Abstract
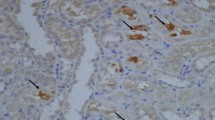
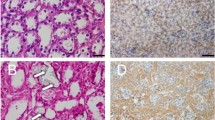
Crystal–cell interaction has been reported as one of the most crucial steps in urinary stone formation. Hyperoxaluria-induced apoptotic changes in renal tubular epithelial cells is the end-stage of this interaction. We aimed to evaluate the possible pathways responsible in the induction of apoptosis within the involved cells by assessing the receptoral expression of three different pathways. 16 male Spraque–Dowley rats were divided into two groups: Group 1 (n:8) received only distilled water; Group 2 (n:8) received 0.75 % ethylene glycol (EG) in their daily water to induce hyperoxaluria for 2 weeks. After 24 h urine collection, all animals were euthenized and right kidneys were removed and fixed for immunohistochemical evaluation. Oxalate and creatinine levels (in 24 h-urine) and FAS, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and TRAIL receptor-2 expressions (in tissue) have been assessed. In addition to TNF (p = 0.0007) expression; both FAS (p = 0.0129 ) and FASL (p = 0.032) expressions significantly increased in animals treated with EG. The expressions of TRAIL (p = 0.49) and TRAIL-R2 (p = 0.34) receptors did not change statistically after hyperoxaluria induction. Although a positive correlation with cytokine expression density and 24 h-urinary oxalate expression (mg oxalate/mg creatinine) has been assessed with TNF (p = 0.04, r = 0.82), FAS (p = 0.05, r = 0.80), FAS-L (p = 0.04, r = 0.82); no correlation could be demonstrated between TRAIL and TRAIL R2 expressions. Our results indicate that apoptosis induced by oxalate is possibly mediated via TNF and FAS pathways. However, TRAIL and TRAIL-R2 seemed to have no function in the cascade. Correlation with urinary oxalate levels did further strengthen the findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thamilselvan S, Khan SR (1998) Oxalate and calcium oxalate crystals are injurious to renal epithelial cells: results of in vivo and in vitro studies. J Nephrol 11:66–70
Sarıca K, Yagcı F, Bakır K, Erbagcı A, Erturhan S, Uçak R (2001) Renal tubular injury induced by hyperoxaluria: evaluation of apoptotic changes. Urol Res 29(1):34–37
Khan SR, Byer KJ, Thamilselvan S, Hackett RL, McCormack WT, Benson NA et al (1999) Crystal–cell interaction and apoptosis in oxalate-associated injury of renal epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:457–459
Koul H, Kennington L, Nair G, Honeyman T, Menon M, Scheid C (1994) Oxalate-induced initiation of DNA synthesis in LLC-PK1 cells, a line of renal epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 205:1632–1636
Koul S, Fu S, Menon M, Koul H (2000) Oxalate exposure induces apoptosis in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (LLC- PK1 and HK-2 cells) in culture. In: Urolithiasis 2000, 9th International Symposium on Urolithiasis, Proceedings, p 247
Miyazawa K, Suzuki K, Ueda Y, Katsuda S (2000) Demonstration of apoptosis and its related genes in rat tubular epithelium of calcium oxalate crystal formation. Urolithiasis 2000, 9th International Symposium on Urolithiasis, Proceedings, p 253
Scheid C, Koul H, Hill WA, Luber-Narod J, Kennington L, Honeyman T et al (1996) Oxalate toxicity in LLC-PK1 cells: role of free radicals. Kidney Int 49:413–417
Scheid CR, Koul H, Hill WA, Luber-Narod J, Jonassen J, Honeyman T et al (1996) Oxalate toxicity in in LLC-PK1 cells; a line of renal epithelial cells. J Urol 155:1112–1116
Sarıca K, Erbagcı A, Yağcı F, Bakır K, Erturhan S, Uçak R (2004) Limitation of apoptotic changes in renal tubular cell injury induced by hyperoxaluria. Urol Res 32(4):271–277
Krammer PH (1999) CD95 (Apo-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis: live and let die. Adv Immunol 71:163–210
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A (1996) Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem 271:12687–12690
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK et al (1995) Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 3:673–682
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305–1308
Johri N, Cooper B, Robertson W, Choong S, Rickards D, Unwin R (2010) An Update and Practical Guide to Renal Stone Management Nephron Clin Pract 116(3):c159–c171
