Abstract
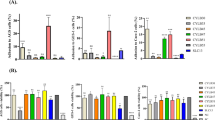
The influence of the industrial process on the properties of probiotics, administered as complex manufactured products, has been poorly investigated. In the present study, we comparatively assessed the cell wall characteristics of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lcr35® together with three of its commercial formulations with intestinal applications. Putative secreted and transmembrane-protein-encoding genes were initially searched in silico in the genome of L. rhamnosus Lcr35®. A total of 369 candidate genes were identified which expressions were followed using a custom Lactobacillus DNA chip. Among them, 60 or 67 genes had their expression either upregulated or downregulated in the Lcr Restituo® packet or capsule formulations, compared to the native Lcr35® strain. Moreover, our data showed that the probiotic formulations (Lcr Lenio®, Lcr restituo® capsule and packet) showed a better capacity to adhere to intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells than the native Lcr35® strain. Microbial (MATS) tests showed that the probiotic was an electron donor and that they were more hydrophilic than the native strain. The enhanced adhesion capacity of the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to epithelial Caco-2 cells and their antipathogen effect could be due to this greater surface hydrophilic character. These findings suggest that the manufacturing process influences the protein composition and the chemical properties of the cell wall. It is therefore likely that the antipathogen effect of the formulation is modulated by the industrial process. Screening of the manufactured products’ properties would therefore represent an essential step in evaluating the effects of probiotic strains.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
An YH, Friedman RJ (1998) Concise review of mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to biomaterial surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res 43(3):338–348
Antoni L, Nuding S, Wehkamp J, Stange EF (2014) Intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 20(5):1165–1179
Botes M, Loos B, van Reenen CA, Dicks LM (2008) Adhesion of the probiotic strains Enterococcus mundtii ST4SA and Lactobacillus plantarum 423 to Caco-2 cells under conditions simulating the intestinal tract, and in the presence of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medicaments. Arch Microbiol 190(5):573–584
Bove P, Capozzi V, Garofalo C, Rieu A, Spano G, Fiocco D (2012) Inactivation of the ftsH gene of Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1: effects on growth, stress tolerance, cell surface properties and biofilm formation. Microbiol Res 167(4):187–193
Candela M, Perna F, Carnevali P, Vitali B, Ciati R, Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Campieri M, Brigidi P (2008) Interaction of probiotic Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains with human intestinal epithelial cells: adhesion properties, competition against enteropathogens and modulation of IL-8 production. Int J Food Microbiol 125(3):286–292
Coudeyras S, Marchandin H, Fajon C, Forestier C (2008a) Taxonomic and strain-specific identification of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus 35 within the Lactobacillus casei group. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(9):2679–2689
Coudeyras S, Jugie G, Vermerie M (2008b) Forestier C (2008b) Adhesion of human probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus to cervical and vaginal cells and interaction with vaginosis-associated pathogens. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol 549640
de Champs C, Maroncle N, Balestrino D, Rich C, Forestier C (2003) Persistence of colonization of intestinal mucosa by a probiotic strain, Lactobacillus casei subsp. rhamnosus Lcr35, after oral consumption. J Clin Microbiol 41(3):1270–1273
Deepika G, Karunakaran E, Hurley CR, Biggs CA, Charalampopoulos D (2012) Influence of fermentation conditions on the surface properties and adhesion of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Microb Cell Fact 11:116
Douillard FP, Ribbera A, Kant R, Pietilä TE, Järvinen HM, Messing M, Randazzo CL, Paulin L, Laine P, Ritari J, Caggia C, Lähteinen T, Brouns SJ, Satokari R, von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Palva A, de Vos WM (2013) Comparative genomic and functional analysis of 100 Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains and their comparison with strain GG. PLoS Genet 9(8):e1003683
Evans DJ Jr, Evans DG (1973) Three characteristics associated with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun 8(3):322–328
FAO/WHO (2002) Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. Working Group Report 2002. Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization, Rome and Geneva
Forestier C, De Champs C, Vatoux C, Joly B (2001) Probiotic activities of Lactobacillus casei rhamnosus: in vitro adherence to intestinal cells and antimicrobial properties. Res Microbiol 152(2):167–173
Fukuda S, Toh H, Hase K, Oshima K, Nakanishi Y, Yoshimura K, Tobe T, Clarke JM, Topping DL, Suzuki T, Taylor TD, Itoh K, Kikuchi J, Morita H, Hattori M, Ohno H (2011) Bifidobacteria can protect from enteropathogenic infection through production of acetate. Nature 469(7331):543–547
Gareau MG, Barrett KE (2013) Fluid and electrolyte secretion in the inflamed gut: a novel targets for treatment of inflammation-induced diarrhea. Curr Opin Pharmacol 13(6):895–899
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) affy–analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20(3):307–315
