Abstract
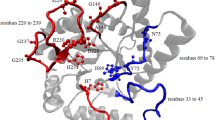
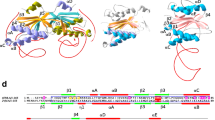
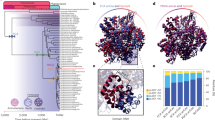
DNA repair refers to a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to genomic DNA molecules. DNA repair processes significantly overcome DNA damage and restore the normal nucleotide sequence and DNA structure. This study focuses on the evolution of the endonuclease III gene/protein family, which plays a key role in the base excision repair pathway. We analyzed 463 homologs of the endonuclease III protein and compared them with the corresponding gene and 16S/18S rRNA sequences to understand the evolutionary processes of this protein family. The sequence analysis and comparison reveal consensus sequence motifs within the ENDO3c and iron–sulfur cluster loop domains that are functionally and structurally important. On the basis of phylogenetic analysis, we propose an evolutionary model of the endonuclease III protein family. Horizontal gene transfer was identified as the key event among bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotic organisms that occurred during the evolution of the endonuclease III gene family among bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotic organisms. This analysis may be exploited to achieve a better prediction of the endonuclease III family gene/protein in unannotated organisms or families of organisms that are completely sequenced as well as in those for which sequencing is ongoing.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DR:
-
Direct repair
- NER:
-
Nucleotide excision repair
- MMR:
-
Mismatch repair
- BER:
-
Base excision repair
- AP:
-
Apurinic/apyrimidinic
- 5′dRP:
-
5′Deoxy ribose phosphate
- HhH:
-
Helix-hairpin-helix
- NCBI:
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information
- EMBOSS:
-
European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite
- ML:
-
Maximum likelihood
- NJ:
-
Neighbor joining
- PDB:
-
Protein Data Bank
- FCL:
-
Iron–sulfur cluster loop
- HGT:
-
Horizontal gene transfer
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al (1990) Basal local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Aziz S (1995) DNA repair in humans. Annu Rev Genet 29:69–105
Aziz S (1996) DNA excision repair. Annu Rev Biochem 65:43–81
Brochier C, Philippe H, Moreira D (2000) The evolutionary history of ribosomal protein RpS14: horizontal gene transfer at the heart of the ribosome. Trends Genet 16:529–533
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E et al (2009) The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37(1):D141–D145
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: a sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14:1188–1190
Denver DR, Swenson SL, Lynch M (2003) An evolutionary analysis of the helix-hairpin-helix superfamily of DNA repair glycosylases. Mol Biol Evol 20:1603–1611
Dmitry GV, Kosuke M (1997) DNA repair enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 7:103–109
Dodson ML, Michaels Mark L, Lloyd RS (1994) Unified catalytic mechanism for DNA glycosylase. J Biol Chem 269:32709–32712
Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, Von HG, Nielsen H (2007) Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc 2:953–971
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fromme JC, Verdine GL (2003) Structure of a trapped endonuclease III-DNA covalent intermediate. EMBO J 22:3461–3471
Garrity GM, Holt JG (2001) The road map to the manual. In: Boone, Castenholz RW, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. The archaea and the deeply branching and phototrophic bacteria, vol 1, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 119–166
Golinelli MP, Chmiel NH, David SS (1999) Site-directed mutagenesis of the cysteine ligands to the [4Fe 4S] cluster of Escherichia coli MutY. Biochemistry 38:6997–7007
Hegde ML, Hazra TK, Mitra S (2008) Early steps in the DNA base excision/single-strand interruption repair pathway in mammalian cells. Cell Res 18:27–47
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8:275–282
Kanchan S, Mehrotra R, Chowdhury S (2014) Evolutionary pattern of four representative DNA repair proteins across six model organisms: an in silico analysis. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinform 3:70
Labahn J, Schärer OD, Long A et al (1996) Structural basis for the excision repair of alkylation-damaged DNA. Cell 86:321–329
Lindahl T (1982) DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 51:61–87
Lukianova OA, David SS (2005) A role for iron–sulfur clusters in DNA repair. Curr Opin Chem Biol 9:145–151
Manuel RC, Hitomi K, Arvai AS et al (2004) Reaction intermediates in the catalytic mechanism of Escherichia coli MutY DNA glycosylase. J Biol Chem 279:46930–46939
Marchler BA, Bryant SH (2004) CD Search: protein domain annotations on the fly. Nucleic Acids Res 32(Web Server issue):W327–W331
Moretti S, Armougom F, Wallace IM et al (2007) The M-Coffee web server: a meta-method for computing multiple sequence alignments by combining alternative alignment methods. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Web Server issue):W645–W648
Nash HM, Bruner SD, Schärer OD et al (1996) Cloning of a yeast 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase reveals the existence of a baseexcision DNA-repair protein superfamily. Curr Biol 6:968–980
Puigbo P, Bravo IG, Garcia-Vallve S (2008) CAIcal: a combined set of tools to assess codon usage adaptation. Biol Direct 3:38
Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A (2000) EMBOSS: the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet 16:276–277
Richard DW (2001) Human DNA repair genes. Science 291:1284–1289
Shida T, Kaneda K, Ogawa T, Sekiguchi J (1999) Abasic site recognition mechanism by the Escherichia coli exonuclease III. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 42:195–196
Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S (2004) Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11030–11035
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N et al (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thayer MM, Ahern H, Xing D et al (1995) Novel DNA binding motifs in the DNA repair enzyme endonuclease Ill crystal structure. EMBO J 14:4108–4120
Thomas AK, Dorothy AE (2005) DNA mismatch repair. Annu Rev Biochem 74:681–710
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustalw: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Whittaker RH (1969) New concepts of kingdoms or organisms. Evolutionary relations are better represented by new classifications than by the traditional two kingdoms. Science 163:150–160
Yang H, Fitz-Gibbon S, Marcotte EM et al (2000) Characterization of a thermostable DNA glycosylase specific for U/G and T/G mismatches from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrobaculum aerophilum. J Bacteriol 182:1272–1279
Acknowledgments
SK is thankful to the University Grant Commission (UGC), Govt. of India, New Delhi for providing the financial support in the form of the Basic Science Research Fellowship. The authors are thankful to Manoj Kannan for critical reading of the manuscript. The authors would also like to acknowledge the infrastructural facilities provided by Department of Biological Sciences, Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani, Rajasthan, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanchan, S., Mehrotra, R. & Chowdhury, S. In Silico Analysis of the Endonuclease III Protein Family Identifies Key Residues and Processes During Evolution. J Mol Evol 81, 54–67 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-015-9689-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-015-9689-5