Abstract
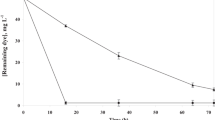
A facultative anaerobic bacteria strain GS-4-08, isolated from an anaerobic sequence batch reactor for synthetic dye wastewater treatment, was investigated for azo-dye decolorization. This bacterium was identified as a member of Klebsiella oxytoca based on Gram staining, morphology characterization and 16S rRNA gene analysis. It exhibited a good capacity of simultaneous decolorization and hydrogen production in the presence of electron donor. The hydrogen production was less affected even at a high Methyl Orange (MO) concentration of 0.5 mM, indicating a superior tolerability of this strain to MO. This efficient bio-hydrogen production from electron donor can not only avoid bacterial inhibition due to accumulation of volatile fatty acids during MO decolorization, but also can recover considerable energy from dye wastewater.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. APHA–AWWA–WEF, Washington
Chen XJ, Xu MY, Wei JB, Sun GP (2010) Two different electron transfer pathway may involve in azoreduction in Shewanella decolorationis S12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:743–751
Daneshvar N, Avazloo M, Khataee AR, Pourhassan M (2007) Biological decolorization of dye solution containing Malachite Green by microalgae Cosmarium sp. Bioresour Technol 98:1176–1182
Isık M, Sponza DT (2004) A batch kinetic study on decolorization and inhibition of Reactive Black and Direct Brown 2 in an anaerobic mixed culture. Chemosphere 55:119–128
Koehler LH (1952) Differentiation of carbohydrates by anthrone reaction rate and color intensity. Anal Chem 24:1576–1579
Liu F, Fang BS (2007) Optimization of bio-hydrogen production from biodiesel wastes by Klebsiella penumoniae. Biotechnol J 2:374–480
Long MN, Jin HL, Wu XB, Xu HQ (2005) Isolation and characterization of a high H2-producing strain Klebsiella oxytoca HP1 from a hot spring. Res Microbiol 156:76–81
Mathews J, Li QZ, Wang GY (2010) Characterization of hydrogen production by engineered Escherichia coli strains using rich defined media. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 15:686–695
Méndez-Paz D, Omil F, Lema JM (2005) Anaerobic treatment of azo dye Acid Orange 7 under fed-batch and continuous conditions. Water Res 39:771–778
Mu Y, Yu HQ, Wang G (2007) A kinetic approach to anaerobic hydrogen-producing process. Water Res 41:1152–1160
O’Nell C, Lopez A, Esteves S, Haekes FR, Hawkes DL, Wilcox S (2000) Azo-dye degradation in an anaerobic–aerobic treatment system operating on simulated textile effluent. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:249–254
Owen WF, Stuckey DC, Healy JB, Young LY, McCarty PL (1979) Bioassay for monitoring biochemical methane potential and anaerobic toxicity. Water Res 13:485–492
Parshetti GK, Telke AA, Kalyani DC, Govindwar SP (2010) Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated azo dye methyl orange by Kocuria rosea MTCC 1532. J Hazard Mater 176:503–509
Rajaguru P, Kalaiselvi K, Palanivel M, Subburam V (2000) Biodegradation of azo dyes in a sequential anaerobic–aerobic system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:268–273
van der Zee FP, Villaverde S (2005) Combined anaerobic–aerobic treatment of azo dyes – a short review of bioreactor studies. Water Res 39:1425–1440
van der Zee FP, Lettinga G, Field JA (2001) Azo dye decolorization by anaerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 44:1169–1176
Wang H, Zheng XW, Su JQ, Tian Y, Xiong XJ, Zheng TL (2009) Biological decolorization of the reactive dyes Reactive Black 5 by a novel isolated bacteria strain Enterobacter sp. EC3. J Hazard Mater 171:654–659
Wong PK, Yuen PY (1996) Decolorization and biodegradation of methyl red by Klebsiella penumoniae RS-13. Water Res 30:1736–1744
Wu KJ, Saratale GD, Lo YC, Chen WM (2008) Simultaneous production of 2,3-butanediol, ethanol and hydrogen with a Klebsiella sp. strain isolated from sewage sludge. Bioresour Technol 99:7966–7970
Xu L, Zhu Y, He XB, Han GM, Tian XJ (2008) Evaluation of a new fungus Ceriporia lacerate strain P2-its ability to decolorize Alizarin Red and Methyl Orange. Word J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:3097–3104
Yu L, Li WW, Lam HW, Yu HQ (2011) Adsorption and decolorization kinetics of methyl orange by anaerobic sludge. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1119–1127
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the NSFC-JST joint project (21021140001), the National 863 Program of China (2008BADC4B18), the JSNSF (BK2010256), the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund and the Suzhou Environmental Protection Technology project for the partial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Li, WW., Lam, M.HW. et al. Isolation and characterization of a Klebsiella oxytoca strain for simultaneous azo-dye anaerobic reduction and bio-hydrogen production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95, 255–262 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3688-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3688-2