Abstract
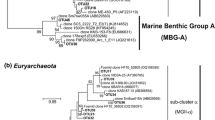
Using the archaeal 16S rRNA gene, we determined the community structures of archaea of subseafloor sediments (∼9–11 m below seafloor) from two geographically distant cores (MD05-2896, south, water depth 1,657 m; MD05-2902, north, water depth 3,697 m) in the South China Sea. Euryarchaeota accounted for 61.4% of total archaeal clone libraries at MD05-2896 and 56.2% at MD05-2902. At both locations, the Euryarchaeota-related sequences were dominated by Marine Benthic Group D, Terrestrial Miscellaneous Eryarchaeotal Group, and South African GoldMine Euryarchaeotal Group; the Crenarchaeota-related sequences were dominated by Marine Benthic Group B, Marine Group I, pSL12, and C3. The community structure showed no significant difference with depth at each location, suggesting the lack of stratification of archaeal populations in the deep-sea marine sediments in the South China Sea. On the other hand, the community structure is significantly different between the two sites, which may be related to geographical difference in the South China Sea.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barns SM, Delwiche CF, Palmer JD, Pace NR (1996) Perspectives on archaeal diversity, thermophily and monophyly from environmental rRNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9188–9193
Biddle JF, Lipp JS, Lever MA, Lloyd KG, Sorensen KB, Anderson R, Fredricks HF, Elvert M, Kelly TJ, Schrag DP, Sogin ML, Brenchley JE, Teske A, House CH, Hinrichs KU (2006) Heterotrophic Archaea dominate sedimentary subsurface ecosystems off Peru. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3846–38513
Brown MV, Bowman JP (2001) A molecular phylogenetic survey of sea-ice microbial communities (SIMCO). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:267–275
Cole JR, Chai B, Marsh TL, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, Chandra S, McGarrell DM, Schmidt TM, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2003) The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): previewing a new autoaligner that allows regular updates and the new prokaryotic taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res 31:442–443
Costa KC, Navarro JB, Shock EL, Zhang CL, Soukup D, Hedlund BP (2009) Microbiology and geochemistry of great boiling and mud hot springs in the United States Great Basin. Extremophiles 13:447–459
Dang H, Zhang X, Sun J, Li T, Zhang Z, Yang G (2008) Diversity and spatial distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing cenarchaeota in response to estuarine and encironmental gradients in the Changjiang Estuary and East China Sea. Environ Microbiol 154:1–12
Dang H, Luan X, Zhao J, Li J (2009) Diverse and novel nifH and nifH-like sequences in the deep-sea methane seep sediments of the Okhotsk Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2238–2245
DeLong EF (1992) Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5685–5689
Francis CA, Beman JM, Kuypers MM (2007) New processes and players in the nitrogen cycle: the microbial ecology of anaerobic and archaeal ammonia oxidation. ISME J 1:19–27
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14683–14688
Fry JC, Parkes RJ, Cragg BA, Weightman AJ, Webster G (2008) Prokaryotic biodiversity and activity in the deep subseafloor biosphere. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:181–196
Fuhrman JA, McCallum K, Davis AA (1992) Novel major archaebacterial group from marine plankton. Nature 356:148–149
Galand PE, Lovejoy C, Vincent WF (2006) Remarkably diverse and contrasting archaeal communities in a large arctic river and the coastal Arctic Ocean. Aquat Microb Ecol 44:115–126
Goni MA, Ruttenberg KC, Eglinton TI (1998) A reassessment of the sources and importance of land-derived organic matter in surface sediments from the Gulf of Mexico. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:3055–3075
Hallam SJ, Mincer TJ, Schleper C, Preston CM, Roberts K, Richardson PM, DeLong EF (2006) Pathways of carbon assimilation and ammonia oxidation suggested by environmental genomic analyses of marine Crenarchaeota. PLoS Biol 4:e95
Hales BA, Edwards C, Ritchie DA, Hall G, Pickup RW, Saunders JR (1996) Isolation and identification of methanogen-specific DNA from blanket bog peat by PCR amplification and sequence analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:668–675
Herndl GJ, Reinthaler T, Teira E, van Aken H, Veth C, Pernthaler A, Pernthaler J (2005) Contribution of Archaea to total prokaryotic production in the deep Atlantic Ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2303–2309
Hoj L, Olsen RA, Torsvik VL (2008) Effects of temperature on the diversity and community structure of known methanogenic groups and other archaea in high Arctic peat. ISME J 2:37–48
Hubert C, Loy A, Nickel M, Arnosti C, Baranyi C, Bruchert V, Ferdelman T, Finster K, Christensen FM, Rosa de Rezende J, Vandieken V, Jorgensen BB (2009) A constant flux of diverse thermophilic bacteria into the cold Arctic seabed. Science 325:1541–1544
Inagaki F, Nunoura T, Nakagawa S, Teske A, Lever M, Lauer A, Suzuki M, Takai K, Delwiche M, Colwell FS, Nealson KH, Horikoshi K, D’Hondt S, Jorgensen BB (2006) Biogeographical distribution and diversity of microbes in methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments on the Pacific Ocean Margin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2815–2820
Inagaki F, Suzuki M, Takai K, Oida H, Sakamoto T, Aoki K, Nealson KH, Horikoshi K (2003) Microbial communities associated with geological horizons in coastal subseafloor sediments from the Sea of Okhotsk. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:7224–7235
Inagaki F, Nakagawa S (2008) Spatial distribution of the subseafloor life: diversity and biogeography. In: Dilek Y, Furnes H, Muehlenbachs K (eds) Links between geological processes, microbial activities & evolution of life, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 135–158
