Abstract
Background
In the field of cosmetic medicine, patient satisfaction is an important and common indicator used to measure the efficacy of the treatment. However, it is insufficient to prove objectively that the benefit of the specific factors involved in the cosmetic outcomes. The practitioner should be aware of these assessment tools, in particular in case of demanding or litigious patients.
Objective
The aim of this review was to establish a list and discuss the subjective and objective methods used to assess facial aesthetic rejuvenation treatments.
Methods
A systematic literature search was performed using the Pubmed search engine. Studies published over the last 5 years, i.e. between January 2010 and January 2015 were considered for review. The following keywords were used: “aesthetic treatment”, “facial rejuvenation”, and “subjective evaluation” or “objective evaluation”.
Results
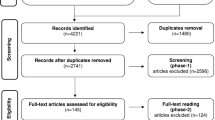
Of the 446 articles identified by the search strategy, 47 articles focused specifically on facial rejuvenation and on the efficacy of aesthetic medical treatments were retrieved for review. Thirty-seven articles used quantitative methods to assess aesthetic treatment outcomes and only 12 used subjective methods. The different assessment methods were listed according to the tools used and treatment indications.
Conclusion
This review will help in choosing adequate methods to assess facial rejuvenation medical treatment. It is important to combine these tools adequately to improve the assessment. There is no current consensus on assess facial rejuvenation treatments but we noted that objective assessment methods seem helpful.
No Level Assigned
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park KY, Ko EJ, Kim BJ, Kim MN, Hong CK, Chang SE, Won CH, Lee YW (2015) A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of PP-501-B in correction of nasolabial folds. Dermatol Surg 41(1):113–120
Shin SJ, Her Y, Yu DS, Kim CW, Kim SS (2014) Twenty-four-week multicenter, evaluator-blinded clinical study of the efficacy and safety of a dextran filler in the treatment of nasolabial folds. Dermatol Surg 40:652–657
Goodier M, Elm K, Wallander I, Zelickson B, Schram S (2014) A randomized comparison of the efficacy of low volume deep placement cheek injection vs. mid- to deep dermal nasolabial fold injection technique for the correction of nasolabial folds. J Cosmet Dermatol 13:91–98
Choi SY, Lee YH, Kim H, Koh HJ, Park SY, Park WS, Bae IH, Park KY, Kim BJ (2014) A combination trial of intradermal radiofrequency and hyaluronic acid filler for treatment of nasolabial fold wrinkles: a pilot study. J Cosmet Laser Ther 16(1):37–42
Brandt F, Bassichis B, Bassichis M, O’Connell C, Lin X (2011) Safety and effectiveness of small and large gel-particle hyaluronic acid in the correction of perioral wrinkles. J Drugs Dermatol 10:982–987
Ascher B, Bayerl C, Brun P, Kestemont P, Rzany B, Poncet M, Guennoun M, Podda M (2011) Efficacy and safety of a new hyaluronic acid dermal filler in the treatment of severe nasolabial lines—6-month interim results of a randomized, evaluator-blinded, intra-individual comparison study. J Cosmet Dermatol 10(2):94–98
Ahn JY, Lee SH, Park KY, Hong CK, Song HJ, Park MY, Choi YS, Seo SJ (2012) Clinical comparison of two hyaluronic acid-derived fillers in the treatment of nasolabial folds: Mesoglow® and IAL System®. Int J Dermatol 51(5):601–608
Sclafani AP (2010) Platelet-rich fibrin matrix for improvement of deep nasolabial folds. J Cosmet Dermatol 9:66–71
Calabrò G, De Vita V, Patalano A, Mazzella C, Lo Conte V, Antropoli C (2014) Confirmed efficacy of topical nifedipine in the treatment of facial wrinkles. J Dermatolog Treat 25:319–325
Buntrock H, Reuther T, Prager W, Kerscher M (2013) Efficacy, safety, and patient satisfaction of a monophasic cohesive polydensified matrix versus a biphasic nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid filler after single injection in nasolabial folds. Dermatol Surg 39:1097–1105
