Abstract
Background
The management of uncomplicated (Modified Hinchey Classification Ia) acute diverticulitis (AD) has become increasingly conservative, with a focus on symptomatic relief and supportive management. Clear criteria for patient selection are required to implement this safely. This retrospective study aimed to identify risk factors for severe clinical course in patients with uncomplicated AD.
Materials and methods
Patients admitted to General Surgery at two New Zealand tertiary centres over a period of 18 months were included. Univariate and multivariate analyses were carried out in order to identify factors associated with a more severe clinical course. This was defined by three endpoints: need for procedural intervention, admission >7 days and 30-day readmission; these were analysed separately and as a combined outcome.
Results
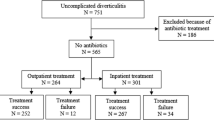
Uncomplicated AD was identified in 319 patients. Fifteen patients (5%) required procedural intervention; this was associated with SIRS (OR 3.92). Twenty-two (6.9%) patients were admitted for >7 days; this was associated with patient-reported pain score >8/10 (OR 5.67). Thirty-one patients (9.8%) required readmission within 30 days; this was associated with pain score >8/10 (OR 6.08) and first episode of AD (OR 2.47). Overall, 49 patients had a severe clinical course, and associated factors were regular steroid/immunomodulator use (OR 4.34), pain score >8/10 (OR 5.9) and higher temperature (OR 1.51) and CRP ≥200 (OR 4.1).
Conclusion
SIRS, high pain score and CRP, first episode and regular steroid/immunomodulator use were identified as predictors of worse outcome in uncomplicated AD. These findings have the potential to inform prospective treatment decisions in this patient group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feingold D, Steele SR, Lee S, Kaiser A et al (2014) Practice parameters for the treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum 57(3):284–294
Etzioni DA, Chiu VY, Cannom RR et al (2010) Outpatient treatment of acute diverticulitis: rates and predictors of failure. Dis Colon Rectum 53(6):861–865
Jamal Talabani A, Lydersen S, Endreseth BH et al (2014) Major increase in admission- and incidence rates of acute colonic diverticulitis. Int J Colorectal Dis 29(8):937–945
Li D, de Mestral C, Baxter NN et al (2014) Risk of readmission and emergency surgery following nonoperative management of colonic diverticulitis: a population-based analysis. Ann Surg 260(3):423–430 discussion 30-1
Vather R, Broad JB, Jaung R et al (2015) Demographics and trends in the acute presentation of diverticular disease: a national study. ANZ J Surg 85(10):744–748
Alonso S, Pera M, Pares D et al (2010) Outpatient treatment of patients with uncomplicated acute diverticulitis. Colorectal Dis Off J Assoc Coloproctol G B Irel 12(10 Online):e278–e282
Etzioni DA, Mack TM, Beart RW Jr et al (2009) Diverticulitis in the United States: 1998-2005: changing patterns of disease and treatment. Ann Surg 249(2):210–217
Ridgway PF, Latif A, Shabbir J et al (2009) Randomized controlled trial of oral vs intravenous therapy for the clinically diagnosed acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. Colorectal Dis 11(9):941–946
Chabok A, Pahlman L, Hjern F et al (2012) Randomized clinical trial of antibiotics in acute uncomplicated diverticulitis. Br J Surg 99(4):532–539. doi:10.1002/bjs.8688
Daniels L, Ünlü Ç, de Korte N et al (2016) Randomized clinical trial of observational versus antibiotic treatment for a first episode of CT-proven uncomplicated acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg. doi:10.1002/bjs.10309
Estrada Ferrer O, Ruiz Edo N, Hidalgo Grau LA et al (2016) Selective non-antibiotic treatment in sigmoid diverticulitis: is it time to change the traditional approach? Tech Coloproctol 20(5):309–315
Isacson D, Thorisson A, Andreasson K et al (2015) Outpatient, non-antibiotic management in acute uncomplicated diverticulitis: a prospective study. Int J Colorectal Dis 30(9):1229–1234
