Abstract
Objective
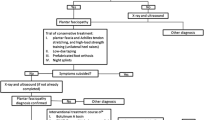
The treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciopathy is often empirical. Imaging is usually in the form of radiographs, if undertaken at all. The aim of this study is to characterise the disease pattern in recalcitrant cases of plantar fasciopathy. This allows classification of the pathology, which in turn allows meaningful evaluation of current and future treatments.
Materials and methods
One hundred and twenty-five consecutive feet with symptoms of ‘plantar fasciitis’ lasting longer than 6 months (all of which had failed to improve with a stepwise conservative management protocol) had confirmed plantar fasciopathy on ultrasound scanning. The disease characteristics were evaluated based on the scan findings.
Results
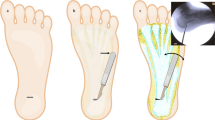
Of the patients evaluated, 66 % had typical insertional disease. The remaining 34 % had atypical distal fascia disease; 22 % had mixed insertional and distal disease, and 12 % had pure distal disease. Patients with pure distal disease were found to have either distal thickening or discrete fibromata.
Conclusion
In this cohort of recalcitrant cases, ultrasound scans detected a high proportion of atypical non-insertional plantar fascia disease. This would not be detected without imaging studies, and therefore we recommend the use of ultrasound scanning in cases of recalcitrant plantar heel pain that have failed proper first-line management, in order to confirm the clinical diagnosis and to classify the disease as either insertional or non-insertional plantar fasciopathy (or mixed disease). Only in this way can treatments for this group of patients be systematically evaluated against different disease patterns to determine their effectiveness.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karabay N, Toros T, Hurel C. Ultrasonographic evaluation in plantar fasciitis. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2007;46(6):442–6.
Aquino A, Payne C. Function of the plantar fascia. Foot. 1999;9(2):73–8.
Lemont H, Ammirati KM, Usen N. Plantar fasciitis: a degenerative process (fasciosis) without inflammation. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2003;93(3):234–7.
Jarde O, Diebold P, Havet E, Boulu G, Vernois J. Degenerative lesions of the plantar fascia: surgical treatment by fasciectomy and excision of the heel spur. A report on 38 cases. Acta Orthop Belg. 2003;69(3):267–74.
Puddu G, Ippolito E, Postacchini F. A classification of Achilles tendon disease. Am J Sports Med. 1976;4(4):145–50.
Maffulli N, Khan KM, Puddu G. Overuse tendon conditions: time to change a confusing terminology. Arthroscopy. 1998;14(8):840–3.
Riddle DL, Schappert SM. Volume of ambulatory care visits and patterns of care for patients diagnosed with plantar fasciitis: a national study of medical doctors. Foot Ankle Int. 2004;25(5):303–10.
Riddle DL, Pulisic M, Pidcoe P, Johnson RE. Risk factors for plantar fasciitis: a matched case-control study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(5):872–7.
Riddle DL, Pulisic M, Sparrow K. Impact of demographic and impairment-related variables on disability associated with plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2004;25(5):311–7.
Rano JA, Fallat LM, Savoy-Moore RT. Correlation of heel pain with body mass index and other characteristics of heel pain. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2001;40(6):351–6.
Prichasuk S, Subhadrabandhu T. The relationship of pes planus and calcaneal spur to plantar heel pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;306:192–6.
Wolgin M, Cook C, Graham C, Mauldin D. Conservative treatment of plantar heel pain: long-term follow-up. Foot Ankle Int. 1994;15(3):97–102.
Crawford F, Thomson C. Interventions for treating plantar heel pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;3:CD000416.
Davis PF, Severud E, Baxter DE. Painful heel syndrome: results of nonoperative treatment. Foot Ankle Int. 1994;15(10):531–5.
Martin RL, Irrgang JJ, Conti SF. Outcome study of subjects with insertional plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19(12):803–11.
Flanigan RM, Nawoczenski DA, Chen L, Wu H, DiGiovanni BF. The influence of foot position on stretching of the plantar fascia. Foot Ankle Int. 2007;28(7):815–22.
DiGiovanni BF, Nawoczenski DA, Lintal ME, Moore EA, Murray JC, Wilding GE, et al. Tissue-specific plantar fascia-stretching exercise enhances outcomes in patients with chronic heel pain. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(7):1270–7.
Griffith JF, Wong TY, Wong SM, Wong MW, Metreweli C. Sonography of plantar fibromatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179(5):1167–72.
