Abstract
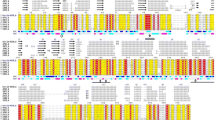
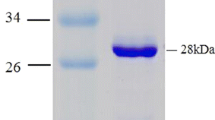
A gene encoding an NADPH-dependent 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7β-HSDH) from Collinsella aerofaciens DSM 3979 (ATCC 25986, formerly Eubacterium aerofaciens) was identified and cloned in this study. Sequence comparison of the translated amino acid sequence suggests that the enzyme belongs to the short-chain dehydrogenase superfamily. This enzyme was expressed in Escherichia coli with a yield of 330 mg (5,828 U) per liter of culture. The enzyme catalyzes both the oxidation of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDA) forming 7-keto-lithocholic acid (KLA) and the reduction of KLA forming UDA acid in the presence of NADP+ or NADPH, respectively. In the presence of NADPH, 7β-HSDH can also reduce dehydrocholic acid. SDS-PAGE and gel filtration of the expressed and purified enzyme revealed a dimeric nature of 7β-HSDH with a size of 30 kDa for each subunit. If used for the oxidation of UDA, its pH optimum is between 9 and 10 whereas for the reduction of KLA and dehydrocholic acid it shows an optimum between pH 4 to 6. Usage of the enzyme for the biotransformation of KLA in a 0.5-g scale showed that this 7β-HSDH is a useful biocatalyst for producing UDA from suitable precursors in a preparative scale.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong MJ, Carey MC (1982) The hydrophobic–hydrophilic balance of bile salts. Inverse correlation between reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatographic mobilities and micellar cholesterol-solubilizing capacities. J Lipid Res 23(1):70–80
Baron SF, Hylemon PB (2000) Biotransformation of bile acids, cholesterol, and steroid hormones. In: Mackie RJ, White BA (eds) Gastrointestinal microbiology, vol 1. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 470–510
Braun M, Lünsdorf H, Bückmann AF (1991) 12α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Clostridium group P, strain c 48-50. Production, purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem 196(2):439–450
Clamp M, Cuff J, Searle SM, Barton GJ (2004) The Jalview Java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 20(3):426–427
Colombo C, Setchell KD, Podda M, Crosignani A, Roda A, Curcio L, Ronchi M, Giunta A (1990) Effects of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy for liver disease associated with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 117(3):482–489
Combes B, Carithers RL Jr, Maddrey WC, Lin D, McDonald MF, Wheeler DE, Eigenbrodt EH, Muñoz SJ, Rubin R, Garcia-Tsao G, Santiago J, Bonner GF, West AB, Boyer JL, Luketic VA, Shiffman ML, Mills AS, Peters MG, White HM, Zetterman RK, Rossi SS, Hofmann AF, Markin RS (1995) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 22(3):759–766
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Relman DA (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308(5728):1635–1638
Fossati E, Polentini F, Carrea G, Riva S (2006) Exploitation of the alcohol dehydrogenase-acetone NADP-regeneration system for the enzymatic preparative-scale production of 12-ketochenodeoxycholic acid. Biotechnol Bioeng 93(6):1216–1220
Hirano S, Masuda N (1981) Epimerization of the 7-hydroxy group of bile acids by the combination of two kinds of microorganisms with 7α- and 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity, respectively. J Lipid Res 22(7):1060–1068
Hirano S, Masuda N (1982) Characterization of NADP-dependent 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases from Peptostreptococcus productus and Eubacterium aerofaciens. Appl Environ Microbiol 43(5):1057–1063
Hofmann A (1963) The preparation of chenodeoxycholic acid and its glycine and taurine conjugates. Acta Chem Scand 17(1):173–186
Huang M (1949) Reduction of steroid ketones and other carbonyl compounds by modified Wolff–Kishner method. J Am Chem Soc 71(10):3301–3303
Hylemon PB, Sherrod JA (1975) Multiple forms of 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in selected strains of Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol 122(2):418–424
Im E, Martinez JD (2004) Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can inhibit deoxycholic acid (DCA)-induced apoptosis via modulation of EGFR/Raf-1/ERK signaling in human colon cancer cells. J Nutr 134(2):483–486
Jörnvall H, Persson B, Krook M, Atrian S, Gonzalez-Duarte R, Jeffery J, Ghosh D (1995) Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR). Biochemistry 34(18):6003–6013
Kanazawa T, Shimazaki A, Sato T, Hoshino T (1955) Study on the ursodeoxycholic acid synthesis. Nippon Kagaku Zasshi 76:297–301
