Abstract
Background
There is a renewed interest in autologous fillers for facial rejuvenation. We used PRP combined with cultured fibroblasts as an attractive alternative to synthetic fillers.
Methods
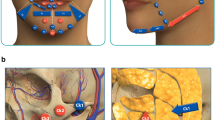
Twenty adults (17 women and 3 men: mean age 45 years: range 36–65 years) participated in a clinical trial to improve the fold in the skin of the nasolabial folds by having 1 ml of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) combined with cultured fibroblasts injected into each side.
Results
Sixteen patients had an 80 % increase in thickness of the skin adjacent to the nasolabial fold at the 9-month follow-up. Fifteen patients also showed an increase in dermal density, and in 7, there was an increase in the hydration of the facial skin. In 16 patients, the sebum quality of the skin either improved on one side or both sides of the cheek (adjacent to the nasolabial fold). Wrinkle depth on either one or both sides of the nasolabial fold was reduced in 15 patients. Seventeen patients (85 %) were satisfied with the result and would undergo the procedure again. In standardised photography, the contour of the nasolabial fold was improved in 15 patients.
Conclusions
This technique softens the nasolabial folds as well as improves the condition of the adjacent skin. This improvement was present after 9 months and did not appear to diminish with time. PRP when combined with cultured fibroblasts can act as an effective autologous filler.
Level of Evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sommeling CE, Heyneman A, Hoeksema H, Verbelen J, Stillaert FB, Monstrey S (2013) The use of platelet-rich plasma in plastic surgery: a systematic review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66:301–312
Cho JM, Lee YH, Baek RM, Lee SW (2011) Effect of platelet-rich plasma on ultraviolet b-induced skin wrinkles in nude mice. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64:e31–e39
Weiss RA, Weiss MA, Beasley KL, Munavalli G (2007) Autologous cultured fibroblast injection for facial contour deformaties: a prospective placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial. Dermatol Surg 33(3):263–268
Alexander H, Miller DL (1979) Determining skin thickness with pulsed ultrasound. J Investig Dermatol 72:17–19
Kirsch JM, Hanson ME, Gibson JR (1984) The determination of skin thickness using conventional diagnostic ultrasound equipment. Clin Exp Dermatol 9:280–285
Gniadecka M (2001) Effects of ageing on dermal echogenicity. Skin Res Technol 7:204–207
Atrix-Talau N et al (2008) Effects of physical and chemical treatments upon biophysical properties and micro-relief on human skin. Arch Dermatol Res 300(5):243–251
Floryan KM, Berghoff WJ (2004) Home study program: intraoperative use of autologous platelet-rich and platelet poor plasma for orthopaedic surgery patients. AORN J 80(4):667–678
Marx E, Carlson ER, Eichstaedt R et al (1998) Platelet rich plasma: growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 85:638
Phinney DG, Prockop DJ (2007) Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair—current views. Stem Cells 25(11):2896–2902, Review
Watson D, Keller GS, Lacombe V, Fodor PB, Rawnsley J, Lask GP (1999) Autologous fibroblasts for treatment of facial rhytids and dermal depression. Arch Facial Plast Surg 1:165–170
Boss WK Jr, Usal H, Chernoff G, Keller GS, Lask GP, Fodor PB (2000) Autologous cultured fibroblasts as cellular therapy in plastic surgery. Clin Plast Surg 27(4):613–626
Eppley BL, Pietrzak WS, Blanton M (2006) Platelet-rich plasma: a review of biology and applications in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(6):147e–159e
Boss WK Jr, Usal H, Fodor PB, Chernoff G (2000) Autologous cultured fibroblasts: a protein repair system. Ann Plast Surg 44(5):536–542
Tan CY, Statham B, Marks R, Payne PA (1982) Skin thickness measurement by pulsed ultrasound: its reproducibility, validation and variability. Br J Dermatol 106:657–667
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
The study has been approved and was conducted in accordance with the protocol, the ICH Guideline for GCP and the Declaration of Helsinki.
Funding
The study has been funded as the company by NHP Ltd. from 2006 until 2011, when it withdrew any financial support.
Conflict of interest
Dr KM Geldenhuys sells the Mycells® tube through Neocell Laboratories to aesthetic doctors and orthopaedic surgeons.
Patient consent
Patients provided written consent prior their inclusion in the study. Additional consent was obtained for the use of their images.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geldenhuys, K.M., Hudson, D.A. A prospective cohort pilot study to assess the safety and efficacy of combining autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) with autologous dermal fibroblast for skin augmentation. Eur J Plast Surg 39, 133–138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-015-1163-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-015-1163-5