Abstract
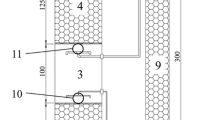
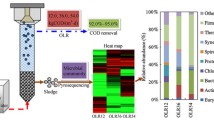
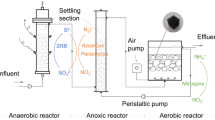
The efficiency of a novel integrated treatment system for biological removal of ammonium, nitrite, nitrate, and heavy metals from fossil power plant effluent was evaluated. Microbial communities were analyzed using bacterial and archaeal 16S rRNA gene clone libraries (Sanger sequences) and 454 pyrosequencing technology. While seasonal changes in microbial community composition were observed, the significant (P = 0.001) changes in bacterial and archaeal communities were consistent with variations in ammonium concentration. Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed an increase of potential ammonium-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus, Planctomycetes, and OD1, in samples with elevated ammonium concentration. Other bacteria, such as Nitrospira, Nitrococcus, Nitrobacter, Thiobacillus, ε-Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, and Acidobacteria, which play roles in nitrification and denitrification, were also detected. The AOB oxidized 56 % of the ammonium with the concomitant increase in nitrite and ultimately nitrate in the trickling filters at the beginning of the treatment system. Thermoprotei within the phylum Crenarchaeota thrived in the splitter box and especially in zero-valent iron extraction trenches, where an additional 25 % of the ammonium was removed. The potential ammonium-oxidizing Archaea (AOA) (Candidatus Nitrosocaldus) were detected towards the downstream end of the treatment system. The design of an integrated treatment system consisting of trickling filters, zero-valent iron reaction cells, settling pond, and anaerobic wetlands was efficient for the biological removal of ammonium and several other contaminants from wastewater generated at a coal burning power plant equipped with selective catalytic reducers for nitrogen oxide removal.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
TVA (2006) Operational improvements to optimize selective catalytic reduction systems for nitrogen oxide control at allen fossil plant units 1, 2, and 3. Tennessee Valley Authority, Shelby County, p 15
Feeley TJ, Pletcher S, Carney B, McNemar AT (2006) Department of Energy/National Energy Technology Laboratory’s Power Plant Water R&D Program. Power-Gen International 2006, available via Google search http://www.netl.doe.gov/technologies/coalpower/ewr/pubs/Power%20Gen%202006_Water%20R∓D.pdf. Accessed 26 Dec 2012
Yost TL, Pier PA, Brodie GA (2007) Fate of As, Se, and Hg in a passive integrated system for treatment of Fossil Plant wastewater. Final Report for DOE Project DE-FC26-03NT41910, pp 86
Zhou JZ, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics, 1st edn. Chichester, Wileys, pp 15–176
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D141–D145. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn879
Vishnivetskaya TA, Mosher JJ, Palumbo AV, Yang ZK, Podar M, Brown SD, Brooks SC, Gu B, Southworth GR, Drake MM, Brandt CC, Elias DA (2011) Mercury and Other Heavy Metals Influence Bacterial Community Structure in Contaminated Tennessee Streams. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:302–311. doi:10.1128/aem.01715-10
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, McGarrell DM, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2005) The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): sequences and tools for high-throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D294–D296
Porat I, Vishnivetskaya TA, Mosher JJ, Brandt CC, Yang ZK, Brooks SC, Liang L, Drake MM, Podar M, Brown SD, Palumbo AV (2009) Characterization of archaeal community in contaminated and uncontaminated surface stream sediments. Microb Ecol 60:784–795. doi:10.1007/s00248-010-9734-2
Haas BJ, Gevers D, Earl AM, Feldgarden M, Ward DV, Giannoukos G, Ciulla D, Tabbaa D, Highlander SK, Sodergren E, Methe B, DeSantis TZ, Petrosino JF, Knight R, Birren BW (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21:494–504. doi:10.1101/gr.112730.110
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal-W–improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Lozupone C, Hamady M, Knight R (2006) UniFrac–an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinforma 7:371–385. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-7-371
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8228–8235. doi:10.1128/aem.71.12.8228-8235.2005
