Abstract
Purpose
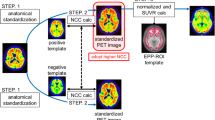
Amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) is an important noninvasive method for detecting amyloid burden in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients. As amyloid PET images have limited anatomical information, magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is usually acquired to perform reliable spatial normalization needed for large-scale analysis. This work proposed and evaluated the performance of new MR-free spatial normalization methods using a perfusion-like template for amyloid PET imaging.
Methods
Amyloid PET and MR images were collected in 35 subjects (cohort 1: 8 AD patients and 6 controls; cohort 2: 15 AD patients and 6 controls). Three ligand-related templates (AD, control, mixed group) and a perfusion-like template (pAV-45) from early time frames of amyloid PET images were constructed from cohort 1. The variations of 18F-AV-45 standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs) among AD patients, controls, and all subjects were tested with repeated two-way (template × brain region) analysis of variance (ANOVA) in cohort 2. 18F-AV-45 SUVRs by region of interest analysis and voxelwise analysis between MR-based and MR-free approaches were compared and correlated to clinical and image parameters. Effect size (group mean SUVR difference between AD and control/standard deviation) was also evaluated for each template method.
Results
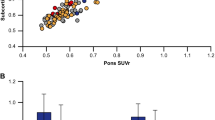
Significantly different 18F-AV-45 SUVRs between MR-free spatial normalization and MR-based reference images were found among AD patients, controls, and all subjects by the effect of template and brain regions. The highest correlation (r=0.991) of 18F-AV-45 SUVR to MR-based reference was found in the pAV-45 group. The SUVR percentage difference to MR-based reference showed the least variation and bias (control: −1.31±3.47 %; AD: −0.36±2.50 %) in the pAV-45 group as well. The voxelwise analysis showed the smallest t statistic value in pAV-45 followed by mixed, control, and AD groups when compared to MR-based reference images. Moreover, an overall larger effect size but compatible to that of MR-based reference result was observed in the pAV-45 group as compared to those of the other MR-free template.
Conclusion
The novel MR-free template based on the early-phase perfusion images pAV-45 approach for amyloid imaging showed significantly better performance in quantitation accuracy, effect size, and stability when compared with other MR-free PET templates and thus has potential for large-scale clinical applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lobo A, Launer LJ, Fratiglioni L, Andersen K, Di Carlo A, Breteler MM, et al. Prevalence of dementia and major subtypes in Europe: a collaborative study of population-based cohorts. Neurologic Diseases in the Elderly Research Group. Neurology 2000;54(11 Suppl 5):S4–9.
Rice DP, Fillit HM, Max W, Knopman DS, Lloyd JR, Duttagupta S. Prevalence, costs, and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia: a managed care perspective. Am J Manag Care 2001;7:809–18.
Alzheimer A. Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. Allg Z Psychiatr Psych-Gerichtl Med 1907;64:146–8.
Mathis CA, Wang Y, Holt DP, Huang GF, Debnath ML, Klunk WE. Synthesis and evaluation of 11C-labeled 6-substituted 2-arylbenzothiazoles as amyloid imaging agents. J Med Chem 2003;46:2740–54.
Verhoeff NP, Wilson AA, Takeshita S, Trop L, Hussey D, Singh K, et al. In-vivo imaging of Alzheimer disease beta-amyloid with [11C]SB-13 PET. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2004;12:584–95.
Shoghi-Jadid K, Barrio JR, Kepe V, Wu HM, Small GW, Phelps ME, et al. Imaging beta-amyloid fibrils in Alzheimer’s disease: a critical analysis through simulation of amyloid fibril polymerization. Nucl Med Biol 2005;32:337–51.
Rowe CC, Ackerman U, Browne W, Mulligan R, Pike KL, O’Keefe G, et al. Imaging of amyloid beta in Alzheimer’s disease with 18F-BAY94-9172, a novel PET tracer: proof of mechanism. Lancet Neurol 2008;7:129–35.
Koole M, Lewis DM, Buckley C, Nelissen N, Vandenbulcke M, Brooks DJ, et al. Whole-body biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of 18F-GE067: a radioligand for in vivo brain amyloid imaging. J Nucl Med 2009;50:818–22.
Choi SR, Golding G, Zhuang Z, Zhang W, Lim N, Hefti F, et al. Preclinical properties of 18F-AV-45: a PET agent for Abeta plaques in the brain. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1887–94.
Lin KJ, Hsu WC, Hsiao IT, Wey SP, Jin LW, Skovronsky D, et al. Whole-body biodistribution and brain PET imaging with [18F]AV-45, a novel amyloid imaging agent–a pilot study. Nucl Med Biol 2010;37:497–508.
Yao CH, Lin KJ, Weng CC, Hsiao IT, Ting YS, Yen TC, et al. GMP-compliant automated synthesis of [(18)F]AV-45 (Florbetapir F 18) for imaging beta-amyloid plaques in human brain. Appl Radiat Isot 2010;68:2293–7.
Kung MP, Weng CC, Lin KJ, Hsiao IT, Yen TC, Wey SP. Amyloid plaque imaging from IMPY/SPECT to AV-45/PET. Chang Gung Med J 2012;35:211–8.
