Abstract
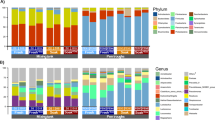
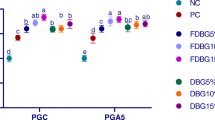
With the increasing production of ethanol for biofuels, a by-product of corn-based ethanol fermentation, dried distillers grains with solubles (DDGS) is finding its way into the feed of agricultural animals including cattle, pigs, poultry, sheep, goats, aquaculture species and horses. Corn DDGS contains very high levels of non-starch polysaccharides and could be considered a good source of fibre. Despite knowledge of the role of the fibre in modulating intestinal microbiota and consequently influencing health, there is currently little information on the interactions between DDGS and intestinal microbiota. We assessed the changes in the cecal microbiota of broilers feed rations supplemented with DDGS (five concentrations: 0, 6, 12, 18 and 24% w/w) with and without presence of digestive enzymes. DDGS concentration was strongly positively correlated (P = 3.7e−17, r = 0.74) with feed conversion efficiency (FCR), diminishing broiler performance with higher concentrations. Additionally, DDGS concentrations positively correlated with Richness index (P = 1.5e−3, r = 0.5), increasing the number of detectable species in the cecum. Among the most affected genera, Faecalibacterium (P = 0.032, r = −0.34) and Streptococcus (P = 7.9e−3, r = −0.39) were negatively correlated with DDGS, while Turicibacter (P = 2.8e−4, r = 0.52) was positively correlated with the DDGS concentration. Enzymes showed minimal effect on cecal microbiota.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abell GC, Cooke CM, Bennett CN, Conlon MA, McOrist AL (2008) Phylotypes related to Ruminococcus bromii are abundant in the large bowel of humans and increase in response to a diet high in resistant starch. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:505–515
Abt MC, Artis D (2009) The intestinal microbiota in health and disease: the influence of microbial products on immune cell homeostasis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 25(6):496–502
Abudabos AM (2014) Effect of fat source, energy level and enzyme supplementation and their interactions on broiler performance. South African J Animal Science 44(3):280–287
Ashelford KE, Chuzhanova NA, Fry JC, Jones AJ, Weightman AJ (2005) At least 1 in 20 16S rRNA sequence records currently held in public repositories is estimated to contain substantial anomalies. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7724–7736
Batal AB, Parsons CM (2002) Effects of age on development of digestive organs and performance of chicks fed a corn-soybean meal versus a crystalline amino acid diet. Poult Sci 81:1338–1341
Bennett GA, Richard JL (1996) Influence of processing on Fusarium mycotoxins in contaminated grains. Food Technol 50:235–238
Bischoff KM, Zhang Y, Rich JO (2016) Fate of virginiamycin through the fuel ethanol production process. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32(5):76
Blaut M, Clavel T (2007) Metabolic diversity of the intestinal microbiota: implications for health and disease. J Nutr 137:751S–755S
Candela M, Biagi E, Maccaferri S, Turroni S, Brigidi P (2012) Intestinal microbiota is a plastic factor responding to environmental changes. Trends Microbiol 20:385–391
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Choo YK, Oh ST, Lee KW, Kang CW, Kim HW, Kim CJ, Kim EJ, Kim HS, An BK (2014) The growth performance, carcass characteristics, and meat quality of egg-type male growing chicken and white-mini broiler in comparison with commercial broiler (Ross 308). Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour 34:622–629
Cowieson AJ (2005) Factors that affect the nutritional value of maize for broilers. Anim Feed Sci Technol 119:293–305
Cromwell GL, Herkelman KL, Stahly TS (1993) Physical, chemical, and nutritional characteristics of distillers dried grains with solubles for chicks and pigs. J Anim Sci 71:679–686
Delcour JA, Aman P, Courtin CM, Hamaker BR, Verbeke K (2016) Prebiotics, fermentable dietary fiber and health claims. Adv Nutr 7:1–4
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072
Dongarra ML, Rizzello V, Muccio L, Fries W, Cascio A, Bonaccorsi I, Ferlazzo G (2013) Mucosal immunology and probiotics. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 13:19–26
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Fadrosh DW, Ma B, Gajer P, Sengamalay N, Ott S, Brotman RM, Ravel J (2014) An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2:6
Ferretti J, Köhler W (2016) History of streptococcal research. In: Ferretti JJ, Stevens DL, Fischetti VA (eds) Streptococcus pyogenes: basic biology to clinical manifestations. The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, pp 1–22
