Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyse the efficacy of modular femoral stems for the treatment of certain post-operative periprosthetic fractures in patients with hip arthroplasty.
Methods
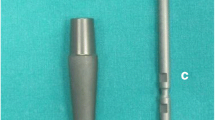
Of a total series of 61 modular revision stems, 17 were used to address periprosthetic femoral fractures and 12 of these are the object of this study. The average follow-up was 3.7 years (range 1–14 years). The evaluations were performed at three and six months, and then annually using the HHS score and radiographic studies for the assessment of loosening, subsidence and bone integration of the stem.
Results
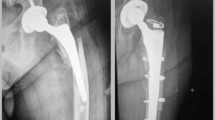
Seven cases had type B2 fractures and five type B3 ones. All patients walked freely, eight of them using canes. HHS improved to a post-operative mean of 78 (range 72–83). Radiographically, fracture healing was observed at three months in nine cases. In six cases stem subsidence of a mean of 3.9 mm (range 2–12 mm) was observed, which stabilized a year following implantation and did not need revision surgery. In two cases a subsequent dislocation (at three and seven months after surgery) occurred, which were treated with constrained acetabular systems. In nine cases hypotrophy of the cortex in the diaphyseal area was noted, which did not alter the patients’ clinical course.
Conclusion
Modular femoral stems are an acceptable treatment in type B2 and B3 periprosthetic fractures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M (2007) Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:780–785
Ohly NE, Whitehouse MR, Duncan CP (2014) Periprosthetic femoral fractures in total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int 24:556–567
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P, Garellick G (2005) Periprosthetic femoral fractures classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J Arthroplasty 20:857–865
Springer BD, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG (2003) Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures following total hip arthroplasty with femoral component revision. J Bone Joint Surg Am 11:2156–2162
Learmonth D (2004) The management of periprosthetic fractures around the femoral stem. J Bone Joint Surg 86-B:13–19
Toogood PA, Vail TP (2015) Periprosthetic fractures: a common problem with a disproportionately high impact on healthcare resources. J Arthroplasty. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2015.04.038
Spina M, Rocca G, Canella A, Scalvi A (2014) Causes of failure in periprosthetic fractures of the hip at 1 to 14 year follow-up. Injury 45(Suppl 6):S85–92
Duncan CP, Masri BA (1995) Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect 44:293–304
Füchtmeier B, Galler M, Müller F (2014) Mid-term results of 121 periprosthetic femoral fractures: increased failure and mortality within but not after one postoperative year. J Arthroplasty 30:669–674
Sung-Rak L, Bostrom MPG (2004) Periprosthetic fractures of the femur after total hip arthroplasty. In: Helfet (ed) AAOS instruct course lect. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, Rosemont, pp 111–118
Duncan CP, Haddad FS (2014) The Unified Classification System (UCS): improving our understanding of periprosthetic fractures. Bone Joint J 96-B:713–716
Pike J, Davidson D, Garbuz D, Duncan CP, O’Brien PJ, Masri BA (2009) Principles of treatment for periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures around well-fixed total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 17:677–688
Müller FJ, Galler M, Füchtmeier B (2014) Clinical and radiological results of patients treated with orthogonal double plating for periprosthetic femoral fractures. Int Orthop (SICOT) 38:2469–2472
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Odén A, Garellick G (2006) Risk factors for failure after treatment of a periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg 88-B:26–30
Drexler M, Dwyer T, Chakravertty R, Backstein D, Gross AE, Ont O, Safir O (2014) The outcome of modified extended trochanteric osteotomy in revision THA for Vancouver B2/B3 periprosthetic fractures of the femur. J Arthroplasty 29:1598–1604
Lakstein D, Backstein D, Safir O, Kosashvili Y, Gross AE (2010) Revision total hip arthroplasty with a porous-coated modular stem. 5 to 10 years follow-up. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:1310–1315
Restrepo C, Mashadi M, Parvizi J, Austin MS, Hozack WJ (2011) Modular femoral stems for revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:476–482
Tangsataporn S, Safir OA, Vincent AD, Abdelbary H, Gross AE, Kuzyk PRT (2015) Risk factors for subsidence of a modular tapered femoral stem used for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 30:1030–1034
Munro JT, Masri BA, Garbuz DS, Duncan CP (2013) Tapered fluted modular titanium stems in the management of Vancouver B2 and B3 peri-prosthetic fractures. Bone Joint J 95-B:17–20
Hartman CW, Garvin KL (2012) Femoral fixation in revision total hip arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect 61:313–325
Stimac JD, Boles J, Parkes N, Gonzalez Della Valle A, Boettner F, Westrich G (2014) Revision total hip arthroplasty with modular femoral stems. J Arthroplasty 29:2167–2170
Patel PD, Klika AK, Murray TG, Elsharkawy KA, Krebs VE, Barsoum WL (2010) Influence of technique with distally fixed modular stems in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 25:926–931
Holt G, McCaul J, Jones B, Ingram R, Stark A (2011) Outcome after femoral revision using the restoration cone/conical femoral revision stem. Orthopedics 34:11
Dzaja I, Lyons ML, McCalden RW, Naudie DDD, Howard JL (2014) Revision hip arthroplasty using a modular revision hip system in cases of severe bone loss. J Arthroplasty 29:1594–1597
Ricci WM (2015) Periprosthetic femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma 29:130–137
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernandez-Vaquero, D., Fernandez-Lombardia, J., de los Rios, J.L. et al. Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures with modular stems. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 39, 1933–1938 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2958-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2958-5