Abstract
Background
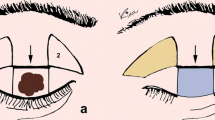
Cicatricial ectropion of the upper eyelid is a serious problem because of the association with exposure keratitis and ulceration. Traditional surgical treatment usually requires skin grafts or local flaps depending on the severity of the defect. However, outcomes have usually been discouraging, especially in terms of cosmetic appearance.
Methods
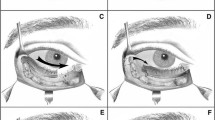
From February 2000 to March 2012, a total of 12 upper eyelids with severe cicatricial ectropion were treated with a retrograde postauricular island flap and were included in this study. Based on the pedicle of the parietal branch of the superficial temporal artery and its choke anastomoses to the posterior auricular artery, the retrograde postauricular island flap was harvested with a supra-auricular incision down to the non-hair-bearing side skin of the postauricular region. The flap was then transferred to the upper-lid lesion by passing it through a subcutaneous tunnel between the pedicle base and the upper-lid lesion. The donor site was directly closed by advancing the postauricular scalp flap into the sulcus. The largest flap was 6.5 × 3.5 cm2.
Results
After 6–12 months of follow-up, flaps survived with good color, texture, and contour. The eyelids moved freely without recurrence of ectropion. The donor site had an inconspicuous scar. No major complications occurred.
Conclusions
The retrograde postauricular island flap can be a safe, simple, and effective procedure for aesthetic correction of severe cicatricial upper-eyelid ectropion with few complications and little donor-site morbidity.
Level of Evidence V
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vallabhanath P, Carter SR (2000) Ectropion and entropion. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 11:345–351
Chua J, Choo CT, Seah LL et al (2011) A 5-year retrospective review of Asian ectropion: how does it compare to ectropion amongst non-Asians? Ann Acad Med Singap 40:84–86
Zurada A, Zielinski A (2005) Surgical management of deep chemical burns of the eyelids. Klin Oczna 107(4–6):275–277
Yoshimura Y, Nakajima T, Yoneda K (1991) Reconstruction of the entire upper eyelid area with a subcutaneous pedicle flap based on the orbicularis oculi muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg 88(1):136–139
Demir Z, Yuce S, Karamursel S et al (2008) Orbicularis oculi myocutaneous advancement flap for upper eyelid reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(2):443–450
Han K (1997) Total reconstruction of a partial-thickness upper eyelid defect with the expanded forehead flap. Ann Plast Surg 39:24–29
Washio H (1969) Retroauricular-temporal flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 43:162–166
Washio H (1972) Further experiences with the retroauricular temporal flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 50:160–162
Maillard GF, Montandon D (1982) The Washio tempororetroauricular flap: its use in 20 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 70:550–560
Guyuron B (1985) Retroauricular island flap for eye socket reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 76:527–533
Song R, Song Y, Qi K et al (1996) The superior auricular artery and retroauricular arterial island flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 98:657–667
Fujino T, Harashina T, Nakajima T (1976) Free skin flap from the retroauricular region to the nose. Plast Reconstr Surg 57:338–341
Li S, Cao W, Cheng K et al (2006) Microvascular reconstruction of nasal ala using a reversed superficial temporal artery auricular flap. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:1300–1304
Pascone M, Papa G (2005) The reverse auricular flap for the reconstruction of extended defects of the lower eyelid. Br J Plast Surg 58:806–811
Benlier E, Top H, Cinar C et al (2007) Reverse-flow retroauricular island flap in facial reconstruction. Dermatol Surg 33:1442–1450
Hassanpour SE, Shariati SM (2008) One stage reconstruction of nasal defect by reverse flow retroauricular island flap - case series and discussion. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61:949–952
Kilinc H, Bilen BT (2006) A new approach to retroauricular flap transfer: parietal branch-based reverse flow superior auricular artery island flap. Ann Plast Surg 56:380–383
Kilinc H, Bilen BT, Ulusoy MG et al (2007) A comparative study on superior auricular artery island flaps with various pedicles for repair of periorbital defects. J Craniofac Surg 18:406–414
Yotsuyanagi T, Watanabe Y, Yamashita K et al (2001) Retroauricular flap: its clinical application and safety. Br J Plast Surg 54:12–19
Oh SH, Kyung HW, Kang N et al (2011) The vascular system of the superior auricular artery: anatomical study and clinical application. Dermatol Surg 37:65–72
Houseman ND, Taylor GI, Pan WR (2000) The angiosomes of the head and neck: anatomic study and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:2287–2313
Abul-Hassan HS, von Drasek Ascher G, Acland RD (1986) Surgical anatomy and blood supply of the fascial layers of the temporal region. Plast Reconstr Surg 77:17–28
Nakajima H, Imanishi N, Minabe T (1995) The arterial anatomy of the temporal region and the vascular basis of various temporal flaps. Br J Plast Surg 48:439–450
Yang D, Morris SF (1998) Vascular basis of the retroauricular flap. Ann Plast Surg 40:28–33
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. None of the authors has a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this article
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, S., Fan, J., Chen, W. et al. Aesthetic Correction of Severe Cicatricial Upper-Eyelid Ectropion with a Retrograde Postauricular Island Flap. Aesth Plast Surg 37, 95–101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-0009-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-0009-9