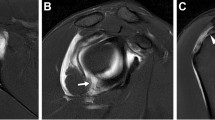
Abstract
Background
Intra-articular corticosteroid injections are a safe and effective treatment for patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The potential scope of care in ultrasound-guided corticosteroid therapy in children and a joint-based corticosteroid dose protocol designed to optimize interdisciplinary care are not found in the current literature.
Objective
The purpose of this study was to report the spectrum of care, technique and safety of ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection therapy in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis and to propose an age-weight-joint-based corticosteroid dose protocol.
Materials and methods
A retrospective analysis was performed of 198 patients (ages 21 months to 28 years) referred for treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis with corticosteroid therapy. Symptomatic joints and tendon sheaths were treated as prescribed by the referring rheumatologist. An age-weight-joint-based dose protocol was developed and utilized for corticosteroid dose prescription.
Results
A total of 1,444 corticosteroid injections (1,340 joints, 104 tendon sheaths) were performed under US guidance. Injection sites included small, medium and large appendicular skeletal joints (upper extremity 497, lower extremity 837) and six temporomandibular joints. For patients with recurrent symptoms, 414 repeat injections were performed, with an average time interval of 17.7 months (range, 0.5–101.5 months) between injections. Complications occurred in 2.6% of injections and included subcutaneous tissue atrophy, skin hypopigmentation, erythema and pruritis.
Conclusion
US-guided corticosteroid injection therapy provides dynamic, precise and safe treatment of a broad spectrum of joints and tendon sheaths throughout the entire pediatric musculoskeletal system. An age-weight-joint-based corticosteroid dose protocol is effective and integral to interdisciplinary care of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balogh Z, Ruzsonyi E (1987) Triamcinolone hexacetonide versus betamethasone. A double-blinded comparative study of the long-term effects of intra-articular steroids in patients with juvenile chronic arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl 67:80–82
Zulian F, Martini G, Gobber D et al (2004) Triamcinolone acetonide and hexacetonide intra-articular treatment of symmetrical joints in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a double-blind trial. Rheumatology 43:1288–1291
Ravelli A, Martini A (2007) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Lancet 369:767–778
Huppertz HI, Tschammler A, Horwitz AE et al (1995) Intraarticular corticosteroids for chronic arthritis in children: efficacy and effects on cartilage and growth. J Pediatr 127:317–321
Hashkes PJ, Laxer RM (2005) Medical treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. JAMA 294:1671–1684
Beukelman T, Guevara JP, Albert DA et al (2008) Optimal treatment of knee monoarthritis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a decision analysis. Arthritis Rheum 59:1580–1588
Padeh S, Passwell JH (1998) Intraarticular corticosteroid injection in the management of children with chronic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41:1210–1214
Furtado RN, Oliveira LM, Natour J et al (2005) Polyarticular corticosteroid injection versus systemic administration in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients: a randomized controlled study. J Rheumatol 32:1691–1698
Harris ED Jr (2006) Glucocorticoid therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: intra-articular injections versus systemic administration. Nat Clin Prac Rheumatol 2:184–185
Raza K, Lee CY, Pilling D et al (2003) Ultrasound guidance allows accurate needle placement and aspiration from small joints in patients with early inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology 42:976–979
Balint PV, Kane D, Hunter J et al (2002) Ultrasound guided versus conventional joint and soft tissue fluid aspiration in rheumatology practice: a pilot study. J Rheumatol 29:2209–2213
Beukelman T, Arabshahi B, Cahill AM et al (2006) Benefit of intraarticular corticosteroid injection under fluoroscopic guidance for subtalar arthritis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 33:2330–2336
Cahill AM, Cho SS, Baskin KM et al (2007) Benefit of fluoroscopically guided intraarticular, long-acting corticosteroid injection for subtalar arthritis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr Radiol 37:544–548
Reach JS, Easley ME, Chuckpaiwong B et al (2009) Accuracy of ultrasound guided injections in the foot and ankle. Foot Ankle Int 30:239–242
Cleary AG, Murphy HD, Davidson JE et al (2003) Intra-articular corticosteroid injections in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arch Dis Child 88:192–196
Jones A, Regan M, Ledingham J et al (1993) Importance of placement of intra-articular steroid injections. BMJ 307:1329–1330
Sethi PM, Kingston S, Elattrache N et al (2005) Accuracy of anterior intra-articular injection of the glenohumeral joint. Arthroscopy 21:77–80
Lopes RV, Furtado RN, Parmigiani L et al (2008) Accuracy of intra-articular injections in peripheral joints performed blindly in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 47:1792–1794
Eustace JA, Brophy DP, Gibney RP et al (1997) Comparison of the accuracy of steroid placement with clinical outcome in patients with shoulder symptoms. Ann Rheum Dis 56:59–63
Jackson DW, Evans NA, Thomas BM et al (2002) Accuracy of needle placement into the intra-articular space of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A:1522–1527
Jeyapalan K, Choudhary S (2009) Ultrasound-guided injection of triamcinolone and bupivicaine in the management of De Quervain’s disease. Skeletal Radiol 38:1099–1103
Akhtar S, Bradley MJ, Quinton DN et al (2005) Management and referral for trigger finger/thumb. BMJ 331:30–33
Peters-Veluthamaningal C, Winters JC, Groenier KH et al (2008) Corticosteroid injections effective for trigger finger in adults in general practice: a double blinded randomised placebo controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1262–1266
Bodor M, Flossman T (2009) Ultrasound-guided first annular pulley injection for trigger finger. J Ultrasound Med 28:737–743
Benson LS, Ptaszek AJ (1997) Injection versus surgery in the treatment of trigger finger. J Hand Surg Am 22:138–144
Kamhin M, Engel J, Heim M et al (1983) The fate of injected trigger fingers. Hand 15:218–220
Taras JS, Raphael JS, Pan WT et al (1998) Corticosteroid injections for trigger digits: is intrasheath injection necessary? J Hand Surg Am 23:717–722
Unverferth LJ, Olix ML (1973) The effect of local steroid injections on tendon. J Sports Med 1:31–37
D’Agostino MA, Ayral X, Baron G et al (2005) Impact of ultrasound imaging on local corticosteroid injections of symptomatic ankle, hind- and mid-foot in chronic inflammatory diseases. Arthritis Rheum 53:284–292
Janow GL, Panghaal V, Trinh A et al (2011) Detection of active disease in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: sensitivity and specificity of the physical examination vs. ultrasound. J Rheumatol 38:2671–2674
Eich GF, Hallé F, Hodler J et al (1994) Juvenile chronic arthritis: imaging of the knees and hips before and after intraarticular steroid injection. Pediatr Radiol 24:558–563
Marti P, Molinari L, Bolt IB et al (2008) Factors influencing the efficacy of intra-articular steroid injections in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Eur J Pediatr 167:425–430
Eberhard BA, Sison MC, Gottlieb BS et al (2004) Comparison of the intraarticular effectiveness of triamcinolone hexacetonide and triamcinolone acetonide in treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 31:2507–2512
Ravelli A, Manzoni SM, Viola S et al (2001) Factors affecting the efficacy of intraarticular corticosteroid injection of knees in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 28:2100–2102
Gaffney K, Williams RB, Jolliffe VA et al (1995) Intra-articular pressure changes in rheumatoid and normal peripheral joints. Ann Rheum Dis 54:670–673
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, C.M., Shiels, W.E., Coley, B.D. et al. Ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection therapy for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: 12-year care experience. Pediatr Radiol 42, 1481–1489 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2487-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2487-y