Royo de la Torre J, Moreno-Moraga J, Isarría MJ, Muñoz E, Cruz I, Pérez G, Cornejo P (2013) The evaluation of hyaluronic acid, with and without lidocaine, in the filling of nasolabial folds as measured by ultrastructural changes and pain management. J Drugs Dermatol 12(3):e46–e52
Savoia A, Landi S, Baldi A (2013) A new minimally invasive mesotherapy technique for facial rejuvenation. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 3:83–93
Lee KR, Lee EG, Lee HJ, Yoon MS (2013) Assessment of treatment efficacy and sebosuppressive effect of fractional radiofrequency microneedle on acne vulgaris. Lasers Surg Med 45:639–647
Lee YB, Song EJ, Kim SS, Kim JW, Yu DS (2014) Safety and efficacy of a novel injectable filler in the treatment of nasolabial folds: polymethylmethacrylate and cross-linked dextran in hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. J Cosmet Laser Ther 16(4):185–190
Pavicic T, Gauglitz GG, Lersch P, Schwach-Abdellaoui K, Malle B, Korting HC, Farwick M (2011) Efficacy of cream-based novel formulations of hyaluronic acid of different molecular weights in anti-wrinkle treatment. J Drugs Dermatol 10(9):990–1000
Bertucci V, Lin X, Axford-Gatley RA, Theisen MJ, Swift A (2013) Safety and effectiveness of large gel particle hyaluronic acid with lidocaine for correction of midface volume loss. Dermatol Surg 39:1621–1629
Rzany B, Cartier H, Kestermont P, Trevidic P, Sattler G, Kerrouche N, Dhuin JC (2012) Correction of tear troughs and periorbital lines with a range of customized hyaluronic acid fillers. J Drugs Dermatol 11(1 Suppl):s27–s34
Kestemont P, Cartier H, Trevidic P, Rzany B, Sattler G, Kerrouche N, Dhuin JC (2012) Sustained efficacy and high patient satisfaction after cheek enhancement with a new hyaluronic acid dermal filler. J Drugs Dermatol 11(1 Suppl):9–16
Luebberding S, Krueger N, Kerscher M (2014) Comparison of Validated Assessment Scales and 3D digital fringe projection method to assess lifetime development of wrinkles in men. Skin Res Technol 20:30–36
Ooe M, Seki T, Miura T, Takada A (2013) Comparative evaluation of wrinkle treatments. Aesthetic Plast Surg 37:424–433
Clementoni MT, Lavagno R, Munavalli G (2012) A new multi-modal fractional ablative CO2 laser for wrinkle reduction and skin resurfacing. J Cosmet Laser Ther 14:244–252
Levenberg A, Halachmi S, Arad-Cohen A, Ad-El D, Cassuto D, Lapidoth M (2010) Clinical results of skin remodeling using a novel pneumatic technology. Int J Dermatol 49:1432–1439
Shin JW, Lee DH, Choi SY, Na JI, Park KC, Youn SW, Huh CH (2011) Objective and non-invasive evaluation of photorejuvenation effect with intense pulsed light treatment in Asian skin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 5:516–522
Olivier Masveyraud F (2011) Facial rejuvenation using l-polylactic acid: about 298 successive cases. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 56:120–127
Lorenc ZP, Bank D, Kane M, Lin X, Smith S (2012) Validation of a four-point photographic scale for the assessment of midface volume loss and/or contour deficiency. Plast Reconstr Surg 130:1330–1336
El-Domyati M, Abd-El-Raheem T, Medhat W, Abdel-Wahab H, Al Anwer M (2014) Multiple fractional erbium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser sessions for upper facial rejuvenation: clinical and histological implications and expectations. J Cosmet Dermatol 13:30–37
Kim JE, Chang S, Won CH, Kim CH, Park KH, Choi JH, Lee MW (2012) Combination treatment using bipolar radiofrequency-based intense pulsed light, infrared light and diode laser enhanced clinical effectiveness and histological dermal remodeling in Asian photoaged skin. Dermatol Surg 38(1):68–76
Prignano F, Bonciani D, Campolmi P, Cannarozzo G, Bonan P, Lotti T (2011) A study of fractional CO2 laser resurfacing: the best fluences through a clinical, histological, and ultrastructural evaluation. J Cosmet Dermatol 10:210–216
Koh BK, Lee CK, Chae K (2010) Photorejuvenation with submillisecond neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (1064 nm) laser: a 24-week follow-up. Dermatol Surg 36:355–362
