Abstract
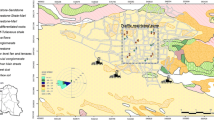
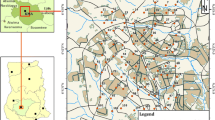
Ingestion of dust or soil particles could pose a potential health risk due to long-term metal trace element (MTE) exposure. Twenty-seven urban topsoil samples (kitchen garden and lawn) were collected and analyzed for Cd, Pb and Zn using the unified Bioaccessibility Research Group of Europe (BARGE) method (UBM) test to estimate the human bioaccessibility of these elements. The quantities of Cd, Pb and Zn extracted from soils indicated, on average, 68, 62 and 47% bioaccessibility, respectively, in the gastric phase and 31, 32 and 23% bioaccessibility, respectively, in the gastro-intestinal phase. Significant positive correlations were observed between concentrations extracted with UBM and total MTE contents. Stepwise multiple regression analysis showed that human bioaccessibility was also affected by some physico-chemical soil parameters (i.e. total nitrogen, carbonates, clay contents and pH). The unified test presents some valuable data for risk assessment. Indeed, the incorporation of oral bioaccessible concentrations into risk estimations could give more realistic information for health risk assessment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino O, Giacomino A, Malandrino M, Mentasti E, Aceto M, Barberis R (2006) Assessment of metal availability in a contaminated soil by sequential extraction. Water Air Soil Pollut 173:315–338
Alloway BJ (1995) Soil processes and the behaviour of metals. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils. Blackwell, Oxford
Alloway BJ (2004) Contamination of soils in domestic gardens and allotments: a brief overview. Land Contam Reclam 12:179–187
Brandon EF, Oomen AG, Rompelberg CJ, Versantvoort CH, van Engelen JG, Sips AJ (2006) Consumer product in vitro digestion model: Bioaccessibility of contaminants and its application in risk assessment. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 44:161–171
Button M, Watts MJ, Cave MR, Harrington CF, Jenkin GT (2009) Earthworms and in vitro physiologically-based extraction tests: complementary tools for a holistic approach towards understanding risk at arsenic-contaminated sites. Environ Geochem Health 31:273–282
Caboche J (2009) Validation d’un test de mesure de bioaccessibilité – Application à 4 éléments traces métalliques dans les sols: As, Cd, Pb et Sb. Ph.D Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine, Nancy
Calabrese EJ, Stanek EJ, James RC, Roberts SM (1999) Soil ingestion. A concern for acute toxicity in children. J Environ Health 61:18–23
Cave M, Wragg J, Klinck B, Grøn C, Oomen AG, van de Wiele T, Ollson I, Koch K, Reimer N, Basta N, Tack K, Casteel S (2006) Preliminary assessment of a unified bioaccessibility method for potentially harmful elements in soils. Epidemiology 17:39
Chatelot J, Bretin P, Lecoffre C (2008) Dépistage du saturnisme de l’enfant en France en 2003 et 2004. Institut de Veille Sanitaire, 59 pp
Chen TB, Wong JWC, Zhou HY, Wong MH (1997) Assessment of trace metal distribution and contamination in surface soils of Hong Kong. Environ Pollut 96:61–68
Chirenje T, Ma LQ, Zillioux EJ (2002) Determining arsenic distribution in urban soils: A comparison with nonurban soils. Sci World J 2:1404–1417
Cotter-Howells J, Thornton I (1991) Sources and pathways of environmental lead to children in a Derbyshire mining village. Environ Geochem Health 13:127–135
Davis S, Mirick DK (2006) Soil ingestion in children and adults in the same family. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 16:63–75
Davis A, Ruby MV, Bergstrom PD (1992) Bioavailability of arsenic and lead in soils from the Butte, Montana, mining district. Environ Sci Technol 26:461–468
Davranche M, Bollinger JC (2000) Release of metals from iron oxyhydroxides under reductive conditions: Effect of metal/solid interactions. J Colloid Interface Sci 232:165–173
De Kimpe CR, Morel JL (2000) Urban soil management: a growing concern. Soil Sci 165:31–40
Declercq C, Beaubois M (2000) Programme de dépistage du saturnisme infantile autour du site de Metaleurop de Noyelles-Godault. Bilan de la campagne 1999-2000. Observatoire Régional de la Santé Nord-Pas de Calais, 38 pp
Declercq C, Ladrière L (2004) Programme de dépistage du saturnisme infantile dans 9 communes du Nord-Pas de Calais – Bilan de la campagne 2003-2004, CLIS Metaleurop
