Abstract
Background
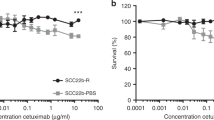
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) may contribute to the antitumor activity of cetuximab. However, the extent of this contribution is unclear. In this study, we investigated the impact of baseline ADCC on the outcome of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma treated with cetuximab and radiotherapy.
Methods
We determined baseline ADCC in 28 patients treated with cetuximab and radiotherapy and in 15 patients treated with chemoradiation. We linked the values observed with complete response and with overall survival. We also considered the role of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression and studied the combined effect of EGFR and ADCC.
Results
We observed a wide range of baseline values of ADCC. Complete response did not correlate with either ADCC or EGFR expression. However, when ADCC and EGFR were considered together using a mixed score, they significantly correlated with achieving a complete response (p = 0.04). High baseline ADCC significantly correlated with outcome compared to low (p = 0.03), but not in patients treated without cetuximab. Patients showing high baseline levels of both ADCC and EGFR3+ achieved the best outcome compared to the others (p = 0.02).
Conclusions
In this study, patients treated with cetuximab and radiotherapy, showing high baseline of both ADCC and EGFR3+, have significant higher probability of achieving a complete response and a long overall survival compared to the others.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADCC:
-
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- CR:
-
Complete response
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin G
- INFγ:
-
Interferon gamma
- iNKT:
-
Invariant natural killer T cells
- mAbs:
-
Monoclonal antibodies
- N:
-
Lymph node status
- OPC:
-
Oropharyngeal cancers
- pts:
-
Patients
- T:
-
Tumor size
References
Dawood S, Broglio K, Buzdar AU et al (2009) Prognosis of women with metastatic breast cancer by HER2 status and trastuzumab treatment: an institutional-based review. J Clin Oncol 28:92–98
Boero S, Morabito A, Banelli B et al (2015) Analysis of in vitro ADCC and clinical response to trastuzumab: possible relevance of FcyRIIIA/FcyRIIA gene polymorphism and HER-2 expression levels on breast cancer cell lines. J Transl Med 13:324
Cartron G, Dacheux L, Salles G et al (2002) Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIIa gene. Blood 99:754–758
Maréchal R, De Schutter J, Nagy N, Demetter P, Lemmers A, Devière J, Salmon I, Tejpar S, Van Laethem JL (2010) Putative contribution of CD56 + positive cells in cetuximab treatment efficacy in first-line metastatic colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer 10:340
Wagner S, Wittekindt C, Reuschenbach M, Hennig B, Thevarajah M, Würdemann N, Prigge ES, von Knebel Doeberitz M, Dreyer T, Gattenlöhner S, Klussmann JP (2016) CD56-positive lymphocyte infiltration in relation to human papillomavirus association and prognostic significance in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 138:2263–2273
Monteverde M, Milano G, Strola G, Maffi M, Lattanzio L, Vivenza D, Tonissi F, Merlano M, Lo Nigro C (2015) The relevance of ADCC for EFGR targeting: a review of the literature and a clinically applicable method of assessment in patients. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 95(2):179–190
Lo Nigro C, Ricci V, Vivenza D, Monteverde M, Strola G, Lucio F, Tonissi F, Miraglio E, Granetto C, Fortunato M, Merlano MC (2016) Evaluation of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity activity and cetuximab response in KRAS wilde-type colorectal cancer patients. World J Gastrointest Oncol 8:222–230
Mickel RA, Kessler DJ, Taylor JM, Lichtenstein A (1988) Natural killer cell cytotoxicity in the peripheral blood, cervical lymph nodes, and tumor of head and neck cancer patients. Cancer Res 48(17):5017–5022
Kono K, Takahashi A, Ichihara F, Sugai H, Fujii H, Matsumoto Y (2002) Impaired antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by herceptin in patients with gastric cancer. Cancer Res 62(20):5813–5817
Taylor RJ, Saloura V, Jain A, Goloubeva O, Wong S, Kronsberg S, Nagilla M, Silpino L, de Souza J, Seiwert T, Vokes E, Villaflor V, Cohen EE (2015) Ex vivo antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity inducibility predicts efficacy of cetuximab. Cancer Immunol Res 3(5):567–574
Terabe M, Berzofsky JA (2008) The role of NKT cells in tumor immunity. Adv Cancer Res 101:277–348
Molling JW, Langius JAE, Langendijk JA et al (2007) Low levels of circulating invariant natural killer T cells predict poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 25:862–868
Chen J, Feng Y, Lu L, Wang H, Dai L, Li Y, Zhang P (2012) Interferon-γ-induced PD-L1 surface expression on human oral squamous carcinoma via PKD2 signal pathway. Immunobiology 217(4):385–393
Acknowledgements
This study has been partially supported by Associazione Ricerca Clinica Oncologica (ARCO) Foundation, Cuneo, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Marco Merlano took part in Merck Serono and MSD advisory boards, and has speaker role in Merck Serono promoted meetings. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lattanzio, L., Denaro, N., Vivenza, D. et al. Elevated basal antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and high epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression predict favourable outcome in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer treated with cetuximab and radiotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 66, 573–579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-1960-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-1960-8