Abstract
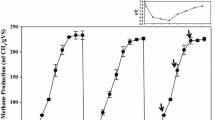
The shift of microbial communities during a transition from mesophilic anaerobic digestion (MAD) to thermophilic anaerobic digestion (TAD) was characterized in two treatments. One treatment was inoculated with sludge and the other was inoculated with manure. In this study, methane was produced both in MAD and TAD, but TAD has slightly more methane produced than MAD. A broad phylogenetic spectrum of bacterial, archaeal, and fungal taxa at thermophilic conditions was detected. Coprothermobacter, Bacillus, Haloplasma, Clostridiisalibacter, Methanobacterium, Methanothermobacter, Saccharomycetales, Candida, Alternaria, Cladosporium, and Penicillium were found almost exclusively in TAD, suggesting their adaptation to thermophilic conditions and ecological roles in digesting the organic compounds. The characterization of the lesser-known fungal community revealed that fungi probably constituted an important portion of the overall community within TAD and contributed to this process by degrading complex organic compounds. The shift of the microbial communities between MAD and TAD implied that temperature drastically affected the microbial diversity in anaerobic digestion. In addition, the difference in microbial communities between sludge and manure indicated that different source of inoculum also affected the microbial diversity and community.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington,D.C.
Blotevogel K-H, Fischer U, Mocha M, Jannsen S (1985) Methanobacteriumthermoalcaliphilum spec. nov., a new moderately alkaliphilic and thermophilic autotrophic methanogen. Arch Microbiol 142(3):211–217
Bond PL, Smriga SP, Banfield JF (2000) Phylogeny of microorganisms populating a thick, subaerial, predominantly lithotrophic biofilm at an extreme acid mine drainage site. Appl Environ Microb 66(9):3842–3849
Boone DR, Liu Y, Zhao Z-J, Balkwill DL, Drake GR, Stevens TO, Aldrich HC (1995) Bacillusinfernus sp. nov., an Fe (III)-and Mn (IV)-reducing anaerobe from the deep terrestrial subsurface. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45(3):441–448
Bouanane-Darenfed A, Fardeau M-L, Grégoire P, Joseph M, Kebbouche-Gana S, Benayad T, Hacene H, Cayol J-L, Ollivier B (2011) Caldicoprobacteralgeriensis sp. nov. A new thermophilic anaerobic, xylanolytic bacterium isolated from an Algerian hot spring. Curr Microbiol 62(3):826–832
Bouanane-Darenfed A, Hania WB, Hacene H, Cayol J-L, Ollivier B, Fardeau M-L (2013) Caldicoprobacterguelmensis sp. nov., a thermophilic, anaerobic, xylanolytic bacterium isolated from a hot spring. Int J Syst Evol Micr 63(Pt 6):2049–2053
Brock TD, Freeze H (1969) Thermusaquaticus gen. n. and sp. n., a nonsporulating extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol 98(1):289–297
Buchan A, Newell SY, Butler M, Biers EJ, Hollibaugh JT, Moran MA (2003) Dynamics of bacterial and fungal communities on decaying salt marsh grass. Appl Environ Microb 69(11):6676–6687
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(Supplement 1):4516–4522
Cheon J, Hong F, Hidaka T, Koshikawa H, Tsuno H (2007) Microbial population dynamics in a thermophilic methane digester fed with garbage. Water Sci Technol 55(10):175–182
Craveri R, Manachini P, Aragozzini F (1972) Thermozymocidin new antifungal antibiotic from a thermophilic eumycete. Experientia 28(7):867–868
Darland G, Brock T (1971) Bacillusacidocaldarius sp. nov., an acidophilic thermophilic spore-forming bacterium. J Gen Microbiol 67(1):9–15
de Boer W, Folman LB, Summerbell RC, Boddy L (2005) Living in a fungal world: impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29(4):795–811
De la Rubia M, Riau V, Raposo F, Borja R (2013) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: focus on the influence of the start-up. A Rev Crit Rev Biotechnol 33(4):448–460
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microb 72(7):5069–5072
Emmerich M, Bhansali A, Lösekann-Behrens T, Schröder C, Kappler A, Behrens S (2012) Abundance, distribution, and activity of Fe (II)-oxidizing and Fe (III)-reducing microorganisms in hypersaline sediments of Lake Kasin, southern Russia. Appl Environ Microb 78(12):4386–4399
Etchebehere C, Pavan M, Zorzopulos J, Soubes M, Muxi L (1998) Coprothermobacterplatensis sp. nov., a new anaerobic proteolytic thermophilic bacterium isolated from an anaerobic mesophilic sludge. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48(4):1297–1304
Ghazifard A, Kasra-Kermanshahi R, Far ZE (2001) Identification of thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria and fungi in Esfahan (Iran) municipal solid waste compost. Waste Manag Res 19(3):257–261
Gujer W, Zehnder A (1983) Conversion processes in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci Technol 15(8–9):127–167
