Abstract
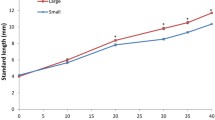
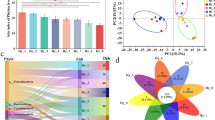
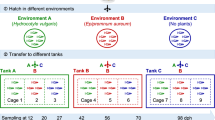
To understand how a bacteria-free fish gut ecosystem develops microbiota as the fish ages, we performed a 1-year study on the gut microbiota of hatchling gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Our results indicate that the gut microbial diversity increases significantly as the fish develop. The gut microbial community composition showed significant shifts corresponding to host age and appeared to shift at two time points despite consistent diet and environmental conditions, suggesting that some features of the gut microbial community may be determined by the host’s development. Dietary and environmental changes also seem to cause significant shifts in the fish gut microbial community. This study revealed that the gut microbiota of gibel carp assemble into distinct communities at different times during the host’s development and that this process is less affected by the surrounding environment than by the host diet and development. Community phylogenetic analyses based on the net relatedness index further showed that environmental filtering (host selection) deterministically governs the gut microbial community composition. More importantly, the influence of host-associated deterministic filtering tends to weaken significantly over the course of the host’s development. However, further studies are needed to assess whether this host development-dependent shift in gut microbiota will still exist under different rearing strategies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, Pettersson S (2012) Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 336:1262–1267
Fraune S, Bosch TCG (2010) Why bacteria matter in animal development and evolution. BioEssays 32:571–580
Sivan A, Corrales L, Hubert N, Williams JB, Aquino-Michaels K, Earley ZM, Benyamin FW, Lei YM, Jabri B, Alegre ML, Chang EB, Gajewski TF (2015) Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science 350:1084–1089
Vetizou M, Pitt JM, Daillere R, Lepage P, Waldschmitt N, Flament C, Rusakiewicz S, Routy B, Roberti MP, Duong CPM, Poirier-Colame V, Roux A, Becharef S, Formenti S, Golden E, Cording S, Eberl G, Schlitzer A, Ginhoux F, Mani S, Yamazaki T, Jacquelot N, Enot DP, Berard M, Nigou J, Opolon P, Eggermont A, Woerther PL, Chachaty E, Chaput N, Robert C, Mateus C, Kroemer G, Raoult D, Boneca IG, Carbonnel F, Chamaillard M, Zitvogel L (2015) Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on the gut microbiota. Science 350:1079–1084
Bakke I, Coward E, Andersen T, Vadstein O (2015) Selection in the host structures the microbiota associated with developing cod larvae (Gadus morhua). Environ Microbiol 17:3914–3924
Bates JM, Mittge E, Kuhlman J, Baden KN, Cheesman SE, Guillemin K (2006) Distinct signals from the microbiota promote different aspects of zebrafish gut differentiation. Dev Biol 297:374–386
Li XM, Yu YH, Feng WS, Yan QY, Gong YC (2012) Host species as a strong determinant of the intestinal microbiota of fish larvae. J Microbiol 50:29–37
Yang RB, Xie CX, Fan QX, Gao C, Fang LB (2010) Ontogeny of the digestive tract in yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco larvae. Aquaculture 302:112–123
He T, Xiao ZZ, Liu QH, Ma DY, Xu SH, Xiao YS, Li J (2012) Ontogeny of the digestive tract and enzymes in rock bream Oplegnathus fasciatus (Temminck et Schlegel 1844) larvae. Fish Physiol Biochem 38:297–308
Fjellheim AJ, Playfoot KJ, Skjermo J, Vadstein O (2012) Inter-individual variation in the dominant intestinal microbiota of reared Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) larvae. Aquac Res 43:1499–1508
Stephens WZ, Burns AR, Stagaman K, Wong S, Rawls JF, Guillemin K, Bohannan BJM (2016) The composition of the zebrafish intestinal microbial community varies across development. ISME J 10:644–654
Austin B (2006) The bacterial microflora of fish, revised. Sci World J 6:931–945
Yan Q, Li J, Yu Y, Wang J, He Z, Van Nostrand JD, Kempher ML, Wu L, Wang Y, Liao L, Li X, Wu S, Ni J, Wang C, Zhou J (2016) Environmental filtering decreases with fish development for the assembly of gut microbiota. Environ Microbiol
Roeselers G, Mittge EK, Stephens WZ, Parichy DM, Cavanaugh CM, Guillemin K, Rawls JF (2011) Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J 5:1595–1608
Rawls JF, Mahowald MA, Ley RE, Gordon JI (2006) Reciprocal gut microbiota transplants from zebrafish and mice to germ-free recipients reveal host habitat selection. Cell 127:423–433
Sullam KE, Essinger SD, Lozupone CA, O’Connor MP, Rosen GL, Knight ROB, Kilham SS, Russell JA (2012) Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: a meta-analysis. Mol Ecol 21:3363–3378
Sullam KE, Rubin BER, Dalton CM, Kilham SS, Flecker AS, Russell JA (2015) Divergence across diet, time and populations rules out parallel evolution in the gut microbiomes of Trinidadian guppies. ISME J 9:1508–1522
Wong SD, Rawls JF (2012) Intestinal microbiota composition in fishes is influenced by host ecology and environment. Mol Ecol 21:3100–3102
Yan QY, Van der Gast CJ, Yu YH (2012) Bacterial community assembly and turnover within the intestines of developing zebrafish. PLoS One 7:e30603
Bakke I, Skjermo J, Vo TA, Vadstein O (2013) Live feed is not a major determinant of the microbiota associated with cod larvae (Gadus morhua). Environ Microbiol Rep 5:537–548
Fishery Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture (2014) China fishery statistical yearbook. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Gui JF, Liang SC (1999) Allogynogenetic silver crucian carp. In: Wu CJ, Gui JF (eds) Fish genetics and breeding engineering. Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, Shanghai
Ye L, Amberg J, Chapman D, Gaikowski M, Liu WT (2014) Fish gut microbiota analysis differentiates physiology and behavior of invasive Asian carp and indigenous American fish. ISME J 8:541–551
