Abstract
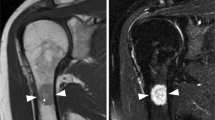
Hibernoma is a benign adipose tumour that contains foetal brown fat cells. We report a case of hibernoma arising in the left ischium of a 65-year-old female with a past history of ovarian carcinoma. The patient presented with a relatively short history of left sacral/hip pain. Radiologically, the lesion, which was large (5 cm) and sclerotic, had been stable for a number of years. Histologically, it was composed mainly of plump cells with foamy, multivacuolated cytoplasm. These cells showed no reaction for epithelial, melanoma or leucocyte markers but expressed FABP4/aP2 and S100, indicating that they were brown fat cells. There was no mitotic activity or nuclear pleomorphism and the lesion was diagnosed as a benign intraosseous hibernoma (IOH). IOH is a recently identified benign adipocytic lesion that presents typically as a sclerotic bone lesion. It has characteristic morphological and immunophenotypic features and should be regarded as a discrete primary bone tumour that needs to be distinguished from metastatic carcinoma/melanoma, chondrosarcoma and metabolic storage diseases containing numerous foamy macrophages.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks JJ, Perosio PM. Adipose tissue. In: Sternberg S, editor. Histology for pathologists. NY: Raven; 1992. p. 33–60.
Neil GP, Mansahl N. Lipoma. In: Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F, editors. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC; 2013. p. 20–1.
Miettinen MMF-S, Mandahl JC, Hibernoma N. In: Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F, editors. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC; 2013. p. 31–3.
Rosenberg AE, Bridge JA. Lipoma. In: Fletcher CDM, Bridge JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F, editors. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC; 2013. p. 341.
Rosenberg AE, Szuhai K. Liposarcoma. In: Fletcher CDM, Bridges JA, Hogendoorn PCW, Mertens F, editors. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC; 2013. p. 342.
Thorns C, Schardt C, Katenkamp D, Kahler C, Merz H, Feller AC. Hibernoma-like fat in the bone marrow; report of a unique case. Virchows Arch. 2008;452:343–5.
Reyes AR IR, Wilson JD, Desai HS. Intraosseous hibernoma of the femur; an unusual case with a review of the literature (poster #20). USCAP 2008; 132: 3.
Kumar R, Deaver MT, Czerniak BA, Madewell JE. Intraosseous hibernoma. Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40:641–5.
Bai S, Mies C, Stephenson J, Zhang PJ. Intraosseous hibernoma: a potential mimic of metastatic carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 2013;17:204–6.
Bonar SF, Watson G, Gragnaniello C, Seex K, Magnussen J, Earwaker J. Intraosseous hibernoma: characterization of five cases and literature review. Skeletal Radiol. 2014;43:939–46.
Hafeez I, Shankman S, Michnovicz J, Vigorita VJ. Intraosseous hibernoma: a case report and review of the literature. Spine. 2015;40:E558–61.
Jerman A, Snoj Ž, Kuzmanov BG, Limpel Novak AK. Intraosseous hibernoma: case report and tumour characterization. BJR Case Reports 2015; 1 (20150204).
Ringe KI, Rosenthal H, Langer F, Callies T, Wacker F, Raatschen HJ. Radiofrequency ablation of a rare case of an intraosseous hibernoma causing therapy-refractory pain. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24:1754–6.
Lynch DT, Dabney RS, Andrews JM. Intraosseous hibernoma or unusual location of brown fat? J Hematop. 2013;6:151–3.
Kashima TG, Turley H, Dongre A, Pezzella F, Athanasou NA. Diagnostic utility of aP2/FABP4 expression in soft tissue tumours. Virchows Arch. 2013;462:465–72.
Heaton JM. The distribution of brown adipose tissue in the human. J Anat. 1972; 35–9.
Nedergaard J, Bergtsson T, Cannon B. Unexpected evidence for active brown adipose tissue in adult humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;293:E444–52.
Maeda T, Tateishi U, Terauchi T, Hamashima C, Moriyama N, Arai Y, et al. Unsuspected bone and soft tissue lesions identified at cancer screening using position emission tomography. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2007;37:207–15.
Schulz TJ, Huang TL, Tran TT, Zhang H, Townsend KL, et al. Identification of inducible brown adipocyte progenitors residing in skeletal muscle and white fat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:143–8.
Krings A, Rahman S, Huang S, Lu Y, Czernik PJ, Lecka-Czernik B. Bone marrow fat has brown adipose tissue characteristics, which are attenuated with aging and diabetes. Bone. 2012;50:546–52.
Takada I, Suzawa M, Matsumoto K, Kato S. Suppression of PPAR transactivation switched cell fate of bone marrow stem cells from adipocytes into osteoblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1116:182–98.
Berendsen AD, Olsen BR. Osteoblast-adipocyte lineage plasticity in tissue development, maintenance and pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71:493–7.
Rahman S, Lu Y, Czernik PJ, Rosen CJ, Enderback S, Lecka-Czernik B. Inducible brown adipose tissue, or beige fat, is anabolic for the skeleton. Endocrinology. 2013;154:2687–701.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent for this study was obtained from the patient. This study was approved by the Central Oxford Research Ethics Committee (C01.070 and C01.071).
Funding
MV was an EU-funded Erasmus plus visitor.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vlychou, M., Teh, J., Whitwell, D. et al. Intraosseous hibernoma: a rare adipocytic bone tumour. Skeletal Radiol 45, 1565–1569 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-016-2460-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-016-2460-1