Abstract
Background
It is increasingly recognized that in children swallowed multiple magnets cause considerable damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
Objective
To emphasize that complications from swallowed magnets are extensive worldwide and throughout childhood.
Materials and methods
The author surveyed radiologists and researched cases of magnet swallowing in the literature and documented age and gender, numbers of magnets, nature of the magnets, reasons for swallowing, and clinical course.
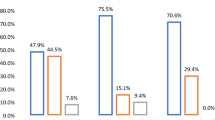
Results
A total of 128 instances of magnet swallowing were identified, one fatal. Cases from 21 countries were found. Magnet swallowing occurred throughout childhood, with most children older than 3 years of age. Numbers of swallowed magnets ranged up to 100. Twelve children were known to be autistic. Many reasons were given for swallowing magnets, and a wide range of gastrointestinal damage was encountered. Considerable delay before seeking medical assistance was frequent, as was delay before obtaining radiographs or US imaging.
Conclusion
Damage from swallowing multiple magnets is a considerable worldwide problem. More educational and preventative measures are needed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuzon WM, McFadyen CA, Moffat FL (1988) Unusual gastric foreign body; a case report. Can J Surg 31:413–417
Honzumi M, Shigemori C, Ito H et al (1995) An intestinal fistula in a 3-year-old child caused by the ingestion of magnets: report of a case. Surg Today 25:552–553
Kubota Y, Tokiwa K, Tanaka S et al (1995) Intestinal obstruction in an infant due to magnet ingestion. Eur J Pediatr 5:119–121
Hong SG, Chung JH, Song YT (2001) Small bowel complication due to magnetic foreign body ingestion in childhood. J Korean Surg Soc 61:224–226
Cauchi JA, Shawis RN (2002) Multiple magnet ingestion and gastrointestinal morbidity. Arch Dis Child 87:539–540
Kim MJ, Kwak AJ, Choi KH (2002) Gastric ulcer due to three magnets ingestion in a 37-month-old girl. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 5:68–72
McCormick S, Brennan P, Yassa J et al (2002) Children and mini-magnets: an almost fatal attraction. Emerg Med J 19:71–73
Chung JH, Kim JS, Song YT (2003) Small bowel complication due to magnetic foreign body ingestion of childhood: two case reports. J Pediatr Surg 38:1548–1550 (same cases as [4])
Tay ET, Weinberg G, Levin TL (2004) Ingested magnets. The force within. Pediatr Emerg Care 20:466–467
Emminger A, Armbruster S, Welzenbach B et al (2005) Multiple small bowel perforations after ingestion of several magnetic toy pieces – case report (in German). Abstracts 101. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Kinder- und Jugendmedizin, 29 September to 2 October, Bremen
Encinas JL, Garcia-Bermejo AM, Andrés AM et al (2005) Multiple intestinal perforations due to ingestion of magnetized pieces of a toy (in Spanish). An Pediatr (Barc) 63:457–458
Etzler A, Schmedding A, Kolb H et al (2005) Bowel perforation after ingestion of several magnetic toy parts (in German). Abstracts 101. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Kinder- und Jugendmedizin, 29 September to 2 October, Bremen
Ishimaru T, Kanamori Y, Sugiyama M et al (2005) A case of intestinal obstruction due to ingestion of multiple magnets. J Jpn Surg Assoc 66:2971–2975
Kwak BG, Moon JS, Jang HO et al (2005) Small bowel-mesentery-small bowel fistula caused by ingested magnets. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 8:60–63
Liu S, de Blacam C, Lim F-Y (2005) Magnetic foreign body ingestions leading to duodenocolonic fistula. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 41:670–672
Löwenstein S, Koltai JL, Jainsch M et al (2005) Complications from ingestion of magnetic foreign bodies (in German). Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 155:S39–S41
Mok E, Bazan HA, Herron DM (2005) An unusual source of abdominal pain after adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis 1:584–587
Nagaraj HS, Sunil I (2005) Multiple foreign body ingestion and ileal perforation. Pediatr Surg Int 21:718–720