Hori T, Haruta S, Sasaki D, Hanajima D, Ueno Y, Ogata A, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2014) Reorganization of the bacterial and archaeal populations associated with organic loading conditions in a thermophilic anaerobic digester. J Biosci Bioeng
Hultman J, Vasara T, Partanen P, Kurola J, Kontro M, Paulin L, Auvinen P, Romantschuk M (2010) Determination of fungal succession during municipal solid waste composting using a cloning-based analysis. J Appl Microbiol 108(2):472–487
Jiang L, Xu H, Zeng X, Wu X, Long M, Shao Z (2015) Thermophilic hydrogen-producing bacteria inhabiting deep-sea hydrothermal environments represented by Caloranaerobacter. Res Microbiol
Kamagata Y, Kawasaki H, Oyaizu H, Nakamura K, Mikami E, Endo G, Koga Y, Yamasato K (1992) Characterization of three thermophilic strains of Methanothrix (“Methanosaeta”) thermophila sp. nov. and rejection of Methanothrix (“Methanosaeta”) thermoacetophila. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42(3):463–468
Kersters I, Maestrojuan GM, Torck U, Vancanneyt M, Kersters K, Verstraete W (1994) Isolation of Coprothermobacterproteolyticus from an anaerobic digest and further characterization of the species. Syst Appl Microbiol 17(2):289–295
Khemkhao M, Nuntakumjorn B, Techkarnjanaruk S, Phalakornkule C (2012) UASB performance and microbial adaptation during a transition from mesophilic to thermophilic treatment of palm oil mill effluent. J Environ Manag 103:74–82
Kirk TK, Farrell RL (1987) Enzymatic “combustion”: the microbial degradation of lignin. Annu Rev Microbiol 41(1):465–501
Kotelnikova S, Macario AJ, Pedersen K (1998) Methanobacteriumsubterraneum sp. nov., a new alkaliphilic, eurythermic and halotolerant methanogen isolated from deep granitic groundwater. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48(2):357–367
Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Walters WA, González A, Caporaso JG, Knight R (2012) Using QIIME to analyze 16S rRNA gene sequences from microbial communities. Curr Protoc Microbiol:1E. 5.1-1E. 5.20
Kuhar S, Nair LM, Kuhad RC (2008) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic material with fungi capable of higher lignin degradation and lower carbohydrate degradation improves substrate acid hydrolysis and the eventual conversion to ethanol. Can J Microbiol 54(4):305–313
Levén L, Eriksson AR, Schnürer A (2007) Effect of process temperature on bacterial and archaeal communities in two methanogenic bioreactors treating organic household waste. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59(3):683–693
Luo G, Angelidaki I (2013) Co-digestion of manure and whey for in situ biogas upgrading by the addition of H2: process performance and microbial insights. Appl Microbiol Biot 97(3):1373–1381
Maeda K, Hanajima D, Morioka R, Osada T (2010) Characterization and spatial distribution of bacterial communities within passively aerated cattle manure composting piles. Bioresource Technol 101(24):9631–9637
Margesin R, Fonteyne P-A, Redl B (2005) Low-temperature biodegradation of high amounts of phenol by Rhodococcus spp. and basidiomycetous yeasts. Res Microbiol 156(1):68–75
Menes RJ, Fernández A, Muxí LA (2001) Physiological and molecular characterisation of an anaerobic thermophilic oleate-degrading enrichment culture. Anaerobe 7(1):17–24
Merlino G, Rizzi A, Schievano A, Tenca A, Scaglia B, Oberti R, Adani F, Daffonchio D (2013) Microbial community structure and dynamics in two-stage vs single-stage thermophilic anaerobic digestion of mixed swine slurry and market bio-waste. Water Res 47(6):1983–1995
Nallathambi Gunaseelan V (1997) Anaerobic digestion of biomass for methane production: a review. Biomass Bioenerg 13(1):83–114
Orcutt BN, Bach W, Becker K, Fisher AT, Hentscher M, Toner BM, Wheat CG, Edwards KJ (2010) Colonization of subsurface microbial observatories deployed in young ocean crust. ISME J 5(4):692–703
Osono T (2003) Effects of prior decomposition of beech leaf litter by phyllosphere fungi on substrate utilization by fungal decomposers. Mycoscience 44(1):41–45
Panswad T, Doungchai A, Anotai J (2003) Temperature effect on microbial community of enhanced biological phosphorus removal system. Water Res 37(2):409–415
Park Y, Hong F, Cheon J, Hidaka T, Tsuno H (2008) Comparison of thermophilic anaerobic digestion characteristics between single-phase and two-phase systems for kitchen garbage treatment. J Biosci Bioeng 105(1):48–54
Parkin GF, Owen WF (1986) Fundamentals of anaerobic digestion of wastewater sludges. J Environ Eng 112(5):867–920
Rademacher A, Nolte C, Schönberg M, Klocke M (2012) Temperature increases from 55 to 75 °C in a two-phase biogas reactor result in fundamental alterations within the bacterial and archaeal community structure. Appl Microbiol Biot 96(2):565–576