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Raes J, Korbel JO, Lercher MJ, von Mering C, Bork P (2007) Prediction of effective genome size in metagenomic samples. Genome Biol 8:11. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-1-r10
Angly FE, Willner D, Prieto-Dava A, Edwards RA, Schmieder R, Vega-Thurber R, Antonopoulos DA, Barott K, Cottrell MT, Desnues C, Dinsdale EA, Furlan M, Haynes M, Henn MR, Hu Y, Kirchman DL, McDole T, McPherson JD, Meyer F, Miller RM, Mundt E, Naviaux RK, Rodriguez-Mueller B, Stevens R, Wegley L, Zhang L, Zhu B, Rohwer F (2009) The GAAS metagenomic tool and its estimations of viral and microbial average genome size in four major biomes. PLoS Comput Biol 5:e1000593
Ellenbroek FM, Cappenberg TE (1991) DNA-synthesis and tritiated-thymidine incorporation by heterotrophic fresh-water bacteria in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1675–1682
de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Ingalls AE, Konneke M, Stahl DA (2008) Cultivation of a thermophilic ammonia oxidizing archaeon synthesizing crenarchaeol. Environ Microbiol 10:810–818. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01506.x
Ohmori M, Ohmori K, Strotmann H (1977) Inhibition of nitrate uptake by ammonia in a blue-green alga, Anabaena cylindrica. Arch Microbiol 114:225–229. doi:10.1007/Bf00446866
Belser LW (1979) Population ecology of nitrifying bacteria. Ann Rev Microbiol 33:309–333
Huber H, Stetter KO (2006) Desulfurococcales. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes archaea bacteria: Firmicutes. Actinomycetes Springer, New York, pp 52–68
Kemnitz D, Kolb S, Conrad R (2007) High abundance of Crenarchaeota in a temperate acidic forest soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:442–448
Brochier-Armanet C, Boussau B, Gribaldo S, Forterre P (2008) Mesophilic Crenarchaeota: proposal for a third archaeal phylum, the Thaumarchaeota. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:245–252. doi:10.1038/Nrmicro1852
Konneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546. doi:10.1038/nature03911
You J, Das A, Dolan EM, Hu ZQ (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea involved in nitrogen removal. Water Res 43:1801–1809. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2009.01.016
Walker CB, de la Torre JR, Klotz MG, Urakawa H, Pinel N, Arp DJ, Brochier-Armanet C, Chain PSG, Chan PP, Gollabgir A, Hemp J, Hugler M, Karr EA, Konneke M, Shin M, Lawton TJ, Lowe T, Martens-Habbena W, Sayavedra-Soto LA, Lang D, Sievert SM, Rosenzweig AC, Manning G, Stahl DA (2010) Nitrosopumilus maritimus genome reveals unique mechanisms for nitrification and autotrophy in globally distributed marine Crenarchaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:8818–8823. doi:10.1073/pnas.0913533107
Jetten MSM, Sliekers O, Kuypers M, Dalsgaard T, van Niftrik L, Cirpus I, van de Pas-Schoonen K, Lavik G, Thamdrup B, Le Paslier D, Op den Camp HJM, Hulth S, Nielsen LP, Abma W, Third K, Engstrom P, Kuenen JG, Jorgensen BB, Canfield DE, Damste JSS, Revsbech NP, Fuerst J, Weissenbach J, Wagner M, Schmidt I, Schmid M, Strous M (2003) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation by marine and freshwater planctomycete-like bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:107–114. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1422-4
Strous M, Fuerst JA, Kramer EHM, Logemann S, Muyzer G, van de Pas-Schoonen KT, Webb R, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (1999) Missing lithotroph identified as new planctomycete. Nature 400:446–449
Kirkpatrick J, Oakley B, Fuchsman C, Srinivasan S, Staley JT, Murray JW (2006) Diversity and distribution of Planctomycetes and related bacteria in the suboxic zone of the Black Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3079–3083
Kenealy WR, Thompson TE, Schubert KR, Zeikus JG (1982) Ammonia assimilation and synthesis of alanine, aspartate, and glutamate in Methanosarcina barkeri and Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol 150:1357–1365
Kessler PS, Leigh JA (1999) Genetics of nitrogen regulation in Methanococcus maripaludis. Genetics 152:1343–1351
Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (2007) The prokaryotes: a hand book on the biology of bacteria. Archaea. Bacteria: Firmicutes, Actinomycetes. Springer, New York
Brooijmans RJ, de Vos WM, Hugenholtz J (2009) Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 electron transport chains. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3580–3585