Nui A, Hirama T, Katsuramaki T et al (2005) An intestinal volvulus caused by multiple magnet ingestion: an unexpected risk in children. J Pediatr Surg 40:E9–E11
Oestreich AE (2006) Danger of multiple magnets beyond the stomach in children. J Natl Med Assoc 98:277–279
Wildhaber BE, Le Coultre C, Genin B (2005) Ingestion of magnets: innocent in solitude, harmful in groups. J Pediatr Surg 40:e33–e35
Arbman G, Jonsberg T (2006) Risk of severe complications following ingestion of small magnets (in Swedish). Lakartidningen 103:4028
Berg DA, Tynan M, Grewal H (2006) Magnets in the stomach. J Pediatr Surg 41:1037–1039
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2006) Gastrointestinal injuries from magnet ingestion in children – United States, 2003–2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 55:1296–1300
Cortés CA, Silva CF (2006) Accidental ingestion of magnets in children, report of three cases. Rev Med Chil 134:1315–1319
Gerlach K, Schaper D (2006) Bowel perforation and ileus after ingestion of magnets. PedRad [serial online] vol 6, no. 9. www.PedRad.info/?search=20060928135619. Accessed 31 October 2008
Goo MJ, Park JS, Kang SJ et al (2006) A case of two ingested magnets attracted to each other that were holding gastric mucosa. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc 32:275–277
Mumme S, Beck O, Leenen A (2006) What is the diagnosis? – Ingestion of a 19-piece magnetic toy (in German). Kinder Jugedarzt 37:43–44
Reed SF (2006) Complications of ingesting metallic objects and a magnet. Surg Rounds 29:120–123
Vijaysadan V, Perez M, Kuo D (2006) Revisiting swallowing troubles: intestinal complications caused by two magnets – a case report, review and proposed revision to the algorithm for the management of foreign body ingestion. J Am Board Fam Med 19:511–516
Alzahem AM, Soundappan SS, Jefferies H et al (2007) Ingested magnets and gastrointestinal complications. J Paediatr Child Health 43:497–498
CNN (2007) Mom: girl got sick after swallowing Mattel magnets. http://edition.cnn.com/2007/US/08/14/toy.victim/index.html. Accessed 31 October 2008
Anselmi EH, San Román CG, Barrios Fontoba JE et al (2007) Intestinal perforation caused by magnetic toys. J Pediatr Surg 42:E13–E16
Astrup JG, Nordentoft T (2007) Magnetic items cause perforation of the bowel (in Danish). Ugeskr Laeger 169:4240–4241
Butterworth J, Feitis B (2007) Toy magnet ingestion in children: revising the algorithm. J Pediatr Surg 42:e3–e5
Callahan P (2007) Tribune investigation: hidden hazards. Kids at risk. Chicago Tribune. http://www.chicagotribune.com/news/specials/chi-magnetpart1-special,0,1564070.special. Accessed 31 October 2008
Carlsen CG, Floyd AK, Lundhus E (2007) Multiple bowel perforations after swallowing magnetic toys (in Danish). Ugeskr Laeger 169:4242–4243
Czwianianc DA, Bak-Romaniszyn L, Malecka-Pana E (2007) Accidental ingestion of two magnets – aggressive or prolonged approach? (in Polish). Pol Merkur Lekarski 22:416–418
Farr S (2007) Near-fatal attraction. Philadelphia Daily News. 14 December 2007
Fenton SJ, Torgenson M, Holsti M et al (2007) Magnetic attraction leading to a small bowel obstruction in a child. Pediatr Surg Int 23:1245–1247
Hwang J-B, Park MH, Choi S-O (2007) How strong construction toy magnets are! A gastro-gastro-duodenal fistula formation. Letter to the editor. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 44:291–292
Ilce Z, Samsum H, Mammadov E et al (2007) Intestinal volvulus and perforation caused by multiple magnet ingestion: report of a case. Surg Today 37:50–52
Kim K-J, Ju Y-T, Jeong C-Y et al (2007) Gastrointestinal complication caused by ingestion of multiple magnets in children (in Korean). J Korean Surg Soc 73:355–358
Kircher MF, Milla S, Callahan MJ (2007) Ingestion of magnetic foreign bodies causing multiple bowel perforations. Pediatr Radiol 37:933–936
Palanivelu C, Rangarajan M, Rajapandian S et al (2007) Laparoscopic retrieval of “stubborn” foreign bodies in the foregut. A case report and literature survey. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 17:528–531
Pryor HI, Lange PA, Bader A et al (2007) Multiple magnetic foreign body ingestion: a surgical problem. J Am Coll Surg 205:182–186
