Abstract
Purpose
Elastography is a non-invasive method to quantify fibrosis based on tissue mechanical properties. We performed a meta-analysis to assess the diagnostic accuracy of two such techniques: Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging (ARFI) or Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) for staging hepatic fibrosis.
Materials and Methods
Literature databases were searched until June 2013. Inclusion criteria were evaluation of MRE or ARFI, liver biopsy, and reported sensitivity and specificity. A random effects model was used to combine sensitivity and specificity, from which positive (LR+) and negative (LR−) likelihood ratios, diagnostic odds ratios, and area under receiver operating characteristics curve (AUROC) were derived. Differences between MRE and ARFI were compared with t tests (P < 0.05 considered significant).
Results
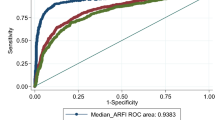
Eleven MRE studies including 982 patients and fifteen ARFI studies including 2,128 patients were selected. AUROC for MRE staging fibrosis were 0.94, 0.97, 0.96, and 0.97 for F1–F4, respectively, whereas AUROC for ARFI staging were 0.82, 0.85, 0.94, and 0.94 for F1–F4, respectively. Significance was found in AUROC between MRE and ARFI for the diagnosis of stage 1 and 2 fibrosis.
Conclusion
MRE is more accurate than ARFI with a higher combination of sensitivity, specificity, LR, and AUROC particularly in diagnosing early stages of hepatic fibrosis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APRI:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index
- ARFI:
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse
- AUROC:
-
Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve
- ALD:
-
Alcoholic liver disease
- AIH:
-
Autoimmune hepatitis
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CLD:
-
Chronic liver disease
- CHC:
-
Chronic hepatitis C
- CHB:
-
Chronic hepatitis B
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- DOR:
-
Diagnostic odds ratio
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- FP:
-
False positive
- FN:
-
False negative
- HIV:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- kPa:
-
kilopascal
- LR+:
-
Positive likelihood ratio
- LR−:
-
Negative likelihood ratio
- MRE:
-
Magnetic resonance elastography
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- NAFLD:
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- NASH:
-
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- PBC:
-
Primary biliary cirrhosis
- PSC:
-
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristics
- Se:
-
Sensitivity
- Sp:
-
Specificity
- TE:
-
Transient elastography
- TP:
-
True positive
- TN:
-
True negative
- US:
-
Ultrasound
Reference
Manning DS, Afdhal NH (2008) Diagnosis and quantitation of fibrosis. Gastroenterology 134(6):1670–1681. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.001
Afdhal NH, Nunes D (2004) Evaluation of liver fibrosis: a concise review. Am J Gastroenterol 99(6):1160–1174. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.30110
Martinez SM, Crespo G, Navasa M, Forns X (2011) Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 53(1):325–335. doi:10.1002/hep.24013
Bruguera M, Bordas JM, Mas P, Rodes J (1974) A comparison of the accuracy of peritoneoscopy and liver biopsy in the diagnosis of cirrhosis. Gut 15(10):799–800
Poniachik J, Bernstein DE, Reddy KR, et al. (1996) The role of laparoscopy in the diagnosis of cirrhosis. Gastrointest Endosc 43(6):568–571
Maharaj B, Maharaj RJ, Leary WP, et al. (1986) Sampling variability and its influence on the diagnostic yield of percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver. Lancet 1(8480):523–525
Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, et al. (2002) Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 97(10):2614–2618. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.06038.x
Merriman RB, Ferrell LD, Patti MG, et al. (2006) Correlation of paired liver biopsies in morbidly obese patients with suspected nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 44(4):874–880. doi:10.1002/hep.21346
Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A, et al. (2005) Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, Gastroenterology 128(7):1898–1906
Grant A, Neuberger J (1999) Guidelines on the use of liver biopsy in clinical practice, British Society of Gastroenterology. Gut 45(Suppl 4):IV1–IV11
Perrault J, McGill DB, Ott BJ, Taylor WF (1978) Liver biopsy: complications in 1000 inpatients and outpatients. Gastroenterology 74(1):103–106
Lindor KD, Bru C, Jorgensen RA, et al. (1996) The role of ultrasonography and automatic-needle biopsy in outpatient percutaneous liver biopsy. Hepatology 23(5):1079–1083. doi:10.1002/hep.510230522
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, et al. (2008) Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135(1):32–40. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.076
Castera L, Vergniol J, Foucher J, et al. (2005) Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest, APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 128(2):343–350