Vlassenko AG, Mintun MA, Xiong C, Sheline YI, Goate AM, Benzinger TL, et al. Amyloid-beta plaque growth in cognitively normal adults: longitudinal [11C]Pittsburgh compound B data. Ann Neurol 2011;70:857–61.
Raniga P, Bourgeat P, Fripp J, Acosta O, Villemagne VL, Rowe C, et al. Automated (11)C-PiB standardized uptake value ratio. Acad Radiol 2008;15:1376–89.
Rosario BL, Weissfeld LA, Laymon CM, Mathis CA, Klunk WE, Berginc MD, et al. Inter-rater reliability of manual and automated region-of-interest delineation for PiB PET. Neuroimage 2011;55:933–41.
Kemppainen NM, Aalto S, Wilson IA, Någren K, Helin S, Brück A, et al. Voxel-based analysis of PET amyloid ligand [11C]PIB uptake in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2006;67:1575–80.
Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Hum Brain Mapp 1999;7:254–66.
Meyer JH, Gunn RN, Myers R, Grasby PM. Assessment of spatial normalization of PET ligand images using ligand-specific templates. Neuroimage 1999;9:545–53.
Frisoni GB, Lorenzi M, Caroli A, Kemppainen N, Någren K, Rinne JO. In vivo mapping of amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2009;72:1504–11.
Hsiao IT, Huang CC, Hsieh CJ, Hsu WC, Wey SP, Yen TC, et al. Correlation of early-phase 18F-florbetapir (AV-45/Amyvid) PET images to FDG images: preliminary studies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2012;39:613–20.
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984;34:939–44.
Association AP. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
Joshi A, Koeppe RA, Fessler JA. Reducing between scanner differences in multi-center PET studies. Neuroimage 2009;46:154–9.
Mazziotta JC, Toga AW, Evans A, Fox P, Lancaster J. A probabilistic atlas of the human brain: theory and rationale for its development. The International Consortium for Brain Mapping (ICBM). Neuroimage 1995;2:89–101.
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, et al. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 2002;15:273–89.
Joshi AD, Pontecorvo MJ, Clark CM, Carpenter AP, Jennings DL, Sadowsky CH, et al. Performance characteristics of amyloid PET with florbetapir F 18 in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and cognitively normal subjects. J Nucl Med 2012;53:378–84.
Yamaguchi H, Hirai S, Morimatsu M, Shoji M, Nakazato Y. Diffuse type of senile plaques in the cerebellum of Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by beta protein immunostain. Acta Neuropathol 1989;77(3):314–9.
Cohen J. The t test for means. In: Cohen J, editor. Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1988. p. 19–74.
Clark CM, Schneider JA, Bedell BJ, Beach TG, Bilker WB, Mintun MA, et al. Use of florbetapir-PET for imaging beta-amyloid pathology. JAMA 2011;305:275–83.
Nicoll JAR, Wilkinson D, Holmes C, Steart P, Markham H, Weller RO. Neuropathology of human Alzheimer disease after immunization with amyloid-β peptide: a case report. Nat Med 2003;9:448–52.
Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 1991;82:239–59.
Fodero-Tavoletti MT, Cappai R, McLean CA, Pike KE, Adlard PA, Cowie T, et al. Amyloid imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Brain Imaging Behav 2009;3:246–61.
Meyer PT, Hellwig S, Amtage F, Rottenburger C, Sahm U, Reuland P, et al. Dual-biomarker imaging of regional cerebral amyloid load and neuronal activity in dementia with PET and 11C-labeled Pittsburgh compound B. J Nucl Med 2011;52:393–400.
Johnson KA, Albert MS. Perfusion abnormalities in prodromal AD. Neurobiol Aging 2000;21:289–92.
Hu WT, Wang Z, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Detre JA, Grossman M. Distinct cerebral perfusion patterns in FTLD and AD. Neurology 2010;75:881–8.
Clark CM, Pontecorvo MJ, Beach TG, Bedell BJ, Coleman RE, Doraiswamy PM, et al. Cerebral PET with florbetapir compared with neuropathology at autopsy for detection of neuritic amyloid-β plaques: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol 2012;11:669–78.
Camus V, Payoux P, Barré L, Desgranges B, Voisin T, Tauber C, et al. Using PET with 18F-AV-45 (florbetapir) to quantify brain amyloid load in a clinical environment. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2012;39:621–31.
Acknowledgments
We thank Avid Radiopharmaceuticals (Philadelphia, PA, USA) for providing the precursor for the preparation of 18F-AV-45. This study was supported by grant NSC-98-2314-B-182-034-MY2, 99-2314-B-182A-067-MY2, 100-2314-B-182-038, 100-2314-B-182A-092-MY3, 101-2314-B-182-061-MY2, CMRPD1A0312, and CMRPG390793. Statistical analysis was supported by the Resource Center for Clinical Research, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou, Taiwan.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ing-Tsung Hsiao and Chin-Chang Huang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsiao, IT., Huang, CC., Hsieh, CJ. et al. Perfusion-like template and standardized normalization-based brain image analysis using 18F-florbetapir (AV-45/Amyvid) PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 40, 908–920 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2350-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-013-2350-x