Ritari J, Koskinen K, Hultman J, Kurola JM, Kymäläinen M, Romantschuk M, Paulin L, Auvinen P (2012) Molecular analysis of meso- and thermophilic microbiota associated with anaerobic biowaste degradation. BMC Microbiol 12(1):121
Sasaki K, Morita M, Sasaki D, Nagaoka J, Matsumoto N, Ohmura N, Shinozaki H (2011) Syntrophic degradation of proteinaceous materials by the thermophilic strains Coprothermobacter proteolyticus and Methanothermobacterthermautotrophicus. J Biosci Bioeng 112(5):469–472
Shin K-S, Shin YK, Yoon J-H, Park Y-H (2001) Candidathermophila sp. nov., a novel thermophilic yeast isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Micr 51(6):2167–2170
Skirnisdottir S, Hreggvidsson GO, Hjörleifsdottir S, Marteinsson VT, Petursdottir SK, Holst O, Kristjansson JK (2000) Influence of sulfide and temperature on species composition and community structure of hot spring microbial mats. Appl Environ Microb 66(7):2835–2841
Štursová M, Žifčáková L, Leigh MB, Burgess R, Baldrian P (2012) Cellulose utilization in forest litter and soil: identification of bacterial and fungal decomposers. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 80(3):735–746
Sun W, Xiao T, Sun M, Dong Y, Ning Z, Xiao E, Tang S, Li J (2015) Diversity of the sediment microbial community in the Aha watershed (Southwest China) in response to acid mine drainage pollution gradients. Appl Environ Microb 81(15):4874–4884
Tada C, Tsukahara K, Sawayama S (2006) Illumination enhances methane production from thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Appl Microbiol Biot 71(3):363–368
Ueno Y, Tatara M (2008) Microbial population in a thermophilic packed-bed reactor for methanogenesis from volatile fatty acids. Enzyme Microb Tech 43(3):302–308
Walters WA, Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Berg-Lyons D, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) PrimerProspector: de novo design and taxonomic analysis of barcoded polymerase chain reaction primers. Bioinformatics 27(8):1159–1161
Wang X, Hu M, Xia Y, Wen X, Ding K (2012) Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial diversity in 14 wastewater treatment systems in China. Appl Environ Microb 78(19):7042–7047
Wasserfallen A, Nölling J, Pfister P, Reeve J, De Macario EC (2000) Phylogenetic analysis of 18 thermophilic Methanobacterium isolates supports the proposals to create a new genus, Methanothermobacter gen. nov., and to reclassify several isolates in three species, Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus comb. nov., Methanothermobacter wolfeii comb. nov., and Methanothermobacter marburgensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Micr 50(1):43–53
Winter J, Lerp C, Zabel H-P, Wildenauer F, König H, Schindler F (1984) Methanobacterium wolfei, sp. nov., a new tungsten-requiring, thermophilic, autotrophic methanogen. Syst Appl Microbiol 5(4):457–466
Wood TM, Garcia-Campayo V (1991) Enzymology of cellulose degradation physiology of biodegradative microorganisms. Springer, pp 147–161
Wrighton KC, Agbo P, Warnecke F, Weber KA, Brodie EL, DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Andersen GL, Coates JD (2008) A novel ecological role of the Firmicutes identified in thermophilic microbial fuel cells. ISME J 2(11):1146–1156
Yokoyama H, Wagner ID, Wiegel J (2010) Caldicoprobacteroshimai gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic, xylanolytic, extremely thermophilic bacterium isolated from sheep faeces, and proposal of Caldicoprobacteraceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Micr 60(1):67–71
Zbransk J, Wachtl R, Jenek P, Dohnyos M (2000) The activity of anaerobic biomass in thermophilic andmesophilic digesters at different loading rates. Water Sci Technol 42(9):49–56
Zeikus J, Wolee R (1972) Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol 109(2):707–713
Ziganshin AM, Liebetrau J, Pröter J, Kleinsteuber S (2013) Microbial community structure and dynamics during anaerobic digestion of various agricultural waste materials. Appl Microbiol Biot 97(11):5161–5174
Zinder SH, Mah RA (1979) Isolation and characterization of a thermophilic strain of Methanosarcina unable to use H2-CO2 for methanogenesis. Appl Environ Microb 38(5):996–1008
Compliance with ethical standards
ᅟ
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51178093, 51208086), the Shanghai Pujiang Program (13PJ1400100), the DHU Distinguished Young Professor Program, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 213 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Yu, G., Louie, T. et al. From mesophilic to thermophilic digestion: the transitions of anaerobic bacterial, archaeal, and fungal community structures in sludge and manure samples. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 10271–10282 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6866-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6866-9