Abstract
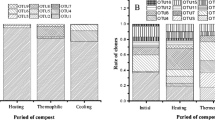
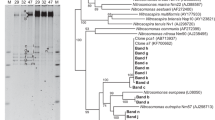
Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) play important roles in nitrification in various environments. They may also be key communities for ammonia oxidation in composting systems, although few studies have discussed their presence. We investigated the relative diversity and abundance of AOB and AOA using cloning procedures, denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis, and real-time PCR during several stages in the process of cattle manure composting. Our results revealed that the AOB community structure changed during the process. At the high-temperature stage (>60°C), a member of the Nitrosomonas europaea/eutropha cluster dominated while the uncultured Nitrosomonas spp. cluster appeared after the temperature decreased. Additionally, our analysis indicated that AOA sequences, which were classified into a soil/sediment cluster, were present after the temperature decreased during the composting process. At these stages, the number of the archaeal amoA gene copies (3.2 or 3.9 × 107 copies per gram freeze-dried compost) was significantly higher than that of bacterial amoA gene copies (2.2–7.2 × 106 copies per gram freeze-dried compost). Our results suggest that both AOB and AOA are actively involved in nitrification of composting systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair KL, Schwartz E (2008) Evidence that ammonia-oxidizing archaea are more abundant than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in semiarid soils of northern Arizona, USA. Microb Ecol 56:420–426
Avrahami S, Liesack W, Conrad R (2003) Effects of temperature and fertilizer on activity and community structure of soil ammonia oxidizers. Microb Ecol 5:691–705
Beman JM, Francis CA (2006) Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the sediments of a hypernutrified subtropical estuary: Bahía del Tóbari, Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7767–7777
Bernal MP, Alburquerque JA, Moral R (2009) Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment. A review. Bioresour Technol 100:5444–5453
Bollmann A, Bär-Gilissen M, Laanbroek H (2002) Growth at low ammonium concentrations and starvation response as potential factors involved in niche differentiation among ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4751–4757
Boyle-Yarwood SA, Bottomley PJ, Myrold DD (2008) Community composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in soils under stands of red alder and Douglas fir in Oregon. Environ Microbiol 10:2956–2965
Chen G, Qiu S, Zhou Y (2009) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in eutrophic and oligotrophic basins of a shallow Chinese lake (Lake Donghu). Res Microbiol 160:173–178
Chen XP, Zhu YG, Xia Y, Shen JP, He JZ (2008) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea: important players in paddy rhizosphere soil? Environ Microbiol 10:1978–1987
Coolen MJL, Abbas B, Bjeilswilk J, Hopmans EC, Kuypers MMM, Wakeham SG, Sinninghe Damsté JS (2007) Putative ammonia-oxidizing Crenarchaeota in suboxic waters of the Black Sea: a basin-wide ecological study using 16S ribosomal and functional genes and membrane lipids. Environ Microbiol 9:1001–1016
de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Ingalls AE, Könneke M, Stahl DA (2008) Cultivation of a thermophilic ammonia oxidizing archaeon synthesizing crenarchaeol. Environ Microbiol 10:810–818
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammoniaoxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:14683–14688
Gale ES, Sullivan DM, Cogger CG, Bary AI, Hemphill DD, Myhre EA (2006) Estimating plant-available N release from manures, composts, and specialty products. J Environ Qual 35:2321–2332
Geets J, Boon N, Verstraete W (2006) Strategies of aerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria for coping with nutrient and oxygen fluctuations. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:1–13
Haga K (1999) Development of composting technology in animal waste treatment. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 12:604–606
Hastings RC, Ceccherini MT, Miclaus N, Saunders JR, Bazzicalupo M, McCarthy AJ (1997) Direct molecular biological analysis of ammonia oxidising bacteria populations in cultivated soil plots treated with swine manure. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 23:45–54
Hatzenpichler R, Lebedeva EV, Spieck E, Stoecker K, Richter A, Daims H, Wagner M (2008) A moderately thermophilic ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeote from a hot spring. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:2134–2139
He JZ, Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zheng YM, Xu MG, Di HJ (2007) Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. Environ Microbiol 9:2364–2374
Herrman M, Saunders AM, Schramm A (2008) Archaea dominate the ammonia-oxidizing community in the rhizosphere of the freshwater macrophyte Littorella uniflora. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3279–3283
Ibekwe AM, Grieve KM, Lyon SR (2003) Characterization of microbial communities and composition in constructed dairy wetland wastewater effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5060–5069
Innerebner G, Knapp B, Vasara T, Romantschuk M, Insam H (2006) Traceability of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in compost-treated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1092–1100
Jarvis Å, Sundberg C, Milenkovsli S, Pell M, Smårs S, Lindgren PE, Hallin S (2009) Activity and composition of ammonia oxidizing bacterial communities and emission dynamics of NH3 and N2O in a compost reactor treating organic household waste. J Appl Microbiol 106:1502–1511
Jia Z, Conrad R (2009) Bacteria rather than Archaea dominate microbial ammonia oxidation in an agricultural soil. Environ Microbiol 11:1658–1671
Könneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546
Koops HP, Purkhold U, Pommerening A, Timmermann G, Wagner M (2006) The lithoautotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. In: Dworkin M, Falkow D, Rosenberg E, Dchleifer KH, Stackebgandt E (eds) Prokaryotes, vol 5, 3rd edn. Springer, New York, pp 778–811
Kowalchuk GA, Naoumenko ZS, Derikx PJL, Felske A, Stephen JR, Arkhlpchenko IA (1999) Molecular analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria of the ß subdivision of the class proteobacteria in compost and composted materials. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:396–403