Li TT, Long M, Gatesoupe FJ, Zhang QQ, Li AH, Gong XN (2015) Comparative analysis of the intestinal bacterial communities in different species of carp by pyrosequencing. Microb Ecol 69:25–36
Yan Q, Bi Y, Deng Y, He ZL, Wu LY, Van Nostrand JD, Shi Z, Li JJ, Wang X, Hu ZY, Yu YH, Zhou JH (2015) Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on microbial structure and potential function. Sci Rep-Uk 5
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, Owens SM, Betley J, Fraser L, Bauer M, Gormley N, Gilbert JA, Smith G, Knight R (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 6:1621–1624
Gilbert JA, Jansson JK, Knight R (2014) The Earth Microbiome project: successes and aspirations. BMC Biol 12:69
Apprill A, McNally S, Parsons R, Weber L (2015) Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquat Microb Ecol 75:129–137
Wu LY, Wen CQ, Qin YJ, Yin HQ, Tu QC, Van Nostrand JD, Yuan T, Yuan MT, Deng Y, Zhou JZ (2015) Phasing amplicon sequencing on Illumina Miseq for robust environmental microbial community analysis. BMC Microbiol 15
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996
Fierer N, Leff JW, Adams BJ, Nielsen UN, Bates ST, Lauber CL, Owens S, Gilbert JA, Wall DH, Caporaso JG (2012) Cross-biome metagenomic analyses of soil microbial communities and their functional attributes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:21390–21395
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26:266–267
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2009) FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol Biol Evol 26:1641–1650
Kembel SW, Cowan PD, Helmus MR, Cornwell WK, Morlon H, Ackerly DD, Blomberg SP, Webb CO (2010) Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 26:1463–1464
Kembel SW (2009) Disentangling niche and neutral influences on community assembly: assessing the performance of community phylogenetic structure tests. Ecol Lett 12:949–960
Webb CO, Ackerly DD, McPeek MA, Donoghue MJ (2002) Phylogenies and community ecology. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 33:475–505
Development Core Team R (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
McMurdie PJ, Holmes S (2013) phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. Plos One 8
Faith DP (1992) Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol Conserv 61:1–10
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens HH, Wanger H (2016) vegan: Community Ecology Package
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S. Springer, New York
Welch BL (1947) The generalization of ‘Student’s’ problem when several different population variances are involved. Biometrika 34:28–35
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4:9
O’Hara AM, Shanahan F (2006) The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep 7:688–693
Backhed F, Manchester JK, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2007) Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:979–984
Faith JJ, Guruge JL, Charbonneau M, Subramanian S, Seedorf H, Goodman AL, Clemente JC, Knight R, Heath AC, Leibel RL, Rosenbaum M, Gordon JI (2013) The long-term stability of the human gut microbiota. Science 341:44
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Costello EK, Berg-Lyons D, Gonzalez A, Stombaugh J, Knights D, Gajer P, Ravel J, Fierer N, Gordon JI, Knight R (2011) Moving pictures of the human microbiome. Genome Biol 12:R50
Benson AK, Kelly SA, Legge R, Ma FR, Low SJ, Kim J, Zhang M, Oh PL, Nehrenberg D, Hua KJ, Kachman SD, Moriyama EN, Walter J, Peterson DA, Pomp D (2010) Individuality in gut microbiota composition is a complex polygenic trait shaped by multiple environmental and host genetic factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:18933–18938
Wu SG, Tian JY, Gatesoupe FJ, Li WX, Zou H, Yang BJ, Wang GT (2013) Intestinal microbiota of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) and its origin as revealed by 454 pyrosequencing. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:1585–1595
Li J, Ni J, Li J, Wang C, Li X, Wu S, Zhang T, Yu Y, Yan Q (2014) Comparative study on gastrointestinal microbiota of eight fish species with different feeding habits. J Appl Microbiol 117:1750–1760
Ni JJ, Yan QY, Yu YH, Zhang TL (2014) Factors influencing the grass carp gut microbiome and its effect on metabolism. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87:704–714
Burns AR, Stephens WZ, Stagaman K, Wong S, Rawls JF, Guillemin K, Bohannan BJM (2016) Contribution of neutral processes to the assembly of gut microbial communities in the zebrafish over host development. ISME J 10:655–664
Li Q (2007) The study on intestinal histology and developing regulation of nutrients of allogynogenetic Crucian. Nanjing Agricultural University
Nayak SK (2010) Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac Res 41:1553–1573
Li XM, Yan QY, Xie SQ, Hu W, Yu YH, Hu ZH (2013) Gut microbiota contributes to the growth of fast-growing transgenic common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Plos One 8
DeLong EF (2014) Alien invasions and gut “island biogeography”. Cell 159:233–235
De Schryver P, Vadstein O (2014) Ecological theory as a foundation to control pathogenic invasion in aquaculture. ISME J 8:2360–2368
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Ellie Lin for help with English. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31400109, 31372202, and 31500417) and the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (No. 2014A030310281).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhou, L., Yu, Y. et al. Composition of Gut Microbiota in the Gibel Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) Varies with Host Development. Microb Ecol 74, 239–249 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0924-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-016-0924-4