Ingalls AE, Shah SR, Hansman RL, Aluwihare LI, Santos GM, Druffel ER, Pearson A (2006) Quantifying archaeal community autotrophy in the mesopelagic ocean using natural radiocarbon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6442–6447
Jiang H, Dong H, Ji S, Ye Y, Wu N (2007) Microbial diversity in the deep marine sediments from the Qiongdongnan Basin in South China Sea. Geomicrobiol J 24:505–517
Jiang L, Peng X, Zhou H, Wang F (2008) Vertical distribution and diversity of archaea in coastal sediments of Qi’ao Island (Zhujiang River Estuary), southern China, estimated by 16S rDNA analysis. Acta Oceanolog Sin 30:114–122
Konneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546
Lepš J, Šmilauer P (2003) Multivariate analysis of ecological data using CANOCO. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Li T, Wang P (2008) Microbial diversity in surface sediments of Xisha Trough, the South China Sea. Acta Ecol Sin 28:1166–1173
Li T, Wang P, Wang P (2008) Bacterial and archaeal diversity in surface sediment from the south slope of the South China Sea. Acta Microbiol Sin 48:323–329
Li Y, Li F, Zhang X, Qin S, Zeng Z, Dang H, Qin Y (2008) Vertical distribution of bacterial and archaeal communities along discrete layers of a deep-sea cold sediment sample at the East Pacific Rise (13°N). Extremophiles 12:573–585
Lipp JS, Morono Y, Inagaki F, Hinrichs KU (2008) Significant contribution of Archaea to extant biomass in marine subsurface sediments. Nature 454:991–994
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar BA, Lai T, Steppi S, Jobb G, Forster W, Brettske I, Gerber S, Ginhart AW, Gross O, Grumann S, Hermann S, Jost R, Konig A, Liss T, Lussmann R, May M, Nonhoff B, Reichel B, Strehlow R, Stamatakis A, Stuckmann N, Vilbig A, Lenke M, Ludwig T, Bode A, Schleifer KH (2004) ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1363–1371
Nicol GW, Schleper C (2006) Ammonia-oxidising Crenarchaeota: important players in the nitrogen cycle? Trends Microbiol 14:207–212
Nunoura T, Inagaki F, Delwiche ME, Colwell FS, Takai K (2008) Subseafloor microbial communities in methane hydrate-bearing sediment at two distinct locations (ODP Leg204) in the Cascadia Margin. Microbes Environ 23:317–325
Ouverney CC, Fuhrman JA (2000) Marine planktonic archaea take up amino acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4829–4833
Parkes RJ, Webster G, Gragg BA, Weightman AJ, Newberry CJ, Ferdelman TG, Kallmeyer J, Jørgensen BB, Aiello IW, Fry JC (2005) Deep sub-seafloor prokaryotes stimulated at interfaces over geological time. Nature 436:390–394
Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2008) Relative contributions of archaea and bacteria to aerobic ammonia oxidation in the environment. Environ Microbiol 10:2931–2941
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35:7188–7196
Reed DW, Fujita Y, Delwiche ME, Blackwelder DB, Sheridan PP, Uchida T, Colwell FS (2002) Microbial communities from methane hydrate-bearing deep marine sediments in a forearc basin. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3759–3770
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1501–1506
Sørensen KB, Teske A (2006) Stratified communities of active Archaea in deep marine subsurface sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4596–4603
Takai K, Moser DP, DeFlaun M, Onstott TC, Fredrickson JK (2001) Archaeal diversity in waters from deep South African gold mines. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5750–5760
ter Braak CJF, Smilauer P (2002) CANOCO Reference manual and CanoDraw for windows user’s guide: software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Teske A, Biddle JF (2008) Analysis of deep subsurface microbial communities by functional genes and genomics. In: Dilek Y, Furnes H, Muehlenbachs K (eds) Links between geological processes, microbial activities & evolution of life, vol 4. Springer, New York, pp 159–176
Tesk A, Sørensen KB (2008) Uncultured archaea in deep marine subsurface sediments: have we caught them all? ISME J 2:3–18
Wang P, Wang F, Xu M, Xiao X (2004) Molecular phylogeny of methylotrophs in a deep-sea sediment from a tropical west Pacific Warm Pool. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:77–84
Yao B (2005) The formin condition and distribution characteristics of the gas hydrate in the South China Sea. Marine Geol and Quatern Geol 25:81–90
Zhang C, Ye Q, Huang Z, Li W, Chen J, Song Z, Zhao W, Bagwell C, Inskeep WP, Ross C, Gao L, Wiegel J, Romanek CS, Shock EL, Hedlund BP (2008) Global occurrence of archaeal amoA genes in terrestrial hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6417–6426
Zhao M (2009) Productivity and nutrient dynamics in the modern South China Sea. In: Wang P, Li Q (eds) The South China Sea, Paleooceanography and sedimentology. Springer, New York, pp 439–457
Acknowledgements
We thank the crew on the MD-147-MARCO POLO cruise of the R/V Marion Dufresne of the French Polar Institute (IPEV). This work is financially supported by the Key Project of China National Programs for Fundamental Research and Development (No. 2007CB815904), National Natural Science Foundation of China (40606032), COMRA fund grant (DYXM-115-02-2-17), and Shanghai Rising-Star Program (A) (08QA14065). Contribution of CLZ is supported by Tongji Lecture Professorship and the University of Mississippi Gulf of Mexico Hydrates Research Consortium.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Chemical information for each layer of MD05-2896 and MD05-2902. (RTF 109 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Li, T., Hu, A. et al. Community Structure of Archaea from Deep-Sea Sediments of the South China Sea. Microb Ecol 60, 796–806 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9746-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9746-y