Leclerc GE, Charleux F, Robert L, et al. (2013) Analysis of liver viscosity behavior as a function of multifrequency magnetic resonance elastography (MMRE) postprocessing. J Magn Reson Imaging 38(2):422–428. doi:10.1002/jmri.23986
Bensamoun SF, Leclerc GE, Debernard L, et al. (2013) Cutoff values for alcoholic liver fibrosis using magnetic resonance elastography technique. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37(5):811–817. doi:10.1111/acer.12025
Guo J, Hirsch S, Streitberger KJ, et al. (2014) Patient-activated three-dimensional multifrequency magnetic resonance elastography for high-resolution mechanical imaging of the liver and spleen. RoFo 186(3):260–266. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1350510
Castera L, Foucher J, Bernard PH, et al. (2010) Pitfalls of liver stiffness measurement: a 5-year prospective study of 13,369 examinations. Hepatology 51(3):828–835. doi:10.1002/hep.23425
Koizumi Y, Hirooka M, Kisaka Y, et al. (2011) Liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: noninvasive diagnosis by means of real-time tissue elastography–establishment of the method for measurement. Radiology 258(2):610–617. doi:10.1148/radiol.10100319
Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Martens S, et al. (2008) Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a metaanalysis. Gastroenterology 134(4):960–974. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.034
Tsochatzis EA, Gurusamy KS, Ntaoula S, et al. (2011) Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Hepatol 54(4):650–659. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.033
Yoneda M, Suzuki K, Kato S, et al. (2010) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: US-based acoustic radiation force impulse elastography. Radiology 256(2):640–647. doi:10.1148/radiol.10091662
Friedrich-Rust M, Wunder K, Kriener S, et al. (2009) Liver fibrosis in viral hepatitis: noninvasive assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging versus transient elastography. Radiology 252(2):595–604. doi:10.1148/radiol.2523081928
Righi S, Fiorini E, De Molo C, et al. (2012) ARFI elastography in patients with chronic autoimmune liver diseases: a preliminary study. J Ultrasound 15(4):226–231. doi:10.1016/j.jus.2012.10.002
Bota S, Herkner H, Sporea I, et al. (2013) Meta-analysis: ARFI elastography versus transient elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis. Liver Int 33(8):1138–1147. doi:10.1111/liv.12240
Rouviere O, Yin M, Dresner MA, et al. (2006) MR elastography of the liver: preliminary results. Radiology 240(2):440–448. doi:10.1148/radiol.2402050606
Bensamoun SF, Wang L, Robert L, et al. (2008) Measurement of liver stiffness with two imaging techniques: magnetic resonance elastography and ultrasound elastometry. J Magn Reson Imaging 28(5):1287–1292. doi:10.1002/jmri.21523
Dodd GD 3rd, Baron RL, Oliver JH 3rd, Federle MP (1999) Spectrum of imaging findings of the liver in end-stage cirrhosis: part I, gross morphology and diffuse abnormalities. AJR Am J Roentgenol 173(4):1031–1036
Ito K, Mitchell DG (2004) Imaging diagnosis of cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis. Intervirology 47(3–5):134–143. doi:10.1159/000078465
Martin DR (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging of diffuse liver diseases. Topics Magn Reson Imaging 13(3):151–163
Bedossa P, Poynard T (1996) An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. Hepatology 24(2):289–293. doi:10.1002/hep.510240201
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J (2003) The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 3:25. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-3-25
Whiting P, Harbord R, de Salis I, Egger M, Sterne J (2008) Evidence-based diagnosis. J Health Serv Res Policy 13(Suppl 3):57–63. doi:10.1258/jhsrp.2008.008025
Glas AS, Lijmer JG, Prins MH, Bonsel GJ, Bossuyt PM (2003) The diagnostic odds ratio: a single indicator of test performance. J Clin Epidemiol 56(11):1129–1135
Zamora J, Abraira V, Muriel A, Khan K, Coomarasamy A (2006) Meta-DiSc: a software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol 6:31. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-6-31
Swets JA (1988) Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 240(4857):1285–1293
Song F, Khan KS, Dinnes J, Sutton AJ (2002) Asymmetric funnel plots and publication bias in meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy. Int J Epidemiol 31(1):88–95
Asbach P, Klatt D, Schlosser B, et al. (2010) Viscoelasticity-based staging of hepatic fibrosis with multifrequency MR elastography. Radiology 257(1):80–86. doi:10.1148/radiol.10092489
Choi YR, Lee JM, Yoon JH, Han JK, Choi BI (2013) Comparison of magnetic resonance elastography and gadoxetate disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of hepatic fibrosis. Investig Radiol 48(8):607–613. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e318289ff8f
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Salameh N, et al. (2007) Liver fibrosis: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography versus aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index. Radiology 245(2):458–466. doi:10.1148/radiol.2452061673
