Abstract
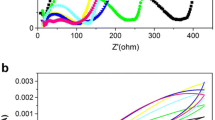
Biofilms on biocathodes can catalyze the cathodic oxygen reduction and accordingly guarantee high cathode redox potentials. The present research assessed the use of biocathodes in full-sediment microbial fuel cells. Carbon felt-based biocathodes were evaluated in freshwater systems, and an extension of their application to brackish systems and/or stainless steel webs as base material was considered. Efficient biocathodes could be developed within days through inoculation with active microorganisms. Carbon felt was found most suited for the biocathodes in freshwater with increased performance at salinities around 80–250 mM. Maximum long-term performance reached 12.3 µW cm−2 cathode. The relative benefit of stainless steel seemed to increase with increasing salinity. A combination of stainless steel cathodes with biofilms could, however, also result in decreased electrical performance. In an efficiently catalyzing cathodic biofilm, an enrichment with an uncultured Proteobacterium—previously correlated with steel waste—was observed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aelterman P, Rabaey K, Pham HT, Boon N, Verstraete W (2006) Continuous electricity generation at high voltages and currents using stacked microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40:3388–3394
Bergel A, Féron D, Mollica A (2005) Catalysis of oxygen reduction in PEM fuel cell by seawater biofilm. Electrochem Commun 7:900–904
Bond DR, Holmes DE, Tender LM, Lovley DR (2002) Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments. Science 295:483–485
Boon N, De Windt W, Verstraete W, Top EM (2002) Evaluation of nested PCR-DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) with group-specific 16 S rRNA primers for the analysis of bacterial communities from different wastewater treatment plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:101–112
Chen GW, Choi SJ, Lee TH, Lee GY, Cha JH, Kim CW (2008) Application of biocathode in microbial fuel cells: cell performance and microbial community. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:379–388
Clauwaert P, Van der Ha D, Boon N, Verbeken K, Verhaege M, Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2007) Open air biocathode enables effective electricity generation with microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 41:7564–7569
De Schamphelaire L, Verstraete W (2009) Revival of the biological sunlight-to-biogas energy conversion system. Biotechnol Bioeng 103:296–304
De Schamphelaire L, van den Bossche L, Dang HS, Höfte M, Boon N, Rabaey K, Verstraete W (2008) Microbial fuel cells generating electricity from rhizodeposits of rice plants. Environ Sci Technol 42:3053–3058
Dumas C, Basseguy R, Bergel A (2008) Microbial electrocatalysis with Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilm on stainless steel cathodes. Electrochim Acta 53:2494–2500
Dumas C, Mollica A, Féron D, Basséguy R, Etcheverry L, Bergel A (2007) Marine microbial fuel cell: use of stainless steel electrodes as anode and cathode materials. Electrochim Acta 53:468–473
Erable B, Vandecandelaere I, Faimali M, Delia M-L, Etcheverry L, Vandamme P, Bergel A (2010) Marine aerobic biofilm as biocathode catalyst. Bioelectrochemistry 78:51–56
Faimali M, Chelossi E, Garaventa F, Corrà C, Greco G, Mollica A (2008) Evolution of oxygen reduction current and biofilm on stainless steels cathodically polarised in natural aerated seawater. Electrochim Acta 54:148–153
Freguia S, Rabaey K, Yuan Z, Keller J (2007) Non-catalyzed cathodic oxygen reduction at graphite granules in microbial fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 53:598–603
Freitas DB, Reis MP, Freitas LM, Assis PS, Chartone-Souza E, Nascimento AMA (2008) Molecular bacterial diversity and distribution in waste from a steel plant. Can J Microbiol 54:996–1005
Hasvold O, Henriksen H, Melvaer E, Citi G, Johansen BO, Kjonigsen T, Galetti R (1997) Sea-water battery for subsea control systems. J Power Sources 65:253–261
He Z, Angenent LT (2006) Application of bacterial biocathodes in microbial fuel cells. Electroanal 18:2009–2015
He Z, Shao HB, Angenent LT (2007) Increased power production from a sediment microbial fuel cell with a rotating cathode. Biosens Bioelectron 22:3252–3255
Holmes DE, Bond DR, O’Neill RA, Reimers CE, Tender LR, Lovley DR (2004) Microbial communities associated with electrodes harvesting electricity from a variety of aquatic sediments. Microbial Ecol 48:178–190
Kielemoes J, Hammes F, Verstraete W (2000a) Measurement of microbial colonisation of two types of stainless steel. Environ Technol 21:831–843
Kielemoes J, De Boever P, Verstraete W (2000b) Influence of denitrification on the corrosion of iron and stainless steel powder. Environ Sci Technol 34:663–671
Little BJ, Lee JS, Ray RI (2008) The influence of marine biofilms on corrosion: a concise review. Electrochim Acta 54:2–7
Liu H, Cheng SA, Logan BE (2005) Power generation in fed-batch microbial fuel cells as a function of ionic strength, temperature, and reactor configuration. Environ Sci Technol 39:5488–5493
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R, Schröder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40:5181–5192
Lowy DA, Tender LM, Zeikus JG, Park DH, Lovley DR (2006) Harvesting energy from the marine sediment-water interface II - Kinetic activity of anode materials. Biosens Bioelectron 21:2058–2063
MacArthur JV (2006) Microbial ecology: an evolutionary approach. Academic, Burlington
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction amplified genes coding for 16s ribosomal RNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Percival SL, Knapp JS, Edyvean RGJ, Wales DS (1998) Biofilms, mains water and stainless steel. Water Res 32:2187–2201
Pham TH, Jang JK, Chang IS, Kim BH (2004) Improvement of cathode reaction of a mediatorless microbial fuel cell. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:324–329
Rabaey K, Read ST, Clauwaert P, Freguia S, Bond PL, Blackall LL, Keller J (2008) Cathodic oxygen reduction catalyzed by bacteria in microbial fuel cells. ISME J 2:519–527
Reimers CE, Girguis P, Stecher HA, Tender LM, Ryckelynck N, Whaling P (2006) Microbial fuel cell energy from an ocean cold seep. Geobiology 4:123–136
Ryckelynck N, Stecher HA, Reimers CE (2005) Understanding the anodic mechanism of a seafloor fuel cell: interactions between geochemistry and microbial activity. Biogeochemistry 76:113–139
Schaetzle O, Barrière F, Schröder U (2009) An improved microbial fuel cell with laccase as the oxygen reduction catalyst. Energy Environ Sci 2:96–99
Tartakovsky B, Guiot SR (2006) A comparison of air and hydrogen peroxide oxygenated microbial fuel cell reactors. Biotechnol Prog 22:241–246
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wilcock WSD, Kauffman PC (1997) Development of a seawater battery for deep-water applications. J Power Sources 66:71–75
Zhao F, Harnisch F, Schröder U, Scholz F, Bogdanoff P, Herrmann I (2006) Challenges and constraints of using oxygen cathodes in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 40:5193–5199
Acknowledgements
LDS was supported through a PhD grant from the Bijzonder Onderzoeks Fonds of Ghent University (grant no. 01D24405). The useful comments of Nico Boon and Jan Arends are kindly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Supplementary material (Table S1, Table S2, Fig. S1 and Fig. S2) can be found in the Online Resource.
ESM 1
(PDF 409 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Schamphelaire, L., Boeckx, P. & Verstraete, W. Evaluation of biocathodes in freshwater and brackish sediment microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87, 1675–1687 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2645-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2645-9