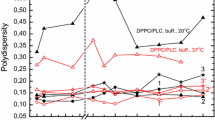
Abstract
In previous studies it was shown that cannabinoids (CBs) bearing a phenolic hydroxyl group modify the thermal properties of lipid bilayers more significantly than methylated congeners. These distinct differential properties were attributed to the fact that phenolic hydroxyl groups constitute an anchoring group in the vicinity of the head-group, while the methylated analogs are embedded deeper towards the hydrophobic region of the lipid bilayers. In this work the thermal effects of synthetic polyphenolic stilbenoid analogs and their methylated congeners have been studied using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations have been performed to explain the DSC results. Thus, two of their phenolic hydroxyl groups orient in the lipid bilayers in such a way that they anchor in the region of the head-group. In contrast, their methoxy congeners cannot anchor effectively and are embedded deeper in the hydrophobic segment of the lipid bilayers. The MD results explain the fact that hydroxystilbenoid analogs exert more significant effects on the pretransition than their methoxy congeners, especially at low concentrations. To maximize the polar interactions, the two phenolic hydroxyl groups are localized in the vicinity of the head-group region, directing the remaining hydroxy group in the hydrophobic region. This topographical position of stilbenoid analogs forms a mismatch that explains the significant broadening of the width of the phase transition and lowering of the main phase-transition temperature in the lipid bilayers. At high concentrations, hydroxy and nonhydroxy analogs appear to form different domains. The correlation of thermal effects with antioxidant activity is discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson J, Epand RF, Epand RM (2008) Tocopherols and tocotrienols in membranes. A critical review. Free Radic Biol Med 44:739–764
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, Dinola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690
BioByte Corp., 201 West 4th St., Suite 204, Claremont, CA 91711, United States
Cegelski L, Rice CV, O' Connor RD, Caruano AL, Tochtrop GR, Cai ZY, Covey DF, Schaefer J (2006) Mapping the locations of estradiol and potent neuroprotective analogues in phospholipid bilayers by REDOR. Drug Dev Res 66:93–102
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577–8592
Fabris S, Federico M, Giampietro R, Stevanato R (2008) Antioxidant properties of resveratrol and piceid on lipid peroxidation in micelles and monolamellar liposomes. Biophys Chem 125:76–83
Fotakis C, Gega S, Siapi E, Potamitis C, Viras K, Moutevelis-Minakakis P, Kokotos G, Durdagi S, Grdadolnik S, Sartori B, Rappolt M, Mavromoustakos T (2010) Drug interactions at the bilayer interface and receptor site induced by the novel synthetic pyrrolidinone analog MMK3. Biochim Biophys Acta 1798:422–432
Guo J, Yang D, Chari R, Tian X, Pavlopoulos S, Lu D, Makriyannis A (2008) Magnetically aligned bicelles to study the orientation of lipophilic ligands in membrane bilayers. J Med Chem 41:6793–6799
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJC, Fraaije JGEM (1997) LINCS: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18:1463–1472
Houslay MD, Stanley KK (1982) Dynamics of biological membranes. Wiley, New York
Kandt C, Ash WL, Tieleman DP (2007) Setting up and running molecular dynamics simulations of membrane proteins. Methods 41:475–488
Koynova R, Caffrey M (1998) Phases and phase transitions of the phosphatidylcholines. Biophys Biochim Acta 1376:91–145 (and reference therein)
Kyrikou I, Hadjikakou SK, Kovala-Demertzi D, Viras K, Mavromoustakos T (2004a) Effects of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs in membrane bilayers. Chem Phys Lipids 132:157–169
Kyrikou I, Daliani I, Mavromoustakos T, Maswadeh H, Demetzos C, Hatziantoniou S, Giatrellis S, Nounesis G (2004b) The modulation of thermal properties of vinblastine by cholesterol in membrane bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1661:1–8
Leo A, Hoekman D (2000) Calculating log P(oct) with no missing fragments; the problem of estimating new interaction parameters. Perspect Drug Discov Design 18:19–38
Lindhal E, Hess B, van der Spoel D (2001) GROMACS 3.0: a package for molecular simulation and trajectory analysis. J Mol Model 7:306–317
Martel P, Makriyannis A, Mavromoustakos T, Kelly K, Jeffrey KR (1993) Topography of tetrahydrocannabinol in model membranes using neutron diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta 1151:51–58
Mavromoustakos T, Daliani I (1999) Effects of cannabinoids in membrane bilayers containing cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta 1420:252–265
Mavromoustakos T, Theodoropoulou E (1998) A combined use of 13C-cross polarization/magic angle spinning, 13C-magic angle spinning and 31P-nuclear magnetic spectroscopy with Differential Scanning Calorimetry to study cannabinoid-membrane interactions. Chem Phys Lipids 92:37–52
Mavromoustakos T, Yang DP, Broderick W, Fournier D, Herbette LG, Makriyannis (1991) A small angle X-Ray diffraction studies on the topography of cannabinoids in synaptic plasma membranes. Pharmacol Biochem 40:547–552