Declercq C, Ladrière L (2005) Programme de dépistage du saturnisme infantile dans 9 communes du Nord-Pas de Calais – Bilan de la campagne 2004–2005, Observatoire régional de la santé Nord-Pas de Calais Comité d’hygiène sociale du Pas de Calais, 12 pp
Denys S, Caboche J, Tack K, Delalain P (2007) Bioaccessibility of lead in high carbonate soils. J Environ Sci Health A 42:1331–1339
Denys S, Tack K, Caboche J, Delalain P (2009) Bioaccessibility, solid phase distribution, and speciation of Sb in soils and in digestive fluids. Chemosphere 74:711–716
Douay F, Lamy I, Citeau L (2002) Programme de Recherches Concertées. Environnement et Activités humaines. Etude d’un secteur pollué par les métaux. Complément sur la caractérisation des transferts de métaux (Pb, Cd et Zn) dans des sols fortement contaminés, 32 pp
Douay F, Pruvot C, MAzzuca M, Howsam M, Fourrier H, de Saint Mahieu AS, Waterlot C (2005) Cadmium, lead and zinc concentrations in soil and vegetables from kitchen gardens in urban and highly-contaminated areas of northern France: evaluation of the risk of population exposure. Proceedings of the 9th International FZK/TNO Conference on Soil-Water Systems, Bordeaux, France
Douay F, Roussel H, Fourrier H, Heyman C, Chateau G (2007) Investigation of heavy metal concentrations on urban soils, dust and vegetables nearby a former smelter site in Mortagne du Nord, Northern France. J Soils Sediments 7:143–146
Douay F, Pruvot C, Roussel H, Ciesielski H, Fourrier H, Proix N, Waterlot C (2008) Contamination of urban soils in an area of northern France polluted by dust emissions of two smelters. Water Air Soil Poll 188:247–260
Duggan MJ, Inskip MJ (1985) Childhood exposure to lead in surface dust and soil: a community health problem. Public Health Rev 13:1–54
Ellickson KM, Meeker RJ, Gallo MA, Buckley BT, Lioy PJ (2001) Oral bioavailability of lead and arsenic from a NIST standard reference soil material. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:128–135
Environment Agency and British Geological Survey (2002) In vitro methods for the measurements of the oral bioaccessibility of selected metals and metalloids in soils: a critical review. E Agency Bristol Environment Agency
Freeman NCG, Sheldon L, Jimenez M, Melnyk L, Pellizzaru E, Berry M (2001) Contribution of children’s activities to lead contamination of food. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 11:407–413
Gasser UG, Walker WJ, Dahlgren RA, Borch RS, Burau RG (1996) Lead release from smelter and mine waste impacted materials under simulated gastric conditions and relation to speciation. Environ Sci Technol 30:761–769
Glorennec P (2006) Analysis and reduction of the uncertainty of the assessment of children’s lead exposure around an old mine. Environ Res 100:150–158
Grøn C, Andersen L (2003) Human bioaccessibility of heavy metals and PAH from soil. Environmental project No. 840, Technology Programme for Soil and Groundwater Contamination. Danish Environmental Protection Agency, 113 pp
IARC (1987) Beryllium, cadmium, mercury, and exposures in the glass manufacturing industry. Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon France 58
Johnson DL, Bretsch JK (2002) Soil lead and children’s blood lead levels in Syracuse, NY, USA. Environ Geochem Health 24:375–385
Lanphear BP, Burgoon DA, Rust SW, Eberly S, Galke W (1998) Environmental exposures to lead and urban children’s blood lead levels. Environ Res A 76:120–130
Leroyer A, Nisse C, Hemon D, Gruchociak A, Salomez JL, Haguenoer JM (2000) Environmental lead exposure in a population of children in northern France: factors affecting lead burden. Am J Ind Med 38:281–289
Lothenbach B, Furrer G, Schärli H, Schulin R (1999) Immobilization of zinc and cadmium by montmorillonite compounds: effect of aging and subsequent acidification. Environ Sci Technol 33:2945–2952
Mehra OP, Jackson ML (1960) Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite-citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. Clays Clay Miner 7:317–327
Merian E, Anke M, Ihnat M, Stoeppler M (2004) Elements and their compound in the environment–vol 2: metals and their compounds. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany
Norra S, Stüben D (2003) Urban soils. J Soils Sediments 3:230–233
Oomen AG (2000) Determinants of oral bioavailability of soil-borne contaminants. Universiteit Utrecht, Utrecht