Tanaka Y, Tsunemi Y, Kawashima M, Tatewaki N, Nishida H (2014) Treatment of skin laxity using multisource, phase-controlled radiofrequency in Asians: visualized 3-dimensional skin tightening results and increase in elastin density shown through histologic investigation. Dermatol Surg 40:756–762
El-Domyati M, El-Ammawi TS, Medhat W, Moawad O, Mahoney MG, Uitto J (2012) Multiple minimally invasive erbium: yttrium aluminum garnet laser mini-peels for skin rejuvenation: an objective assessment. J Cosmet Dermatol 11:122–130
Patriota RC, Rodrigues CJ, Cucé LC (2011) Intense pulsed light in photoaging: a clinical, histopathological and immunohistochemical evaluation. An Bras Dermatol 86:1129–1133
Jegasothy SM, Zabolotniaia V, Bielfeldt S (2014) Efficacy of a new topical nano-hyaluronic acid in humans. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 7:27–29
Manosroi A, Chutoprapat R, Abe M, Manosroi W, Manosroi J (2012) Anti-aging efficacy of topical formulations containing niosomes entrapped with rice bran bioactive compounds. Pharm Biol 50:208–224
Choi M, Choi JW, Lee SY et al (2010) Low-dose 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser for the treatment of melasma. J Dermatolog Treat 21:224–228
Li YH, Chen JZ, Wei HC, Zhang L, Xu HH, Xu TH, Wu Y, Xu YY, Dong GH, Gao XH, Chen HD, Gold MH (2010) A Chinese experience of fractional ultrapulsed CO2 laser for skin rejuvenation. J Cosmet Laser Ther 12(6):250–255
Redaelli A, Romano D, Marcianó A (2010) Face and neck revitalization with platelet-rich plasma (PRP): clinical outcome in a series of 23 consecutively treated patients. J Drugs Dermatol 9:466–472
Mehryan P, Zartab H, Rajabi A, Pazhoohi N, Firooz A (2014) Assessment of efficacy of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on infraorbital dark circles and crow’s feet wrinkles. J Cosmet Dermatol 13:72–78
Panchapakesan V, Klassen AF, Cano SJ, Scott AM, Pusic AL (2013) Development and psychometric evaluation of the FACE-Q aging appraisal scale and patient-perceived age visual analog scale. Aesthet Surg J 33:1099–1109
Lee HJ, Lee EG, Kang S, Sung JH, Chung HM, Kim DH (2014) Efficacy of microneedling plus human stem cell conditioned medium for skin rejuvenation: a randomized, controlled, blinded split-face study. Ann Dermatol 26:584–591
Hong YH, Jung EY, Shin KS, Yu KW, Chang UJ, Suh HJ (2013) Tannase-converted green tea catechins and their anti-wrinkle activity in humans. J Cosmet Dermatol 12:137–143
Min P, Xi W, Grassetti L, Trisliana Perdanasari A, Torresetti M, Feng S, Su W, Pu Z, Zhang Y, Han S, Zhang YX, Di Benedetto G, Lazzeri D (2015) Sebum production alteration after botulinum toxin type a injections for the treatment of forehead rhytides: a prospective randomized double-blind dose-comparative clinical investigation. Aesthet Surg J 35(5):600–610
Rose AE, Goldberg DJ (2013) Safety and efficacy of intradermal injection of botulinum toxin for the treatment of oily skin. Dermatol Surg 39:443–448
Roh M, Goo B, Jung J, Chung H, Chung K (2011) Treatment of enlarged pores with the quasi long-pulsed versus Q-switched 1064 nm Nd:YAG lasers: a split-face, comparative, controlled study. Laser Ther 20:175–180
El-Domyati M, El-Ammawi TS, Moawad O, El-Fakahany H, Medhat W, Mahoney MG, Uitto J (2012) Efficacy of mesotherapy in facial rejuvenation: a histological and immunohistochemical evaluation. Int J Dermatol 51(8):913–919
Mahmood T, Akhtar N (2013) Combined topical application of lotus and green tea improves facial skin surface parameters. Rejuvenation Res 16:91–97
Kim M, Yang H, Kim H, Jung H, Jung H (2014) Novel cosmetic patches for wrinkle improvement: retinyl retinoate and ascorbic acid-loaded dissolving microneedles. Int J Cosmet Sci 36:207–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hersant, B., Abbou, R., SidAhmed-Mezi, M. et al. Assessment Tools for Facial Rejuvenation Treatment: A Review. Aesth Plast Surg 40, 556–565 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0640-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-016-0640-y