Tan HS, Piletic IR, Fayer M (2005) Orientational dynamics of water confined on a nanometer length scale in reverse micelles. J Chem Phys 122(17):174501
Thomsen C, Henriksen O, Ring P (1987) In vivo measurement of water self diffusion in the human brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Radiol 28(3):353–361
Tian KV, Mahmoud MZ, Cozza P, Licoccia S, Fang D-C, Di Tommaso D, Chass G, Greaves GN (2016) Periodic vs. molecular cluster approaches to resolving glass structure and properties: Anorthite a case study. J Non-Cryst Solids 451:138–145
Todorov IT, Smith W, Trachenko K, Dove MT (2006) DL-POLY 3: new dimensions in molecular dynamics simulations via massive parallelism. J Mater Chem 16(20):1911–1918
Wei MJ, Zhou J, Lu X, Zhu Y, Liu W, Lu L, Zhang L (2011) Diffusion of water molecules confined in slits of rutile TiO\(_2\) (110) and graphite (0001). Fluid Phase Equilib 302(1):316–320
Weiner S, Traub W (1986) Organization of hydroxyapatite crystals within collagen fibrils. FEBS Lett 206:262–266
Wierzbicki A, Cheung HS (2000) Molecular modeling of inhibition of hydroxyapatite by phosphocitrate. J Mol Struct (THEOCHEM) 73(1–3):73–82
Xu L, Hu YZ, Ma TB, Wang H (2013) Tunable giant anisotropic diffusion of water sub-monolayers between graphene layers. Nanotechnology 24(50):505504
Yoon YJ, Cowin SC (2008) The estimated elastic constants for a single bone osteonal lamella. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 7(1):1–11
Young T (2016) Aten. coordinate creator and editor for atomistic simulations, including periodic systems. https://www.projectaten.com
Zhao W, Xu Z, Yang Y, Sahai N (2014) Surface energetics of the hydroxyapatite nanocrystal–water interface: a molecular dynamics study. Langmuir 30(44):13283–13292
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the “Institut des sciences de l’ingénierie et des systèmes” (INSIS) of the “Centre national de la recherche scientifique” (CNRS) for financial support through the “HAP-W Nanopores” PEPS grant. The authors are also grateful to “Université Paris-Est Créteil” (UPEC) for the support of the French-English consortium. Finally, Dr. Muthuramalingam Prakash thanks UPEC for the funding of his post-doctoral research grant. This research utilised Queen Mary’s MidPlus computational facilities, supported by QMUL Research-IT, and funded by EPSRC Grant EP/K000128/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, M., Lemaire, T., Caruel, M. et al. Anisotropic diffusion of water molecules in hydroxyapatite nanopores. Phys Chem Minerals 44, 509–519 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-017-0878-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-017-0878-1