Abstract
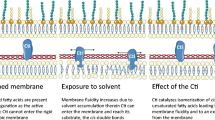
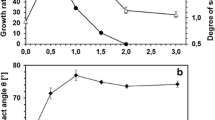
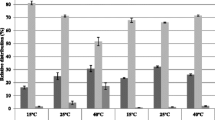
Bacterial cells are known to adapt to challenging environmental conditions such as osmotic stress. However, most of the work done in this field describes the adaptation of growing populations where the new generations acquire traits that improve their ability to survive. In the present study, the responses of Rhodococcus erythropolis cells within the first 30 min after exposure to osmotic stress caused by sodium chloride were studied. The cells changed the total lipid fatty acid composition and also the net surface charge in the 30 min following exposure. Surprisingly, the cells produced a high percentage of polyunsaturated fatty acids. In the presence of 7.5 % NaCl, these polyunsaturated fatty acids, mainly eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5ω3), arachidonic acid (C20:4ω6) and docosapentaenoic acid (C22:5ω3), comprise more than 36 % of the total fatty acids. The possible function of these very uncommon fatty acids in bacteria could be the decrease in the number of negatively charged groups in ion channels resulting in a repellence of the NaCl.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antolín EM, Delange DM, Canavaciolo VG (2008) Evaluation of five methods for derivatization and GC determination of a mixture of very long chain fatty acids (C24:0–C36:0). J Pharm Biomed Anal 46(1):194–199. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2007.09.015
Bell KS, Philp JC, Aw DWJ, Christofi N (1998) A review - The genus Rhodococcus. J Appl Microbiol 85(2):195–210. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.00525.x
Börjesson SI, Elinder F (2011) An electrostatic potassium channel opener targeting the final voltage sensor transition. J Gen Physiol 137(6):563–577. doi:10.1085/jgp.201110599
de Carvalho CCCR (2012) Adaptation of Rhodococcus erythropolis cells for growth and bioremediation under extreme conditions. Res Microbiol 163(2):125–136. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2011.11.003
de Carvalho C, Caramujo M (2012) Lipids of prokaryotic origin at the base of marine food webs. Mar Drugs 10(12):2698–2714. doi:10.3390/md10122698
de Carvalho C, da Fonseca MMR (2002) Maintenance of cell viability in the biotransformation of (-)-carveol with whole cells of Rhodococcus erythropolis. J Mol Catal B: Enzym 19:389-398 doi:10.1016/s1381-1177(02)00190-x
de Carvalho C, da Fonseca MMR (2005) Degradation of hydrocarbons and alcohols at different temperatures and salinities by Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL 14. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 51(3):389–399. doi:10.1016/j.femsec.2004.09.010
de Carvalho CCCR, Fernandes P (2010) Production of metabolites as bacterial responses to the marine environment. Mar Drugs 8(3):705–727
de Carvalho C, Parreno-Marchante B, Neumann G, da Fonseca MMR, Heipieper HJ (2005) Adaptation of Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 to growth on n-alkanes, alcohols and terpenes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67(3):383–388. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1750-z
de Carvalho CCCR, Fatal V, Alves SS, da Fonseca MMR (2007) Adaptation of Rhodococcus erythropolis cells to high concentrations of toluene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(6):1423–1430. doi:10.1007/s00253-007-1103-9
de Carvalho CCCR, Wick LY, Heipieper HJ (2009) Cell wall adaptations of planktonic and biofilm Rhodococcus erythropolis cells to growth on C5 to C16 n-alkane hydrocarbons. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82(2):311–320. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1809-3
DeLong EF, Yayanos AA (1986) Biochemical function and ecological significance of novel bacterial lipids in deep-sea procaryotes. Appl Environ Microbiol 51(4):730–737
Eder K (1995) Gas chromatographic analysis of fatty acid methyl esters. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 671(1–2):113–131. doi:10.1016/0378-4347(95)00142-6
Eggeling L, Sahm H (1980) Degradation of coniferyl alcohol and other lignin-related aromatic compounds by Nocardia sp. DSM 1069. Arch Microbiol 126(2):141–148. doi:10.1007/BF00511219
Fakhru’l-Razi A, Pendashteh A, Abdullah LC, Biak DRA, Madaeni SS, Abidin ZZ (2009) Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J Hazard Mater 170(2–3):530–551. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.044
Finnerty WR (1992) The biology and genetics of the genus Rhodococcus. Annu Rev Microbiol 46:193–218. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.46.1.193
Fulco A (1974) Metabolic alterations of fatty acids. Annu Rev Biochem 43:215–241
Hamamoto T, Takata N, Kudo T, Horikoshi K (1995) Characteristic presence of polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine psychrophilic vibrios. FEMS Microbiol Lett 129(1):51–56. doi:10.1016/0378-1097(95)00134-Q
Hiemenz PC, Rajagopalan R (1997) Principles of colloid and surface chemistry, 3rd edn. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
