Abstract
Objective
Our purpose was to evaluate the sensitivity of multidetector CT for the detection of peritoneal metastases between standard 2.5 mm axial imaging and maximum-intensity-projection (MIP) reconstructions.
Materials and methods
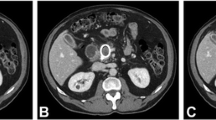
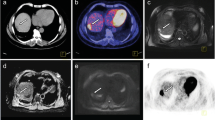
The Institutional Review Board approved this retrospective study and waived the need to obtain patient consent. We retrospectively identified 36 patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma and peritoneal metastatic disease who underwent a pancreatic protocol CT examination of the abdomen and pelvis between January 2012 and January 2014. Three independent radiologists reviewed a randomized combination of standard axial (2.5 mm reconstructed thickness, 2.5 mm interval) and axial MIP reconstructions (6, 3 mm interval) over two sessions. Each reader recorded metastasis location in PACS. Subsequent consensus review by two radiologists determined the final number and size of metastases.
Results
The reviewers found 328 peritoneal implants in 36 patients. After accounting for the size, location, and number of lesions as well as multiple readers, a generalized estimating equations model showed that the statistical combination of MIP with standard technique significantly increased the odds of correctly identifying a lesion (OR 2.16; 95% CI 1.86–2.51; p value < 0.0001) compared to standard technique alone. MIP reconstruction as a standalone technique was less sensitive compared to standard technique alone (OR 0.81; 95% CI 0.65–0.99; p value = 0.0468). When compared to standard axial imaging, evaluation via MIP reconstructions resulted in the identification of an additional 50 (15%), 45 (14%), and 55 (17%) lesions by Readers 1–3, respectively.
Conclusion
The axial 6 mm MIP series is complimentary in the CT evaluation of peritoneal metastases. MIP reconstruction evaluation identified a significant number of additional lesions, but is not adequate as a standalone technique for peritoneal cavity assessment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen VB, et al. (2013) Diagnostic accuracy of laparoscopy following computed tomography (CT) scanning for assessing the resectability with curative intent in pancreatic and periampullary cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11:CD009323
Kim SJ, et al. (2009) Peritoneal metastasis: detection with 16- or 64-detector row CT in patients undergoing surgery for gastric cancer. Radiology 253(2):407–415
Kaneko OF, et al. (2010) Performance of multidetector computed tomographic angiography in determining surgical resectability of pancreatic head adenocarcinoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34(5):732–738
Marin D, et al. (2010) 64-Section multi-detector row CT in the preoperative diagnosis of peritoneal carcinomatosis: correlation with histopathological findings. Abdom Imaging 35(6):694–700
Mazzei MA, et al. (2013) Accuracy of MDCT in the preoperative definition of Peritoneal Cancer Index (PCI) in patients with advanced ovarian cancer who underwent peritonectomy and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC). Abdom Imaging 38(6):1422–1430
Morana G, et al. (2010) Staging cancer of the pancreas. Cancer Imaging 10(Spec no A):S137–S141.
Brunetti J (2013) PET/CT in gynecologic malignancies. Radiol Clin North Am 51(5):895–911
Gruden JF, et al. (2002) Incremental benefit of maximum-intensity-projection images on observer detection of small pulmonary nodules revealed by multidetector CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179(1):149–157
Valencia R, et al. (2006) Value of axial and coronal maximum intensity projection (MIP) images in the detection of pulmonary nodules by multislice spiral CT: comparison with axial 1-mm and 5-mm slices. Eur Radiol 16(2):325–332
Kilburn-Toppin F, et al. (2013) Detection of pulmonary nodules at paediatric CT: maximum intensity projections and axial source images are complementary. Pediatric Radiol 43(7):820–826
Kawel N, et al. (2009) Effect of slab thickness on the CT detection of pulmonary nodules: use of sliding thin-slab maximum intensity projection and volume rendering. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192(5):1324–1329
Jankowski A, et al. (2007) Pulmonary nodule detection on MDCT images: evaluation of diagnostic performance using thin axial images, maximum intensity projections, and computer-assisted detection. Eur Radiol 17(12):3148–3156
Tu XM, et al. (2004) Power analyses for longitudinal trials and other clustered designs. Stat Med 23(18):2799–2815
Coakley FV, et al. (1998) Maximum intensity projection images in the detection of simulated pulmonary nodules by spiral CT. Br J Radiol 71(842):135–140
Buckley JA, et al. (1995) Pulmonary nodules: effect of increased data sampling on detection with spiral CT and confidence in diagnosis. Radiology 196(2):395–400
Urban BA, et al. (1993) Detection of focal hepatic lesions with spiral CT: comparison of 4- and 8-mm interscan spacing. AJR Am J Roentgenol 160(4):783–785
Acknowledgment
The work reported in this article was supported by the National Cancer Institute via Cancer Center Support Grant P30 CA016672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Non-Author Contributor: Eniola Mudasiru-Dawodu MD was invaluable as a reader participant.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jensen, C.T., Vicens-Rodriguez, R.A., Wagner-Bartak, N.A. et al. Multidetector CT detection of peritoneal metastases: evaluation of sensitivity between standard 2.5 mm axial imaging and maximum-intensity-projection (MIP) reconstructions. Abdom Imaging 40, 2167–2172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-015-0370-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-015-0370-7