Gibbon WW, Long G. Ultrasound of the plantar aponeurosis (fascia). Skeletal Radiol. 1999;28(1):21–6.
Jeswani T, Morlese J, McNally EG. Getting to the heel of the problem: plantar fascia lesions. Clin Radiol. 2009;64(9):931–9.
Akfirat M, Sen C, Günes T. Ultrasonographic appearance of the plantar fasciitis. Clin Imaging. 2003;27(5):353–7.
Griffith JF, Wong SM, Li EK. Ultrasound evaluation of plantar fasciitis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2001;30(3):176–7.
Healey K, Chen K. Plantar fasciitis: current diagnostic modalities and treatments. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2010;27(3):369–80.
Buchbinder R, Ptasznik R, Gordon J, Buchanan J, Prabaharan V, Forbes A. Ultrasound-guided extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciitis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2002;288(11):1364–72.
Rompe JD, Cacchio A, Weil Jr L, Furia JP, Haist J, Reiners V, et al. Plantar fascia-specific stretching versus radial shock-wave therapy as initial treatment of plantar fasciopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(15):2514–22.
Jozsa L, Kannus P. Histopathological findings in spontaneous tendon ruptures. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 1997;7(2):113–8.
Jarvinen TA, Kannus P, Maffulli N, Khan KM. Achilles tendon disorders: etiology and epidemiology. Foot Ankle Clin. 2005;10(2):255–66.
Jarvinen M, Jozsa L, Kannus P, Jarvinen TL, Kvist M, Leadbetter W. Histopathological findings in chronic tendon disorders. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 1997;7(2):86–95.
Khan KM, Maffulli N. Tendinopathy: an Achilles' heel for athletes and clinicians. Clin J Sport Med. 1998;8(3):151–4.
Astrom M, Rausing A. Chronic Achilles tendinopathy. A survey of surgical and histopathologic findings. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;316:151–64.
Leadbetter WB. Cell-matrix response in tendon injury. Clin Sports Med. 1992;11(3):533–78.
Maffulli N, Wong J, Almekinders LC. Types and epidemiology of tendinopathy. Clin Sports Med. 2003;22(4):675–92.
Bestwick CS, Maffulli N. Reactive oxygen species and tendinopathy: do they matter? Br J Sports Med. 2004;38(6):672–4.
Goodship AE, Birch HL, Wilson AM. The pathobiology and repair of tendon and ligament injury. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 1994;10(2):323–49.
Selvanetti A, Cipolla M, Puddu G. Overuse tendon injuries: basic science and classification. Oper Tech Sports Med. 1997;5(3):110–7.
Arndt AN, Komi PV, Brüggemann G, Lukkariniemi J. Individual muscle contributions to the in vivo achilles tendon force. Clin Biomech. 1998;13(7):532–41.
Robert FK. The implications of the adaptable fatigue quality of tendons for their construction, repair and function. Comp Biochem Physiol - Part A: Mol Integr Physiol. 2002;133(4):987–1000.
Schepsis AA, Leach RE, Gorzyca J. Plantar fasciitis. Etiology, treatment, surgical results, and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;266:185–96.
Tountas AA, Fornasier VL. Operative treatment of subcalcaneal pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;332:170–8.
Snider MP, Clancy WG, McBeath AA. Plantar fascia release for chronic plantar fasciitis in runners. Am J Sports Med. 1983;11(4):215–9.
Puttaswamaiah R, Chandran P. Degenerative plantar fasciitis: a review of current concepts. Foot. 2007;17(1):3–9.
Clain MR, Baxter DE. Achilles tendinitis. Foot Ankle. 1992;13(8):482–7.
McNally EG, Shetty S. Plantar fascia: imaging diagnosis and guided treatment. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2010;14(3):334–43.
Sabir N, Demirlenk S, Yagci B, Karabulut N, Cubukcu S. Clinical utility of sonography in diagnosing plantar fasciitis. J Ultrasound Med. 2005;24(8):1041–8.
Kane D, Greaney T, Shanahan M, Duffy G, Bresnihan B, Gibney R, et al. The role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis and management of idiopathic plantar fasciitis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001;40(9):1002–8.
Conflict of interest or grants
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ieong, E., Afolayan, J., Carne, A. et al. Ultrasound scanning for recalcitrant plantar fasciopathy. Basis of a new classification. Skeletal Radiol 42, 393–398 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-012-1470-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-012-1470-x