Kankainen M, Paulin L, Tynkkynen S, von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Partanen P, Satokari R, Vesterlund S, Hendrickx AP, Lebeer S, De Keersmaecker SC, Vanderleyden J, Hämäläinen T, Laukkanen S, Salovuori N, Ritari J, Alatalo E, Korpela R, Mattila-Sandholm T, Lassig A, Hatakka K, Kinnunen KT, Karjalainen H, Saxelin M, Laakso K, Surakka A, Palva A, Salusjärvi T, Auvinen P, de Vos WM (2009) Comparative genomic analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reveals pili containing a human- mucus binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(40):17193–17198
Kos B, Susković J, Vuković S, Simpraga M, Frece J, Matosić S (2003) Adhesion and aggregation ability of probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus M92. J Appl Microbiol 94(6):981–987
Lebeer S, Claes I, Tytgat HL, Verhoeven TL, Marien E, von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Palva A, Vos WM, Keersmaecker SC, Vanderleyden J (2012) Functional analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG pili in relation to adhesion and immunomodulatory interactions with intestinal epithelial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(1):185–193
Lesuffleur T, Porchet N, Aubert JP, Swallow D, Gum JR, Kim YS, Real FX, Zweibaum A (1993) Differential expression of the human mucin genes MUC1 to MUC5 in relation to growth and differentiation of different mucus-secreting HT-29 cell subpopulations. J Cell Sci 106(Pt 3):771–783
Levine MM, Nataro JP, Karch H, Baldini MM, Kaper JB, Black RE, Clements ML, O'Brien AD (1985) The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis 152(3):550–559
Mahler GJ, Esch MB, Glahn RP, Shuler ML (2009a) Characterization of a gastrointestinal tract microscale cell culture analog used to predict drug toxicity. Biotechnol Bioeng 104(1):193–205
Mahler GJ, Shuler ML, Glahn RP (2009b) Characterization of Caco-2 and HT29-MTX cocultures in an in vitro digestion/cell culture model used to predict iron bioavailability. J Nutr Biochem 20(7):494–502
Nivoliez A, Camares O, Paquet-Gachinat M, Bornes S, Forestier C, Veisseire P (2012) Influence of manufacturing processes on in vitro properties of the probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lcr35®. J Biotechnol 160(3–4):236–241
Ojeda JJ, Romero-Gonzalez ME, Bachmann RT, Edyvean RG, Banwart SA (2008) Characterization of the cell surface and cell wall chemistry of drinking water bacteria by combining XPS, FTIR spectroscopy, modeling, and potentiometric titrations. Langmuir 24(8):4032–4040
Pinto M, Robine-Leon S, Appay MD, Kedinger M, Triadou N, Dussaulx E, Lacroix B, Simon-Assmann P, Haffen K, Fogh J, Zweibaum A (1983) Enterocyte-like differentiation and polarization of the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture. Biol Cell 41:323
Rosenberg M, Gutnick D, Rosenberg E (1980) Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: a simple method for measuring cell-surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 9:29–33
Santivarangkna C, Wenning M, Foerst P, Kulozik U (2007) Damage of cell envelope of Lactobacillus helveticus during vacuum drying. J Appl Microbiol 102(3):748–756
Saxelin M, Lassig A, Karjalainen H, Tynkkynen S, Surakka A, Vapaatalo H, Järvenpää S, Korpela R, Mutanen M, Hatakka K (2010) Persistence of probiotic strains in the gastrointestinal tract when administered as capsules, yoghurt, or cheese. Int J Food Microbiol 144(2):293–300
Schär-Zammaretti P, Dillmann ML, D'Amico N, Affolter M, Ubbink J (2005) Influence of fermentation medium composition on physicochemical surface properties of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8165–8173
Smyth GK, Michaud J, Scott HS (2005) Use of within-array replicate spots for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Bioinformatics 21(9):2067–2075
Suzuki C, Kimoto-Nira H, Kobayashi M, Nomura M, Sasaki K, Mizumachi K (2008) Immunomodulatory and cytotoxic effects of various Lactococcus strains on the murine macrophage cell line J774.1. Int J Food Microbiol 123(1–2):159–165
Todorov SD, Furtado DN, Saad SM, de Melo Franco BD G (2011) Bacteriocin production and resistance to drugs are advantageous features for Lactobacillus acidophilus La-14, a potential probiotic strain. New Microbiol 34(4):357–370
Tripathi P, Beaussart A, Alsteens D, Dupres V, Claes I, von Ossowski I, de Vos WM, Palva A, Lebeer S, Vanderleyden J, Dufrêne YF (2013) Adhesion and Nanomechanics of Pili from the Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. ACS Nano. Mar 26
Tuomola EM, Ouwehand AC, Salminen SJ (2000) Chemical, physical and enzymatic pre-treatments of probiotic lactobacilli alter their adhesion to human intestinal mucus glycoproteins. Int J Food Microbiol 60(1):75–81
von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Satokari R, Vesterlund S, Kankainen M, Huhtinen H, Tynkkynen S, Salminen S, de Vos WM, Palva A (2010) Mucosal adhesion properties of the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG SpaCBA and SpaFED pilin subunits. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(7):2049–2057
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the European funds FEDER, Auvergne Region, and Lyocentre S.A. We thank Aurélie Lacalmontie and Amandine Pralus for their technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
Adrien Nivoliez, Elina Alaterre, and Caroline Dausset have an institutional affiliation with the company which manufactures the products.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nivoliez, A., Veisseire, P., Alaterre, E. et al. Influence of manufacturing processes on cell surface properties of probiotic strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lcr35® . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 399–411 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6110-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6110-z