Khare S, Cerda S, Wali RK, von Lintig FC, Tretiakova M, Joseph L, Stoiber D, Cohen G, Nimmagadda K, Hart J, Sitrin MD, Boss GR, Bissonnette M (2003) Ursodeoxycholic acid inhibits Ras mutations, wild-type Ras activation, and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in colon cancer. Cancer Res 63(13):3517–3523
Lepercq P, Gérard P, Béguet F, Raibaud P, Grill JP, Relano P, Cayuela C, Juste C (2004) Epimerization of chenodeoxycholic acid to ursodeoxycholic acid by Clostridium baratii isolated from human feces. FEMS Microbiol Lett 235(1):65–72
MacDonald IA, Roach PD (1981) Bile induction of 7α- and 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in Clostridium absonum. Biochim Biophys Acta 665(2):262–269
MacDonald IA, Rochon YP, Hutchison DM, Holdeman LV (1982) Formation of ursodeoxycholic acid from chenodeoxycholic acid by a 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-elaborating Eubacterium aerofaciens strain cocultured with 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-elaborating organisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 44(5):1187–1195
MacDonald IA, White BA, Hylemon PB (1983) Separation of 7α- and 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities from Clostridium absonum ATCC# 27555 and cellular response of this organism to bile acid inducers. J Lipid Res 24(9):1119–1126
Makino I, Shinozaki K, Yoshino K, Nakagawa S (1975) Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by long-term administration of ursodeoxycholic acid. Nippon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 72(6):690–702
Maser E, Möbus E, Xiong G (2000) Functional expression, purification, and characterization of 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/carbonyl reductase from Comamonas testosteroni. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 272(2):622–628
Möbus E, Maser E (1998) Molecular cloning, overexpression, and characterization of steroid-inducible 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/carbonyl reductase from Comamonas testosteroni: a novel member of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase superfamily. J Biol Chem 273(47):30888–30896
Monti D, Ferrandi E, Zanellato I, Hua L, Polentini F, Carrea G, Riva S (2009) One-pot multienzymatic synthesis of 12-ketoursodeoxycholic acid: subtle cofactor specificities rule the reaction equilibria of five biocatalysts working in a row. Adv Synth Catal 351(9):1303–1311
Persson B, Krook M, Jörnvall H (1991) Characteristics of short-chain alcohol dehydrogenases and related enzymes. Eur J Biochem 200(2):537–543
Salen G, Colalillo A, Verga D, Bagan E, Tint GS, Shefer S (1980) Effect of high and low doses of ursodeoxycholic acid on gallstone dissolution in humans. Gastroenterology 78(6):1412–1418
Schroer K, Tacha E, Lütz S (2007) Process intensification for substrate-coupled whole cell ketone reduction by in situ acetone removal. Org Process Res Dev 11(5):836–841
Sherrod JA, Hylemon PB (1977) Partial purification and characterization of NAD-dependent 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Biochim Biophys Acta 486(2):351–358
Stiehl A, Czygan P, Kommerell B, Weis HJ, Holtermüller KH (1978) Ursodeoxycholic acid versus chenodeoxycholic acid. Comparison of their effects on bile acid and bile lipid composition in patients with cholesterol gallstones. Gastroenterology 75(6):1016–1020
Sutherland JD, MacDonald IA (1982) The metabolism of primary, 7-oxo, and 7β-hydroxy bile acids by Clostridium absonum. J Lipid Res 23(5):726–732
Sutherland JD, Williams CN (1985) Bile acid induction of 7α- and 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in Clostridium limosum. J Lipid Res 26(3):344–350
Sutherland JD, MacDonald IA, Forrest TP (1982) The enzymic and chemical synthesis of ursodeoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic acid from cholic acid. Prep Biochem 12(4):307–321
Tanaka N, Nonaka T, Yoshimoto T, Tsuru D, Mitsui Y (1996) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 52(Pt 1):215–217
Tancrede C (1992) Role of human microflora in health and disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 11(11):1012–1015
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal_X Windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Acknowledgments
We thank the BMBF (German Federal Ministry of Education and Research), Grant No. FKZ 0315269, for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Aigner, A. & Schmid, R.D. Identification, cloning, heterologous expression, and characterization of a NADPH-dependent 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Collinsella aerofaciens . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90, 127–135 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3052-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3052-y