Iwabuchi N, Sunairi M, Anzai H, Nakajima M, Harayama S (2000) Relationships between colony morphotypes and oil tolerance in Rhodococcus rhodochrous. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(11):5073–5077. doi:10.1128/aem.66.11.5073-5077.2000
Izumi Y, Ohshiro T, Ogino H, Hine Y, Shimao M (1994) Selective desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(1):223–226
Kaszycki P, Walski T, Hachicho N, Heipieper H (2013) Biostimulation by methanol enables the methylotrophic yeasts Hansenula polymorpha and Trichosporon sp. to reveal high formaldehyde biodegradation potential as well as to adapt to this toxic pollutant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(12):5555–5564. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-4796-y
Kawamoto J, Kurihara T, Yamamoto K, Nagayasu M, Tani Y, Mihara H, Hosokawa M, Baba T, Sato SB, Esaki N (2009) Eicosapentaenoic acid plays a beneficial role in membrane organization and cell division of a cold-adapted bacterium, Shewanella livingstonensis Ac10. J Bacteriol 191(2):632–640. doi:10.1128/jb.00881-08
Larkin MJ, Kulakov LA, Allen CCR (2005) Biodegradation and Rhodococcus - masters of catabolic versatility. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16(3):282–290. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2005.04.007
Lee TS, Pacheco MA, Monticello DJ, Lange E, Patnaik R (1999) Biotransformation of sulfur heterocycles in fossil fuel by Rhodococcus erythropolis-application of metabolic engineering to increase biocatalyst longevity. Abstr Pap Am Chem Soc 217:U199–U200
Lichtinger T, Reiss G, Benz R (2000) Biochemical identification and biophysical characterization of a channel-forming protein from Rhodococcus erythropolis. J Bacteriol 182(3):764–770. doi:10.1128/jb.182.3.764-770.2000
Liu C-W, Liang M-S, Chen Y-C, Sayavedra-Soto LA, Liu H-S (2012) Biodegradation of n-alkanes at high concentration and correlation to the accumulation of H+ ions in Rhodococcus erythropolis NTU-1. Biochem Eng J 63:124–128. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2011.11.007
Matys VY, Baryshnikova LM, Golovlev EL (1998) Adaptation of bacteria of the genera Rhodococcus and Gordona to stress conditions. Microbiology 67(6):616–619
McLeod MP, Warren RL, Hsiao WWL, Araki N, Myhre M, Fernandes C, Miyazawa D, Wong W, Lillquist AL, Wang D, Dosanjh M, Hara H, Petrescu A, Morin RD, Yang G, Stott JM, Schein JE, Shin H, Smailus D, Siddiqui AS, Marra MA, Jones SJM, Holt R, Brinkman FSL, Miyauchi K, Fukuda M, Davies JE, Mohn WW, Eltis LD (2006) The complete genome of Rhodococcus sp. RHA1 provides insights into a catabolic powerhouse. PNAS 103(42):15582–15587. doi:10.1073/pnas.0607048103
Metz JG, Roessler P, Facciotti D, Levering C, Dittrich F, Lassner M, Valentine R, Lardizabal K, Domergue F, Yamada A, Yazawa K, Knauf V, Browse J (2001) Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids by polyketide synthases in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Science 293(5528):290–293. doi:10.1126/science.1059593
Michel EMB, Sokolovska I, Agathos SN (2004) Biodegradation of diesel fuel in soil at low temperature by Rhodococcus erythropolis. In: Verstraete W (ed) European symposium on environmental biotechnology, ESEB 2004. A. A. Balkema, Leiden, pp 843–846
Mutnuri S, Vasudevan N, Kastner M, Heipieper HJ (2005) Changes in fatty acid composition of Chromohalobacter israelensis with varying salt concentrations. Curr Microbiol 50(3):151–154. doi:10.1007/s00284-004-4396-2
Nichols DS (2003) Prokaryotes and the input of polyunsaturated fatty acids to the marine food web. FEMS Microbiol Lett 219(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/s0378-1097(02)01200-4
Nicolaus B, Manca MC, Lama L, Esposito E, Gambacorta A (2001) Lipid modulation by environmental stresses in two models of extremophiles isolated from Antarctica. Polar Biol 24(1):1–8. doi:10.1007/s003000000156
Ohshiro T, Hirata T, Izumi Y (1996) Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene derivatives by whole cells of Rhodococcus erythropolis H-2. FEMS Microbiol Lett 142(1):65–70. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1996.tb08409.x
Okuyama H, Orikasa Y, Nishida T, Watanabe K, Morita N (2007) Bacterial genes responsible for the biosynthesis of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids and their heterologous expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(3):665–670. doi:10.1128/aem.02270-06
Pirog T, Sofilkanych A, Shevchuk T, Shulyakova M (2013) Biosurfactants of Rhodococcus erythropolis IMV DN-5017: synthesis intensification and practical application. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170(4):880–894. doi:10.1007/s12010-013-0246-7
Portevin D, de Sousa-D’Auria C, Houssin C, Grimaldi C, Chami M, Daffé M, Guilhot C (2004) A polyketide synthase catalyzes the last condensation step of mycolic acid biosynthesis in mycobacteria and related organisms. PNAS 101(1):314–319. doi:10.1073/pnas.0305439101
Russell NJ, Nichols DS (1999) Polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine bacteria—a dogma rewritten. Microbiology 145(4):767–779. doi:10.1099/13500872-145-4-767