Goodlad RA (2001) Dietary fibre and the risk of colorectal cancer. Gut 48(5):587–589
Hegde SN, Rolls BA, Turvey A, Coates ME (1978) The effects on chicks of dietary fibre from different sources: a growth factor in wheat bran. Br J Nutr 40(1):63–68
Hijova E, Chmelarova A (2007) Short chain fatty acids and colonic health. Bratisl Lek Listy 108(8):354–358
Hutkins RW, Krumbeck JA, Bindels LB, Cani PD, Fahey G Jr, Goh YJ, Hamaker B, Martens EC, Mills DA, Rastal RA, Vaughan E, Sanders ME (2016) Prebiotics: why definitions matter. Curr Opin Biotechnol 37:1–7
Jung BM, Hoerler AB, Batal, Mitchell R (2011) Evaluation of feeding distillers dried grains with solubles and the effects of dietary enzymes on broiler performance and carcass characteristics. Poultry Science Association Annual Meeting. Poult Sci 90:18
Kumar V, Sinha AK, Makkar HP, de Boeck G, Becker K (2012) Dietary roles of non-starch polysaccharides in human nutrition: a review. Crit Rev. Food Sci Nutr 52:899–935
Latymer EA, Low AG, Fadden K, Sambrook IE, Woodley SC, Keal HD (1990) Measurement of transit time of digesta through sections of gastrointestinal tract of pigs fed with diets containing various sources of dietary fibre (non-starch polysaccharides). Arch Tierernahr 40(8):667–680
Liu J, Xu T, Zhu W, Mao S (2014) High-grain feeding alters caecal bacterial microbiota composition and fermentation and results in caecal mucosal injury in goats. Br J Nutr 112:416–427
Liu JH, Zhang ML, Zhang RY, Zhu WY, Mao SY (2016) Comparative studies of the composition of bacterial microbiota associated with the ruminal content, ruminal epithelium and in the faeces of lactating dairy cows. Microb Biotechnol 9:257–268
Lumpkins BS, Batal AB, Dale NM (2004) Evaluation of distillers dried grains with solubles as a feed ingredient for broilers. Poult Sci 83:1891–1896
Madar Z (1987) New sources of dietary fibre. Int J Obes 11(Suppl 1):57–65
Malkki A (2001) Physical properties of dietary fiber as keys to physiological functions. Cereal Foods World 46:196–199
Miquel S, Martin R, Rossi O, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Chatel JM, Sokol H, Thomas M, Wells JM, Langella P (2013) Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr Opin Microbiol 16:255–261
Munyaka PM, Rabbi MF, Khafipour E, Ghia JE (2016) Acute dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis promotes gut microbial dysbiosis in mice. J Basic Microbiol 56:986–998
Mushtaq T, Sarwar M, Ahmad G, Nisa MU, Jamil A (2006) The influence of exogenous multienzyme preparation and graded levels of digestible lysine in sunflower meal-based diets on the performance of young broiler chicks two weeks posthatching. Poult Sci 85:2180–2185
Opoku EY, Classen HL, Scott TA (2015) Effects of wheat distillers dried grains with solubles with or without protease and beta-mannanase on the performance of turkey hen poults. Poult Sci 94(2):207–214
Razin S (1985) Molecular biology and genetics of mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Microbiol Rev 49(4):419–455
Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J, Duncan AE, Kau AL, Griffin NW, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Ilkayeva O, Semenkovich CF, Funai K, Hayashi DK, Lyle BJ, Martini MC, Ursell LK, Clemente JC, Van Treuren W, Walters WA, Knight R, Newgard CB, Heath AC, Gordon JI (2013) Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science 341:1241214
Santiago-Rodriguez TM, Fornaciari G, Luciani S, Dowd SE, Toranzos GA, Marota I, Cano RJ (2015) Gut microbiome of an 11th century a.d. Pre-Columbian Andean mummy. PLoS One 10:e0138135
Shirey TB, Dykes JK, Luquez C, Maslanka SE, Raphael BH (2015) Characterizing the fecal microbiota of infants with botulism. Microbiome 3:54
Skraban J, Dzeroski S, Zenko B, Tusar L, Rupnik M (2013) Changes of poultry faecal microbiota associated with Clostridium difficile colonisation. Vet Microbiol 165:416–424
Sokol H, Seksik P, Furet JP, Firmesse O, Nion-Larmurier I, Beaugerie L, Cosnes J, Corthier G, Marteau P, Dore J (2009) Low counts of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in colitis microbiota. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15:1183–1189
Stanley D, Keyburn AL, Denman SE, Moore RJ (2012) Changes in the caecal microflora of chickens following Clostridium perfringens challenge to induce necrotic enteritis. Vet Microbiol 159:155–162
Stanley D, Geier MS, Hughes RJ, Denman SE, Moore RJ (2013) Highly variable microbiota development in the chicken gastrointestinal tract. PLoS One 8:e84290