Cotta M, Forster R (2006) The family Lachnospiraceae, including the genera Butyrivibrio, Lachnospira, and Roseburia. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp 1002–1021
Ward NL, Challacombe JF, Janssen PH, Henrissat B, Coutinho PM, Wu M, Xie G, Haft DH, Sait M, Badger J, Barabote RD, Bradley B, Brettin TS, Brinkac LM, Bruce D, Creasy T, Daugherty SC, Davidsen TM, Deboy RT, Detter JC, Dodson RJ, Durkin AS, Ganapathy A, Gwinn-Giglio M, Han CS, Khouri H, Kiss H, Kothari SP, Madupu R, Nelson KE, Nelson WC, Paulsen I, Penn K, Ren QH, Rosovitz MJ, Selengut JD, Shrivastava S, Sullivan SA, Tapia R, Thompson LS, Watkins KL, Yang Q, Yu CH, Zafar N, Zhou LW, Kuske CR (2009) Three genomes from the phylum Acidobacteria provide insight into the lifestyles of these microorganisms in soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2046–2056. doi:10.1128/aem.02294-08
Nakamura K, Hagimine M, Sakai M, Furukawa K (1999) Removal of mercury from mercury-contaminated sediments using a combined method of chemical leaching and volatilization of mercury by bacteria. Biodegradation 10:443–447
Olson GJ, Porter FD, Rubinstein J, Silver S (1982) Mercuric reductase enzyme from a mercury-volatilizing strain of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 151:1230–1236
Beller HR, Chain PS, Letain TE, Chakicherla A, Larimer FW, Richardson PM, Coleman MA, Wood AP, Kelly DP (2006) The genome sequence of the obligately chemolithoautotrophic, facultatively anaerobic bacterium Thiobacillus denitrificans. J Bacteriol 188:1473–1488
Beller HR (2005) Anaerobic, nitrate-dependent oxidation of U(IV) oxide minerals by the chemolithoautotrophic bacterium Thiobacillus denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2170–2174. doi:10.1128/aem.71.4.2170-2174.2005
Lopez-Cortes A, Fardeau M-L, Fauque G, Joulian C, Ollivier B (2006) Reclassification of the sulfate- and nitrate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio vulgaris subsp. oxamicus as Desulfovibrio oxamicus sp. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1495–1499. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64074-0
Kuever J, Rainey FA, Widdel F (2005) Family II. Syntrophaceae fam. nov. In: Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, p 1033
Bahr M, Crump BC, Klepac-Ceraj V, Teske A, Sogin ML, Hobbie JE (2005) Molecular characterization of sulfate-reducing bacteria in a New England salt marsh. Environ Microbiol 7:1175–1185
Isaksen MF, Bak F, Jorgensen BB (1994) Thermophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria in cold marine sediment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 14:1–8
Campbell BJ, Engel AS, Porter ML, Takai K (2006) The versatile epsilon-Proteobacteria: key players in sulphidic habitats. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:458–468
Sievert SM, Scott KA, Klotz MG, Chain PSG, Hauser LJ, Hemp J, Hugler M, Land M, Lapidus A, Larimer FW, Lucas S, Malfatti SA, Meyer F, Paulsen IT, Ren Q, Simon J (2008) Genome of the epsilonproteobacterial chemolithoautotroph Sulfurimonas denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1145–1156. doi:10.1128/aem.01844-07
Larkin JM, Shinabarger DL (1983) Characterization of Thiothrix nivea. Int J Syst Bacteriol 33:841–846
Ito T, Sugita K, Yumoto I, Nodasaka Y, Okabe S (2005) Thiovirga sulfuroxydans gen. nov., sp. nov., a chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a microaerobic waste-water biofilm. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1059–1064
Rittle KA, Drever JI, Colberg PJS (1995) Precipitation of arsenic during bacterial sulfate reduction. Geomicrobiol J 13:1–11
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Acknowledgments
This research was sponsored by the U. S. Department of Energy Office of Fossil Energy and Office of Science Biological and Environmental Research, Environmental Remediation Sciences Program and performed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle, LLC, for the U. S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725. We thank Zamin Yang and Marilyn Kerley for help with 454 FLX pyrosequencing and Sanger sequencing, respectively. We would also like to thank Alan Mays, David Lane, Mark Wolfe, and Roy Quinn of TVA for help with sampling and maintaining the ATOXIC/ASSET field sites.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vishnivetskaya, T.A., Fisher, L.S., Brodie, G.A. et al. Microbial Communities Involved in Biological Ammonium Removal from Coal Combustion Wastewaters. Microb Ecol 66, 49–59 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0152-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0152-5