Schenkels P, Duine JA (2000) Nicotinoprotein (NADH-containing) alcohol dehydrogenase from Rhodococcus erythropolis DSM 1069: an efficient catalyst for coenzyme-independent oxidation of a broad spectrum of alcohols and the interconversion of alcohols and aldehydes. Microbiology 146(4):775–785
Schreiberova O, Hedbavna P, Cejkova A, Jirku V, Masak J (2012) Effect of surfactants on the biofilm of Rhodococcus erythropolis, a potent degrader of aromatic pollutants. New Biotechnol 30(1):62–68. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2012.04.005
Sebastian Y, Madupu R, Durkin AS, Torralba M, Methe B, Sutton GG, Strausberg RL, Nelson K.E. (2009) Submitted (APR-2009) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases (Entry name: C3JH63_RHOER)
Shaikh SR, Edidin M (2008) Polyunsaturated fatty acids and membrane organization: elucidating mechanisms to balance immunotherapy and susceptibility to infection. Chem Phys Lipids 153(1):24–33. doi:10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2008.02.008
Solyanikova I, Golovleva L (2011) Biochemical features of the degradation of pollutants by Rhodococcus as a basis for contaminated wastewater and soil cleanup. Microbiology 80(5):591–607. doi:10.1134/s0026261711050158
Takarada H, Sekine M, Hosoyama A, Yamada R, Fujisawa T, Omata S, Shimizu A, Tsukatani N, Tanikawa S, Fujita N, Harayama S (2005) Comparison of the complete genome sequences of Rhodococcus erythropolis PR4 and Rhodococcus opacus B4. Submitted (MAR-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases (e.g. Entry names: C0ZQM2_RHOE4; C0ZX03_RHOE4; C1A1S4_RHOE4)
Takeyama H, Takeda D, Yazawa K, Yamada A, Matsunaga T (1997) Expression of the eicosapentaenoic acid synthesis gene cluster from Shewanella sp. in a transgenic marine cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. Microbiology 143(8):2725–2731. doi:10.1099/00221287-143-8-2725
Tomiyasu I, Yano I (1984) Separation and analysis of novel polyunsaturated mycolic acids from a psychrophilic, acid-fast bacterium, Gordona aurantiaca. Eur J Biochem 139(1):173–180. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07991.x
Trojanowski J, Haider K, Sundman V (1977) Decomposition of 14C-labelled lignin and phenols by a Nocardia sp. Arch Microbiol 114(2):149–153. doi:10.1007/bf00410776
Valentine RC, Valentine DL (2004) Omega-3 fatty acids in cellular membranes: a unified concept. Prog Lipid Res 43(5):383–402. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2004.05.004
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ, Oren A (1998) Biology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62(2):504–544
Wang P, Krawiec S (1996) Kinetic analyses of desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by Rhodococcus erythropolis in batch and fed-batch cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(5):1670–1675
Warhurst AM, Fewson CA (1994) Biotransformations catalyzed by the genus Rhodococcus. Crit Rev Biotechnol 14(1):29–73. doi:10.3109/07388559409079833
Xiao YF, Kang JX, Morgan JP, Leaf A (1995) Blocking effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids on Na+ channels of neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. PNAS 92(24):11000–11004
Xiao YF, Sigg DC, Leaf A (2005) The antiarrhythmic effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: modulation of cardiac ion channels as a potential mechanism. J Membr Biol 206(2):141–154. doi:10.1007/s00232-005-0786-z
Yano Y, Nakayama A, Yoshida K (1997) Distribution of polyunsaturated fatty acids in bacteria present in intestines of deep-sea fish and shallow-sea poikilothermic animals. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(7):2572–2577
Yano Y, Nakayama A, Ishihara K, Saito H (1998) Adaptive changes in membrane lipids of barophilic bacteria in response to changes in growth pressure. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(2):479–485
Yu B, Xu P, Shi Q, Ma CQ (2006) Deep desulfurization of diesel oil and crude oils by a newly isolated Rhodococcus erythropolis strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(1):54–58. doi:10.1128/aem.72.1.54-58.2006
Acknowledgments
CCCR de Carvalho and MPC Marques would like to thank the Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (Portugal) for financial support (programs "Ciência 2007" and "FCT Investigators 2013", and SFRH/BPD/64160/2009, respectively) and Prof. Susete M. Dias and Joana Duarte for the help in the GC-MS analysis. This work was partially supported by a Portuguese-German integrated action (A-15/11) awarded by the Conselho de Reitores das Universidades Portuguesas (CRUP) and the Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (DAAD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 229 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Carvalho, C.C.C.R., Marques, M.P.C., Hachicho, N. et al. Rapid adaptation of Rhodococcus erythropolis cells to salt stress by synthesizing polyunsaturated fatty acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 5599–5606 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5549-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5549-2