Stamatiou KN, Karanasiou VI, Lacroix RE, Kavouras NG, Papadimitriou VT, Chlopsios C et al (2006) Prevalence of urolithiasis in rural Thebes. Greece. Rural Remote Health 6(4):610
Ramello A, Vitale C, Marangella M (2000) Epidemiology of nephrolithiasis. J Nephrol, suppl:13: S45
Hackett RL, Shevock PN, Khan SR (1990) Cell injury associated with calcium oxalate crystalluria. J Urol 144:1535–1539
Hackett RL, Shevock PN, Khan SR (1994) Madin-Darby canine kidney cells are injured by exposure to oxalate and to calcium oxalate crystals. Urol Res 22:197–201
Hackett RL, Shevock PN, Khan SR (1995) Alterations in MDCK and LLC-PK1 cells exposed to oxalate and calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals. Scanning Micorosc 9:587–590
Koul H, Kennington L, Honeyman T, Jonassen J, Menon M, Scheid C (1996) Activation of c-myc gene mediates the mitogenic effects of oxalate in LLC-PK1 cells, a line of renal epithelial cells. Kidney Int 50:1520–1525
Finlayson B (1978) Physicochemical aspects of urolithiasis. Kidney Int 13:344–347
Khan SR, Shevock PN, Hackett RL (1989) Urinary enzymes and calcium oxalate urolithiasis. J Urol 142:846–850
Lieske JC, Norris R, Swift H, Toback FG (1997) Adhesion, internalization and metabolism of calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals by renal epithelial cells. Kidney Int 52:1291–1294
Selvam R, Bijikurien T (1992) Effect of citrate feeding on free radical induced changes in experimental urolithiasis. Indian J Exp Biol 30:705–710
Strohmaier WL, Bichler KH, Koch J, Balk KN, Wilbert DM (1993) Protective effect of verapamil on shock wave-induced renal tubular dysfunction. J Urol 150:27–29
Thamilselvan S, Hackett RL, Khan SR (1997) Lipid peroxidation in ethylene glycol induced hyperoxaluria and calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. J Urol 157:1059–1063
Scheid CR, Koul H, Kennington L, Hill WA, Luber-Narod J, Jonassen J (1995) Oxalate-induced damage to renal tubular cells. Scanning Microsc 9:1097–1101
Miller C, Kennington L, Cooney R, Kohjimoto Y, Cao LC, Honeyman T (2000) Oxalate toxicity in renal epithelial cells: characteristics of apoptosis and necrosis. Toxicol Pharmacol 162:132–136
Benyi L, Weilherg Z, Puyun L (1995) Protective effects of nifedipine and allopurinol on high energy shock wave induced acute changes of renal function. J Urol 153:596–599
Sarıca K, Bakır K, Yagcı F, Topcu O, Akbay C, Sayın N et al (1999) Limitation of possible enhanced crystal deposition by verapamil in renal parenchyma after shock wave application in rabbit model. J Endourol 13:343–347
Strohmaier WL, Abelius A, Billes J, Grossmann T, Wilbert DM, Bichler KH (1994) Verapamil limits shock wave-induced renal tubular damage in vivo. J Endourol 8:269–273
Strohmaier WL, Bichler KH, Koch J, Balk KN, Wilbert DM (1993) Protective effect of verapamil on shock wave-induced renal tubular dysfunction. J Urol 150:27–32
Sarıca K, Bakır K, Yagcı F, Erbagcı A, Topcu O, Uysal O (2000) Unilateral testicular torsion; protective effect of verapamil on contralateral testicular histology. Urol Int 62:159–163
Reilly P, Schiller HJ, Bulkley GB (1992) Pharmacologic approach to tissue injury mediated by free radicals and other reactive oxygen metabolites. Am J Surg 161:488–492
Tanriverdi O, Telci D, Aydin M, Ekici ID, Miroglu C, Sarıca K (2012) Hyperoxaluria-induced tubular ischemia: the effects of verapamil and vitamin E on apoptotic changes with an emphasis on renal papilla in rat model. Urol Res 40(1):17–25
Huang HS, Ma MC, Chen J (2009) Low-vitamin E diet exacerbates calcium oxalate crystal formation via enhanced oxidative stress in rat hyperoxaluric kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 296(1):F34–F45
Baker SJ, Reddy EP (1998) Modulation of life and death by the TNF receptor superfamily. Oncog. 17:3261–3270
Acknowledgments
They also declare that the manuscript has been read and approved by all the authors, the requirements for authorship have been met, and each author believes that the manuscript represents honest work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horuz, R., Göktaş, C., Çetinel, C.A. et al. Role of TNF-associated cytokines in renal tubular cell apoptosis induced by hyperoxaluria. Urolithiasis 41, 197–203 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-013-0559-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-013-0559-6