Mavromoustakos T, Yang D, Makriyannis A (1994) Topography of Alphaxalone and ∆16-alphaxalone in membrane bilayers containing cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta 1194:69–74
Mavromoustakos T, Yang DP, Makriyannis A (1995a) Small angle x-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetric studies on O-methyl-(-)-∆8-Tetrahydrocannabinol and its 5′ iodinated derivative in membrane bilayers Biochim. Biophys Acta-Biomembranes 1237:183–188
Mavromoustakos T, Yang DP, Makriyannis A (1995b) Effects of the anesthetic steroids alphaxalone and its inactive analog ∆16 -analog on the thermotropic properties of membrane bilayers. A model for membrane perturbation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1239:257–264
Mavromoustakos T, De-Ping Yang, Makriyannis A (1996a) Topography and thermotropic properties of cannabinoids in brain sphingomyelin bilayers. Life Sci 59:1969–1979
Mavromoustakos T, Theodoropoulou E, Papahatjis D, Kourouli T, De-Ping Yang, Trumbore M, Makriyannis A (1996b) Studies on the thermotropic effects of cannabinoids on phosphatidylcholine bilayers using differential scanning calorimetry and small angle X-ray diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta 1281:235–244
Mavromoustakos T, Theodoropoulou E, Yang DP (1997) The use of high-resolution solid-state NMR spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry to study interactions of anaesthetic steroids with membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 1328:65–73
Mavromoustakos T, Papahatjis D, Laggner P (2001) Differential membrane fluidization by active and inactive cannabinoid analogs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1512:183–190
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys 52:182–190
Patra M, Karttunen M, Hyvönen M, Falck E, Lindqvist P, Vattulainen I (2003) Molecular dynamics simulations of lipid bilayers: major artifacts due to truncating electrostatic interactions. Biophys J 84:3636–3645
Patra M, Karttunen M, Hyvönen M, Falck E, Vattulainen P (2004) Lipid bilayers driven to a wrong lane in molecular dynamics simulations by subtle changes in long-range electrostatic interactions. J Phys Chem B 108:4485–4494
Privat C, Telo JP, Bernardes-Genisson V, Vieira A, Souchard JP, Nepveu F (2002) Antioxidant properties of trans-E-Viniferin as compared to stilbene derivatives in aqueous and nonaqueous media. J Agric Food Chem 50:1213–1217
Sarpietro MG, Spatafora C, Tringali C, Micieli D, Castelli F (2007) Interaction of resveratrol and its trimethyl and triacetyl derivatives with biomembrane models studied by differential scanning calorimetry. J Agric Food Chem 55:3720–3728
Simpkins JW, Yi KD, Yang SH, Dykens JA (2010) Mitochondrial mechanisms of estrogen neuroprotection. Biophys Acta 1800:1113–1120
Skretas G, Meligova A, Villalonga-Barber C, Mitsiou DJ, Alexis MN, Micha-Screttas M, Steele BR, Screttas CG, Wood DW (2007) Engineered chimeric enzymes as tools for drug discovery: generating reliable bacterial screens for the detection, discovery, and assessment of estrogen receptor modulators. J Am Chem Soc 129:8443–8457
Van Gunsteren WF, Billeter SR, Eising AA, Hunenberger PH, Kruger P, Mark AE, Scott WRP, Tironi IG (1996) Biomolecular simulation: the GROMOS96 manual and user guide.Vdf Hochschulverlag
Villalonga-Barber C, Meligova AK, Alexi X, Steele BR, Kouzinos CE, Screttas CG, Katsanou ES, Micha-Screttas M, Alexis MN (2011) New hydroxystilbenoid derivatives endowed with neuroprotective activity and devoid of interference with estrogen and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated transcription. Bioorg Med Chem 19:339–351
Wesolowska O, Kuzdzal M, Strancar J, Michalak K (2009) Interaction of the chemopreventive agent resveratrol and its metabolite, piceatannol, with model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:1851–1860
Yang DP, Mavromoustakos T, Beshah K, Makriyannis A (1992) Amphipathic interactions of cannabinoids with membranes. A comparison between ∆8-THC and its O-methyl analog using differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction and solid state 2H-NMR. Biochim Biophys Acta 1103:25–36
Yang DP, Mavromoustakos T, Makriyannis A (1993) Small angle X-ray diffraction studies of ∆8-tetrahydrocannabinol and its O-methyl analog in membranes. Life Sci 53:117–122
Zoumpoulakis P, Daliani I, Zervou M, Kyrikou I, Siapi E, Lamprinidis G, Mikros E, Mavromoustakos T (2003) Losartan’s molecular basis of interaction with membranes and AT1 receptor. Chem Phys Lipids 125:13–25
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the EU Marie Curie Host Fellowship for Early Stage Research Training (EST) Programme MEST-CT-2005-020575 and a Center of Excellence Research program from the General Secretariat for Research and Technology. C. Koukoulitsa is a recipient of a Hrakleitos II scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koukoulitsa, C., Durdagi, S., Siapi, E. et al. Comparison of thermal effects of stilbenoid analogs in lipid bilayers using differential scanning calorimetry and molecular dynamics: correlation of thermal effects and topographical position with antioxidant activity. Eur Biophys J 40, 865–875 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-011-0705-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-011-0705-4