Dharmarajan S, Hunt SR, Birnbaum EH et al (2011) The efficacy of nonoperative management of acute complicated diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum 54(6):663–671
Costi R, Cauchy F, Le Bian A et al (2012) Challenging a classic myth: pneumoperitoneum associated with acute diverticulitis is not an indication for open or laparoscopic emergency surgery in hemodynamically stable patients. A 10-year experience with a nonoperative treatment. Surg Endosc 26(7):2061–2071
McDermott FD, Collins D, Heeney A et al (2014) Minimally invasive and surgical management strategies tailored to the severity of acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg 101(1):e90–e99
Li D, Baxter NN, McLeod RS et al (2014) Evolving practice patterns in the management of acute colonic diverticulitis: a population-based analysis. Dis Colon Rectum 12:1397–1405
Tursi A, Brandimarte G, Giorgetti G et al (2008) The clinical picture of uncomplicated versus complicated diverticulitis of the colon. Dig Dis Sci 53(9):2474–2479 Epub 2008/01/31
Abbas MA, Cannom RR, Chiu VY et al (2013) Triage of patients with acute diverticulitis: are some inpatients candidates for outpatient treatment? Colorectal Dis 15(4):451–457
Wasvary H, Turfah F, Kadro O et al (1999) Same hospitalization resection for acute diverticulitis. Am Surg 65(7):632–635 discussion 6
Jaung R, Robertson J, Rowbotham D et al (2016) Current management of acute diverticulitis: a survey of Australasian surgeons. N Z Med J 129(1431):23–29
Kaiser AM, Jiang JK, Lake JP et al (2005) The management of complicated diverticulitis and the role of computed tomography. Am J Gastroenterol 100(4):910–917
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB et al (1992) Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 101(6):1644–1655
Ribas Y, Bombardo J, Aguilar F et al (2010) Prospective randomized clinical trial assessing the efficacy of a short course of intravenously administered amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid followed by oral antibiotic in patients with uncomplicated acute diverticulitis. Int J Colorectal Dis 25(11):1363–1370
de Korte N, Kuyvenhoven JP, van der Peet DL et al (2012) Mild colonic diverticulitis can be treated without antibiotics. A case-control study. Colorectal Dis Off J Assoc Coloproctol G B Irel 14(3):325–330
Isacson D, Andreasson K, Nikberg M et al (2014) No antibiotics in acute uncomplicated diverticulitis: does it work? Scand J Gastroenterol 49(12):1441–1446
Biondo S, Golda T, Kreisler E et al (2014) Outpatient versus hospitalization management for uncomplicated diverticulitis: a prospective, multicenter randomized clinical trial (DIVER Trial). Ann Surg 259(1):38–44
Ritz JP, Lehmann KS, Frericks B et al (2011) Outcome of patients with acute sigmoid diverticulitis: multivariate analysis of risk factors for free perforation. Surgery 149(5):606–613
Kaser SA, Fankhauser G, Glauser PM et al (2010) Diagnostic value of inflammation markers in predicting perforation in acute sigmoid diverticulitis. World J Surg 34(11):2717–2722. doi:10.1007/s00268-010-0726-7
Alvarez JA, Baldonedo RF, Bear IG et al (2007) Presentation, management and outcome of acute sigmoid diverticulitis requiring hospitalization. Dig Surg 24(6):471–476
Ballian N, Rajamanickam V, Harms BA et al (2013) Predictors of mortality after emergent surgery for acute colonic diverticulitis: analysis of National Surgical Quality Improvement Project data. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 74(2):611–616
Al-Sahaf O, Al-Azawi D, Fauzi MZ et al (2008) Early discharge policy of patients with acute colonic diverticulitis following initial CT scan. Int J Clorectal Dis 23(8):817–820
Acknowledgements
RJ is funded through a Doctoral Scholarship provided by the Auckland Medical Research Foundation (Reference No. 1214005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaung, R., Kularatna, M., Robertson, J.P. et al. Uncomplicated Acute Diverticulitis: Identifying Risk Factors for Severe Outcomes. World J Surg 41, 2258–2265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4012-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4012-9