Stanley D, Hughes RJ, Moore RJ (2014) Microbiota of the chicken gastrointestinal tract: influence on health, productivity and disease. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:4301–4310
Stanley D, Hughes RJ, Geier MS, Moore RJ (2016) Bacteria within the gastrointestinal tract microbiota correlated with Improved growth and feed conversion: challenges presented for the identification of performance enhancing probiotic bacteria. Front Microbiol 7:187
Sun Y, Zhou L, Fang L, Su Y, Zhu W (2015) Responses in colonic microbial community and gene expression of pigs to a long-term high resistant starch diet. Front Microbiol 6:877
Swiatkiewicz S, Koreleski J (2007) Effect of dietary level of maize- and rye distiller dried grains with solubles on nutrient utilization and digesta viscosity in laying hens. J Anim Feed Sci 16:668–667
Swiatkiewicz S, Swiatkiewicz M, Arczewska-Wlosek A, Jozefiak D (2016) Efficacy of feed enzymes in pig and poultry diets containing distillers dried grains with solubles: a review. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 100(1):15–26
Tan KY, Seow-Choen F (2007) Fiber and colorectal diseases: separating fact from fiction. World J Gastroenterol 13(31):4161–4167
Tap J, Furet JP, Bensaada M, Philippe C, Roth H, Rabot S, Lakhdari O, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Corthier G, Fontaine E, Dore J, Leclerc M (2015) Gut microbiota richness promotes its stability upon increased dietary fibre intake in healthy adults. Environ Microbiol 17:4954–4964
Tuohy K, Brown DT, Klinder A, Costabile A, Fava F (2015) Shaping the human microbiome with prebiotiv foods—current perspectives for continued development. In: Tuohy K, Del Rio D (eds) Diet-microbiome interactions in the gut, effects on human health and disease. Elsevier, London, pp 53–71
Turnbaugh PJ, Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Knight R, Gordon JI (2009) The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: A metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci Transl Med 1:6ra14
USGC (2012) A guide to distiller’s dried grains with solubles (DDGS), 3rd Edition of the DDGS User Handbook, p 5
Valcheva R, Dieleman LA (2016) Prebiotics: Definition and protective mechanisms. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 30:27–37
Vohra P, Kratzer FH (1964) Growth inhibitory effect of certain polysaccharides for chickens. Poult Sci 43(5):1164–1170
Ward NT, Zijlstra RT, Parsons C, Starkey C (2008) Non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) content of US commercial corn distiller’s dried grains with solubles (DDGS). Poult Sci 87:39
Wong C, Harris PJ, Ferguson LR (2016) Potential benefits of dietary fibre intervention in inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Sci 17(6):919. doi:10.3390/ijms17060919
Yu Z, Morrison M (2004) Improved extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from digesta and fecal samples. Biotechniques 36:808–812
Zakrzewski M, Proietti C, Ellis JJ, Hasan S, Brion MJ, Berger B, Krause L (2017) Calypso: a user-friendly web-server for mining and visualizing microbiome-environment interactions. Bioinformatics 33:782–783
Zhong Y, Nyman M, Fak F (2015) Modulation of gut microbiota in rats fed high-fat diets by processing whole-grain barley to barley malt. Mol Nutr Food Res 59:2066–2076
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the National Plan for Science, Technology and Innovation (MAARIFAH), King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Award Number (12-AGR-2495-02). Dragana Stanley is an ARC DECRA fellow. All data analyses were performed on the Isaac Newton High Performance Computing System at Central Queensland University, Australia, and we acknowledge the support received from Jason Bell in all aspects of High Performance Computing. We also thank Professors Robert Moore and Kerry Walsh for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This project was internally funded by King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This project was approved by the Departmental Board of Studies on Ethics, Methodology and Welfare, King Saud University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 304 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abudabos, A.M., Al-Atiyat, R.M., Albatshan, H.A. et al. Effects of concentration of corn distillers dried grains with solubles and enzyme supplementation on cecal microbiota and performance in broiler chickens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 7017–7026 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8448-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8448-5