Oomen AG, Hack A, Minekus M, Zeijdner E, Schoeters G, Verstraete W, Von de Wiele T, Wragg J, Rompelberg CJM, Sips AJAM, Wijnen JHV (2002) Comparison of five in vitro digestion models to study the bioaccessibility of soil contaminants. Environ Sci Technol 36:3326–3334
Oomen AG, Rompelberg CJ, Bruil MA, Dobbe CJ, Pereboom DP, Sips AJ (2003) Development of an in vitro digestion model for estimating the bioaccessibility of soil contaminants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 44:281–287
Oomen AG, Brandon EFA, Swartjes FA, Sips AJAM (2006) How can information on oral bioavailability improve human health risk assessment for lead-contaminated soils? Report 711701042/2006, RIVM, 108 pp
Paterson E, Sanka M, Clark LM (1996) Urban soils as pollutant sinks–a case study from Aberdeen, Scotland. Appl Geochem 11:129–131
Peltola P, Astrom M (2003) Urban geochemistry: a multimedia and multielement survey of a small town in northern Europe. Environ Geochem Health 25:397–419
Pierzynsky GM, Sims JT, Vance GF (2005) Soils and environmental quality. CRC, Taylor & Francis, New York, USA
Pruvot C, Douay F, Fourrier H, Waterlot C (2006) Heavy metals in soil, crops and grass as a source of human exposure in the former mining areas. J Soils Sediments 6:215–220
Quevauviller P, Rauret G, Muntau H, Ure AM, Rubio R, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Fiedler HD, Griepink B (1994) Evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure for the determination of extractable metal contents in sediments. Fresenius J Anal Chem 349:808–814
Quevauviller P, Rauret G, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Rubio R, Ure A, Muntau H (1997) Certification of trace metal extractable contents in a sediment reference material (CRM 601) following a three-step sequential extraction procedure. Sci Total Environ 205:223–234
Rauret G, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1:57–61
Rotard W, Christmann W, Knoth W, Mailahn W (1995) Bestimmung der resorptionsverfügbaren PCDD/PCDF aus Kieslrot. Z Umweltchem 7:3–9
Sterckeman T, Douay F, Proix N, Fourrier H (2000) Vertical distribution of Cd, Pb and Zn in soils near smelters in the North of France. Environ Pollut 107:377–389
Sterckeman T, Douay F, Proix N, Fourrier H, Perdrix E (2002) Assessment of the contamination of cultivated soils by eighteen trace elements around smelters in the North of France. Water Air Soil Pollut 135:173–194
Van de Wiele T, Oomen AG, Wragg J, Cave M, Minekus M, Hack A, Cornelis C, Rompelberg CJM, de Zwart LL, Klinck B, van Wijnen J, Verstraete W, Sips AJAM (2007) Comparison of five in vitro digestion models to in vivo experimental results: lead bioaccessibility in the human gastrointestinal tract. J Environ Sci Health A 42:1203–1211
Violante A, Ricciardella M, Pigna M (2003) Adsorption of heavy metals on mixed Fe-Al oxides in the absence or presence of organic ligands. Water Air Soil Pollut 145:289–306
Vostal JJ, Taves E, Sayre JW, Charney E (1974) Lead analysis of housedust: a method for the detection of another source of lead exposure in inner city children. Environ Health Perspect 7:91–97
Waterlot C, Bidar G, Douay F, Daurangeon F (2008) Analysis of trace elements in solution, assessment of a background compensation technique on the As interference in the Cd analysis. Spectra Analyse 261:48–52
Wragg J, Cave M, Taylor H, Basta N, Brandon E, Casteel S, Grøn C, Oomen AG, Van de Wiele T (2009) Inter-laboratory trial of a unified bioaccessibility procedure. Chemical & Biological Hazards Programme, Report OR/07/027, British Geological Survey
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thanks the Nord-Pas de Calais Council, the French Ministry of Research and the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER), for financial support. They thank Sébastien Denys, Karine Tack and Julien Caboche (Institut National de l’Environnement Industriel et des Risques) as well as the BARGE members (Bioaccessiblity Research Group of Europe) for scientific and technical help for the realization of the bioaccessibility tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roussel, H., Waterlot, C., Pelfrêne, A. et al. Cd, Pb and Zn Oral Bioaccessibility of Urban Soils Contaminated in the Past by Atmospheric Emissions from Two Lead and Zinc Smelters. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 58, 945–954 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9425-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9425-5