Salomon S, Clausen CH, Hollegaard S et al (2007) Perforations after ingestion of magnetic items (in Danish). Ugeskr Laeger 169:4239–4240
Canadian Paediatric Surveillance Program (2008) Magnets in the bowel: a sticky problem! Paediatr Child Health 13:118
Demir M, Cevizci N, Dokucu AI (2008) Intestinal perforation due to multiple magnet ingestion: case report. Türkiye Çocuk Cerrahisi Derneği (Turkish Association of Pediatric Surgeons). http://www.tccd.org.tr/egitim/kongre/bilver.php?yil=2006&git=P-11. Accessed 31 October 2008
Dutta S, Barzin A (2008) Multiple magnet ingestion as a source of severe gastrointestinal complications requiring surgical intervention. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 162:123–125
Raquillet C, Guérin F, Martelli H et al (2008) To swallow magnets: a dangerous game. A case report (in French). Arch Pediatr 15:1095–1098
Schierling S, Snyder SK, Custer M et al (2008) Magnet ingestion. J Pediatr 252:294
Anderson RC, Walker MK, Viner JM et al (2004) Adjustment and malfunction of a programmable valve after exposure to toy magnets. Case report. J Neurosurg 101(2 Suppl):222–225
Oestreich AE (2007) The usefulness of magnification in postgastric magnetopathy – technical innovation. Pediatr Radiol 37:1268–1269
Acknowledgements
I thank all colleagues, both medical and in other professions (such as reporters, lawyers, and government workers), who contributed material to this survey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Addendum: Postgastric Magnetopathy Survey (as distributed to colleagues worldwide)
Addendum: Postgastric Magnetopathy Survey (as distributed to colleagues worldwide)
Dear Colleagues,
Many dozens of postgastric magnetopathy case reports have appeared in the medical literature throughout the world. These are children who have swallowed multiple magnets from toys, jewelry, home remedies, industrial uses, and perhaps other sources. These magnets often (I believe usually) attract each other across bowel walls, especially once they are beyond the stomach. Many abdominal complications have been found surgically (or occasionally endoscopically), often severe, despite relatively mild clinical symptoms, which often have delayed seeking medical help and then delayed radiographing or ultrasound imaging. One death, from the USA state of Washington, is known.
For a brief forum to be held during the ESPR meeting in Scotland this June, I would greatly appreciate input in regard to patients encountered with this problem. In addition to real-time audience discussion, I request information in advance by e-mail. To make the tabulations non-redundant, please provide some identifying data (but not patient name!)
My questions:
-
1.
Your name and city/country and hospital/institution/praxis; and e-mail address (for me personally, not to be published)
-
2.
Have you or your colleagues encountered children (or former children) who have swallowed multiple magnets?
-
3.
Please list any patients involved by age at time of diagnosis, gender, and city/country where encountered.
-
4.
What was swallowed specifically? How many? Brand name? Did patient or parent state WHY they were swallowed?
-
5.
How was diagnosis made?
-
6.
What were the known symptoms? How long a delay before seeking medical attention? How long a delay from seeking medical attention until diagnosis was made? What manner of imaging led to the diagnosis?
-
7.
What damage was encountered in the abdomen (or elsewhere in body)?
-
8.
Outcome or follow-up?
-
9.
Was the child autistic?
-
10.
If case(s) were published could you provide reference, please? Or was it presented at a congress or meeting?
-
11.
Further comments?
-
12.
I have reviewed many published articles (in English, German, and Spanish at least) but I would greatly appreciate any references from the world literature that you could quote to me (beyond your own cases).
Many thanks in advance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oestreich, A.E. Worldwide survey of damage from swallowing multiple magnets. Pediatr Radiol 39, 142–147 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-1059-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-1059-7