Kowalchuk GA, Stienstra AW, Hans G, Heilig J, Stephen JR, Woldendorp JW (2000) Molecular analysis of ammonia-oxidising bacteria in soil of successional grasslands of the Drentsche A (The Netherlands). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31:207–215
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol G, Prosser J, Schuster S, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Limpiyakorn T, Kurisu F, Sakamoto Y, Yagi O (2007) Effects of ammonium and nitrite on communities and populations of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in laboratory-scale continuous-flow reactors. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:501–512
Lin C (2008) A negative-pressure aeration system for composting food wastes. Bioresour Technol 99:7651–7656
Maeda K, Toyoda S, Shimojima R, Osada T, Hanajima D, Morioka R, Yoshida N (2010) Source of nitrous oxide emissions during the cow manure composting process as revealed by isotopomer analysis of and amoA abundance in betaproteobacterial ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:1555–1562
Martens-Habbena W, Berube P, Urakawa H, de la Torre J, Stahl D (2009) Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying Archaea and Bacteria. Nature 461:976–979
Muyzer G, de Waal E, Uitterlinden A (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nicol GW, Leininger S, Schleper C, Prosser JI (2008) The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ Microbiol 10:2966–2978
Norton JM, Alzerreca JJ, Suwa Y, Klotz MG (2002) Diversity of ammonia monooxygenase operon in autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Arch Microbiol 177:139–149
Otawa K, Asano R, Ohba Y, Sasaki T, Kawamura E, Koyama F, Nakamura S, Nakai Y (2006) Molecular analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria community in intermittent aeration sequencing batch reactors used for animal wastewater treatment. Environ Microbiol 8:1985–1996
Park HD, Wells GF, Bae H, Criddle CS, Francis CA (2006) Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in wastewater treatment plant bioreactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5643–5647
Phillips CJ, Harris D, Dollhopf SL, Gross KL, Prosser JI, Paul EA (2000) Effects of agronomic treatments on structure and function of ammonia-oxidizing communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5410–5418
Purkhold U, Pommerening-Röser A, Juretschko S, Schmid MC, Koops HP, Wagner M (2000) Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis—implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5368–5382
Reigstad LJ, Richter A, Daims H, Urich T, Schwark L, Schleper C (2008) Nitrification in terrestrial hot springs of Iceland and Kamchatka. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64:167–174
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Shimaya C, Hashimoto T (2008) Improvement of media for high temperature ammnonia-oxidizing bacteria in compost. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 54:529–533
Sorokin D, Tourova T, Schmid MC, Wagner M, Koops HP, Kuenen JG, Jetten M (2001) Isolation and properties of obligately chemolithoautotrophic and extremely alkali-tolerant ammonia-oxidizing bacteria from Mongolian soda lakes. Arch Microbiol 176:170–177
Stephen J, McCaig A, Smith Z, Prosser J, Embley T (1996) Molecular diversity of soil and marine 16S rRNA gene sequences related to beta-subgroup ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4147–4154
Taiganides EP (1977) Bio-engineering properties of feedlot wastes. In: Taiganides EP (ed) Animal wastes. Applied Science, London, pp 131–153
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tiquia SM (2002) Microbial transformation of nitrogen during composting. In: Insam H, Riddech N, Klammer S (eds) Microbiology of composting. Springer, New York, pp 237–246
Tourna M, Freitag TE, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2008) Growth, activity and temperature responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in soil microcosms. Environ Microbiol 10:1357–1364
Treusch AH, Leininger S, Kletzin A, Schuster SC, Klenk HP, Schleper C (2005) Novel genes for nitrite reductase and Amo-related proteins indicate a role of uncultivated mesophilic crenarchaeota in nitrogen cycling. Environ Microbiol 7:1985–1995
Yamada T, Miyauchi K, Ueda H, Ueda Y, Sugawara H, Nakai Y, Endo G (2007) Composting Cattle Dung Wastes by Using a Hyperthermophilic Pre-treatment Process: Characterization by Physicochemical and Molecular Biological Analysis. J Biosci Bioeng 104:408–415
'Venter J, Remington K, Heidelberg J, Halpern A, Rusch D, Eisen J, Wu D, Paulsen I, Nelson K, Nelson W, Fouts D, Levy S, Knap A, Lomas M, Nealson K, White O, Peterson J, Hoffman J, Parsons R, Baden-Tillson H, Pfannkoch C, Rogers Y, Smith H (2004) Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 304:66–74
Wells G, Park H, Yeung C, Eggleston B, Francis C, Criddle C (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing communities in a highly aerated full-scale activated sludge bioreactor: betaproteobacterial dynamics and low relative abundance of Crenarchaea. Environ Microbiol 11:2310–2328
Weidler GW, Dornmayr M, Gerbl FW, Heinen W, Stan H (2007) Communities of archaea and bacteria in a subsurface radioactive thermal spring in the Austrian Central Alps, and evidence of ammonia-oxidizing Crenarchaeota. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:259–270
Zhang CL, Ye Q, Huang Z, Li WJ, Chen J, Song Z, Zhao W, Bagwell C, Inskeep WP, Ross C, Gao L, Wiegel J, Romanek CS, Shock EL, Hedlund BP (2008) Global occurrence of archaeal amoA genes in terrestrial hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6417–6426
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, by the Foundation of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan, as a “Project of Integrated Compost Science” and by a grant from the Livestock Technology Association, Japan. We thank people from the Miyagi Agriculture Corporation for providing compost samples. We would also like to thank Ryoki Asano, Osamu Ichihashi, and Kayako Hirooka for providing helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, N., Otawa, K. & Nakai, Y. Diversity and Abundance of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria and Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea During Cattle Manure Composting. Microb Ecol 60, 807–815 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9714-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9714-6