Ichikawa S, Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, et al. (2012) Magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Magn Reson Med Sci 11(4):291–297
Kamphues C, Klatt D, Bova R, et al. (2012) Viscoelasticity-based magnetic resonance elastography for the assessment of liver fibrosis in hepatitis C patients after liver transplantation. Rofo 184(11):1013–1019. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1313126
Kim BH, Lee JM, Lee YJ, et al. (2011) MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: experience from a tertiary center in Asia. J Magn Reson Imaging 34(5):1110–1116. doi:10.1002/jmri.22723
Kim D, Kim WR, Talwalkar JA, Kim HJ, Ehman RL (2013) Advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: noninvasive assessment with MR elastography. Radiology 268(2):411–419. doi:10.1148/radiol.13121193
Rustogi R, Horowitz J, Harmath C, et al. (2012) Accuracy of MR elastography and anatomic MR imaging features in the diagnosis of severe hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 35(6):1356–1364. doi:10.1002/jmri.23585
Wang Y, Ganger DR, Levitsky J, et al. (2011) Assessment of chronic hepatitis and fibrosis: comparison of MR elastography and diffusion-weighted imaging. AJR A J Roentgenol 196(3):553–561. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.4580
Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ, et al. (2007) Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5(10):1207–1213. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.06.012
Ye XP, Ran HT, Cheng J, et al. (2012) Liver and spleen stiffness measured by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis and esophageal varices in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Ultrasound Med 31(8):1245–1253
Friedrich-Rust M, Buggisch P, de Knegt RJ, et al. (2013) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat 20(4):240–247. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2893.2012.01646.x
Crespo G, Fernandez-Varo G, Marino Z, et al. (2012) ARFI, FibroScan, ELF, and their combinations in the assessment of liver fibrosis: a prospective study. J Hepatol 57(2):281–287. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.016
Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C, Andronescu D, Usvat R, et al. (2009) Acoustic radiation force imaging sonoelastography for noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 15(44):5525–5532
Karlas T, Pfrepper C, Wiegand J, et al. (2011) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) for noninvasive detection of liver fibrosis: examination standards and evaluation of interlobe differences in healthy subjects and chronic liver disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 46(12):1458–1467. doi:10.3109/00365521.2011.610004
Noruegas MJ, Matos H, Goncalves I, Cipriano MA, Sanches C (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse-imaging in the assessment of liver fibrosis in children. Pediatric Radiol 42(2):201–204. doi:10.1007/s00247-011-2257-2
Rizzo L, Calvaruso V, Cacopardo B, et al. (2011) Comparison of transient elastography and acoustic radiation force impulse for non-invasive staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 106(12):2112–2120. doi:10.1038/ajg.2011.341
Sporea I, Badea R, Sirli R, et al. (2011) How efficient is acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for the evaluation of liver stiffness? Hepat Mon 11(7):532–538
Sporea I, Bota S, Peck-Radosavljevic M, et al. (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for fibrosis evaluation in patients with chronic hepatitis C: an international multicenter study. Eur J Radiol 81(12):4112–4118. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.08.018
Takahashi H, Ono N, Eguchi Y, et al. (2010) Evaluation of acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for fibrosis staging of chronic liver disease: a pilot study. Liver Int 30(4):538–545. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02130.x
Toshima T, Shirabe K, Takeishi K, et al. (2011) New method for assessing liver fibrosis based on acoustic radiation force impulse: a special reference to the difference between right and left liver. J Gastroenterol 46(5):705–711. doi:10.1007/s00535-010-0365-7
Chen SH, Li YF, Lai HC, et al. (2012) Effects of patient factors on noninvasive liver stiffness measurement using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in patients with chronic hepatitis C. BMC Gastroenterol 12:105. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-12-105
Sohrabpour AA, Mohamadnejad M, Malekzadeh R (2012) Review article: the reversibility of cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther . doi:10.1111/apt.12044
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Parthasarathy, S., Goyal, P. et al. Magnetic resonance elastography and acoustic radiation force impulse for staging hepatic fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Abdom Imaging 40, 818–834 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0137-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0137-6