Abstract
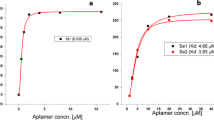
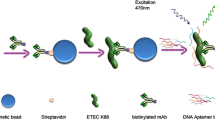
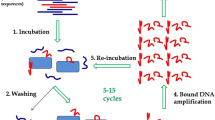
Alternative ligands such as nucleic acid aptamers can be used for pathogen capture and detection and offer advantages over antibodies, including reduced cost, ease of production and modification, and improved stability. DNA aptamers demonstrating binding specificity to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium were identified by whole-cell-systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) beginning with a combinatorial library of biotin-labeled single stranded DNA molecules. Aptamer specificity was achieved using whole-cell counter-SELEX against select non-Salmonella genera. Aptamers binding to Salmonella were sorted, cloned, sequenced, and characterized for binding efficiency. Out of 18 candidate aptamers screened, aptamer S8-7 showed relatively high binding affinity with an apparent dissociation constant (K d value) of 1.73 ± 0.54 μM and was selected for further characterization. Binding exclusivity analysis of S8-7 showed low apparent cross-reactivity with other foodborne bacteria including Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Citrobacter braakii and moderate cross-reactivity with Bacillus cereus. Aptamer S8-7 was successfully used as a ligand for magnetic capture of serially diluted Salmonella Typhimurium cells, followed by downstream detection using qPCR. The lower limit of detection of the aptamer magnetic capture-qPCR assay was 102–103 CFU equivalents of Salmonella Typhimurium in a 290-μl sample volume. Mean capture efficiency ranged from 3.6 to 12.6 %. Unique aspects of the study included (a) the use of SELEX targeting whole cells; (b) the application of flow cytometry for aptamer pool selection, thereby favoring purification of ligands with both high binding affinity and targeting abundant cell surface moieties; and (c) the use of pre-labeled primers that circumvented the need for post-selection ligand labeling. Taken together, this study provides proof-of-concept that biotinylated aptamers selected by whole-cell SELEX can be used in a qPCR-based capture-detection platform for Salmonella Typhimurium.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao X, Li S, Chen L, Ding H, Xu H, Huang Y, Li J, Liu N, Cao W, Zhu Y, Shen B, Shao N (2009) Combining use of a panel of ssDNA aptamers in the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res 37(14):4621–4628
CDC (2007) Salmonella surveillance: annual summary, 2005. US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, Atlanta
Chen F, Zhou J, Luo F, Mohammed AB, Zhang XL (2007) Aptamer from whole-bacterium SELEX as new therapeutic reagent against virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357(3):743–748
Cullison MA, Jaykus LA (2002) Magnetized carbonyl iron and insoluble zirconium hydroxide mixture facilitates bacterial concentration and separation from nonfat dry milk. J Food Prot 65(11):1806–1810
Duan N, Wu S, Chen X, Huang Y, Wang Z (2012) Selection and identification of a DNA aptamer targeted to Vibrio parahemolyticus. J Agric Food Chem 60(16):4034–4038
Dwivedi HP, Jaykus LA (2011) Detection of pathogens in foods: the current state-of-the-art and future directions. Crit Rev Microbiol 37(1):40–63
Dwivedi HP, Smiley RD, Jaykus LA (2010) Selection and characterization of DNA aptamers with binding selectivity to Campylobacter jejuni using whole-cell SELEX. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(6):2323–2334
Dwivedi HP, Rule P, Mills JC (2012) Detection and identification of bacterial pathogens in food using biochemical and immunological assays. In: Microbiological research and development for the food industry. CRC, Boca Raton, p 229
Farokhzad OC, Jon S, Khademhosseini A, Tran TN, Lavan DA, Langer R (2004) Nanoparticle–aptamer bioconjugates: a new approach for targeting prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 64(21):7668–7672
Foddai A, Strain S, Whitlock RH, Elliott CT, Grant IR (2011) Application of a peptide-mediated magnetic separation-phage assay for detection on viable Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in bulk tank milk and feces samples. J Clin Microbiol 49(5):2017–2019
Guo KT, Paul A, Schichor C, Ziemer G, Wendel HP (2008) CELL-SELEX: novel perspectives of aptamer-based therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci 9(4):668–678
Hein I, Flekna G, Krassnig M, Wagner M (2006) Real-time PCR for the detection of Salmonella spp. in food: an alternative approach to a conventional PCR system suggested by the FOOD-PCR project. J Microbiol Methods 66(3):538–547
Hsih HY, Tsen HY (2001) Combination of immunomagnetic separation and polymerase chain reaction for the simultaneous detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp. in food samples. J Food Prot 64(11):1744–1750
Hyeon JY, Chon JW, Choi IS, Park C, Kim DE, Seo KH (2012) Development of RNA aptamers for detection of Salmonella Enteritidis. J Microbiol Methods 89(1):79–82
Jacobsen CS, Rasmussen OF (1992) Development and application of a new method to extract bacterial DNA from soil based on separation of bacteria from soil with cation-exchange resin. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(8):2458–2462
Jayasena SD (1999) Aptamers: an emerging class of molecules that rival antibodies in diagnostics. Clin Chem 45(9):1628–1650
Joshi R, Janagama H, Dwivedi HP, Senthil Kumar TM, Jaykus LA, Schefers J, Sreevatsan S (2009) Selection, characterization, and application of DNA aptamers for the capture and detection of Salmonella enterica serovars. Mol Cell Probes 23(1):20–28
Labib M, Zamay AS, Kolovskaya OS, Reshetneva IT, Zamay GS, Kibbee RJ, Sattar SA, Zamay TN, Berezovski MV (2012a) Aptamer-based viability impedimetric sensor for bacteria. Anal Chem 84(21):8966–8969
Labib M, Zamay AS, Kolovskaya OS, Reshetneva IT, Zamay GS, Kibbee RJ, Sattar SA, Zamay TN, Berezovski MV (2012b) Aptamer-based impedimetric sensor for bacterial typing. Anal Chem 84(19):8114–8117
Li D, Baert L, Xia M, Zhong W, Van Coillie E, Jiang X, Uyttendaele M (2012) Evaluation of methods measuring the capsid integrity and/or functions of noroviruses by heat inactivation. J Virol Methods 181(1):1–5
Maeng JS, Kim N, Kim CT, Han SR, Lee YJ, Lee SW, Lee MH, Cho YJ (2012) Rapid detection of food pathogens using RNA aptamers-immobilized slide. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12(7):5138–5142
Mercanoglu B, Griffiths MW (2005) Combination of immunomagnetic separation with real-time PCR for rapid detection of Salmonella in milk, ground beef, and alfalfa sprouts. J Food Prot 68(3):557–561
Meyer C, Hahn U, Rentmeister A (2011) Cell-specific aptamers as emerging therapeutics. J Nucleic Acids 2011:904750
Pan Q, Zhang XL, Wu HY, He PW, Wang F, Zhang MS, Hu JM, Xia B, Wu J (2005) Aptamers that preferentially bind type IVB pili and inhibit human monocytic-cell invasion by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(10):4052–4060
Pestourie C, Cerchia L, Gombert K, Aissouni Y, Boulay J, De Franciscis V, Libri D, Tavitian B, Duconge F (2006) Comparison of different strategies to select aptamers against a transmembrane protein target. Oligonucleotides 16(4):323–335
Scallan E, Hoekstra RM, Angulo FJ, Tauxe RV, Widdowson MA, Roy SL, Jones JL, Griffin PM (2011) Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—major pathogens. Emerg Infect Dis 17(1):7–15
Shamah SM, Healy JM, Cload ST (2008) Complex target SELEX. Acc Chem Res 41(1):130–138
Shangguan D, Li Y, Tang Z, Cao ZC, Chen HW, Mallikaratchy P, Sefah K, Yang CJ, Tan W (2006) Aptamers evolved from live cells as effective molecular probes for cancer study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(32):11838–11843
Stanlis KK, McIntosh JR (2003) Single-strand DNA aptamers as probes for protein localization in cells. J Histochem Cytochem 51(6):797–808
Tombelli S, Minunni M, Mascini M (2005) Analytical applications of aptamers. Biosens Bioelectron 20(12):2424–2434
Ulrich H, Magdesian MH, Alves MJ, Colli W (2002) In vitro selection of RNA aptamers that bind to cell adhesion receptors of Trypanosoma cruzi and inhibit cell invasion. J Biol Chem 277(23):20756–20762
Vivekananda J, Kiel JL (2006) Anti-Francisella tularensis DNA aptamers detect tularemia antigen from different subspecies by aptamer-linked immobilized sorbent assay. Lab Invest 86(6):610–618
Ye M, Hu J, Peng M, Liu J, Liu J, Liu H, Zhao X, Tan W (2012) Generating aptamers by cell-SELEX for applications in molecular medicine. Int J Mol Sci 13(3):3341–3353
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3406–3415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, H.P., Smiley, R.D. & Jaykus, LA. Selection of DNA aptamers for capture and detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using a whole-cell SELEX approach in conjunction with cell sorting. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 3677–3686 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4766-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4766-4