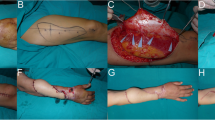
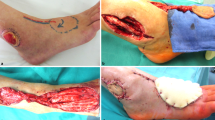
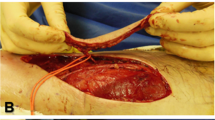
Abstract
Improvements in microsurgical techniques and perioperative management have led to more attempts at limb salvage surgery after severe extremity trauma. Although some microsurgery-trained orthopedic surgeons will perform extremity soft tissue reconstruction, many rely on plastic surgeons or hand surgeons. However, the orthopedic trauma surgeon often remains the principle decision maker in the follow-up of these patients. Therefore, orthopedic surgeons should have a clear understanding of the planning and execution of flap reconstruction of the traumatized extremities. Collaboration with the microsurgery team will also improve planning of orthopedic procedures and facilitate a better understanding of the expected outcomes after tissue transfer. This becomes especially important when considering, debridement, early amputation versus extensive soft tissue reconstruction and when discussing these alternatives with patients and family as well as postoperative course. The goals of this article are to provide orthopedic trauma surgeons with an understanding of the selection, planning, and execution of tissue transfers for posttraumatic extremity reconstruction and to review their successes and outcomes in the literature. Communication between teams involved in reconstruction of the traumatized extremity and an understanding of limitations are paramount to successful outcomes after reconstruction.
Level of Evidence: Not ratable.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parrett BM, Matros E, Pribaz JJ, Orgill DP (2006) Lower extremity trauma: trends in the management of soft-tissue reconstruction of open tibia-fibula fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(4):1314–1315
Francel TJ (1992) Salvage of the massively traumatized lower extremity. Clin Plast Surg 19(4):871–880.
Heitmann C, Levin LS (2003) The orthoplastic approach for management of the severely traumatized foot and ankle. J Trauma 54(2):379–390
American College of Surgeons (2004) Trauma AC of SC on advanced trauma life support program for doctors. 7th ed. American College of Surgeons, Chicago, IL
Arnez ZM (1991) Immediate reconstruction of the lower extremity–an update. Clin Plast Surg 18(3):449–457.
Gopal S, Majumder S, Batchelor AG, Knight SL, De Boer P, Smith RM (2000) Fix and flap: the radical orthopaedic and plastic treatment of severe open fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 82(7):959–966.
Johansen K, Daines M, Howey T, Helfet D, Hansen ST (1990) Objective criteria accurately predict amputation following lower extremity trauma. J Trauma 30(5):568–72; discussion 572–3
Russell WL, Sailors DM, Whittle TB, Fisher Jr. DF, Burns RP (1991) Limb salvage versus traumatic amputation. A decision based on a seven-part predictive index. Ann Surg 213(5):471–473
Krettek C, Seekamp A, Köntopp H, Tscherne H (2001) Hannover Fracture Scale ’98–re-evaluation and new perspectives of an established extremity salvage score. Injury 32(4):317–28
Bosse MJ, MacKenzie EJ, Kellam JF et al (2001) A prospective evaluation of the clinical utility of the lower-extremity injury-severity scores. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A(1):3–14
Goldberg JA, Alpert BS, Lineaweaver WC, Buncke HJ (1991) Microvascular reconstruction of the lower extremity in the elderly. Clin Plast Surg 18(3):459–465
MacKenzie EJ, Bosse MJ, Pollak AN et al (2005) Long-term persistence of disability following severe lower-limb trauma. Results of a seven-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(8):1801–1809
Dagum AB, Best AK, Schemitsch EH, Mahoney JL, Mahomed MN, Blight KR (1999) Salvage after severe lower-extremity trauma: are the outcomes worth the means? Plast Reconstr Surg 103(4):1212–1220
Yazar S, Lin CH, Lin YT, Ulusal AE, Wei FC (2006) Outcome comparison between free muscle and free fasciocutaneous flaps for reconstruction of distal third and ankle traumatic open tibial fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(7):2467–2468
Mathes SJ, Nahai F (1997) In: Mathes SJ, Nahai F (eds) Reconstructive surgery principles, anatomy, and technique. 1st ed. Churchill and Livingstone Inc, New York
Godina M (1986) Early microsurgical reconstruction of complex trauma of the extremities. Plast Reconstr Surg 78(3):285–292
Breidenbach 3rd WC (1989) Emergency free tissue transfer for reconstruction of acute upper extremity wounds. Clin Plast Surg 16(3):505–514
Pollak AN, McCarthy ML, Burgess AR (2000) Short-term wound complications after application of flaps for coverage of traumatic soft-tissue defects about the tibia. The Lower Extremity Assessment Project (LEAP) Study Group. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82-A(12):1681–1691
Beck JB, Stile F, Lineaweaver W (2003) Reconsidering the soleus muscle flap for coverage of wounds of the distal third of the leg. Ann Plast Surg 50(6):631–635
Hung LK, Lao J, Ho PC (1996) Free posterior tibial perforator flap: anatomy and a report of 6 cases. Microsurgery 17(9):503–511
Gir P, Cheng A, Oni G, Mojallal A, Saint-Cyr M (2012) Pedicled-perforator (propeller) flaps in lower extremity defects: a systematic review. J Reconstr Microsurg 28(9):595–601
Russell RC, Graham DR, Feller AM, Zook EG, Mathur A (1988) Experimental evaluation of the antibiotic carrying capacity of a muscle flap into a fibrotic cavity. Plast Reconstr Surg 81(2):162–170
Francel TJ, Vander Kolk CA, Hoopes JE, Manson PN, Yaremchuk MJ (1992) Microvascular soft-tissue transplantation for reconstruction of acute open tibial fractures: timing of coverage and long-term functional results. Plast Reconstr Surg 89(3):478–479
Pelissier P, Boireau P, Martin D, Baudet J (2003) Bone reconstruction of the lower extremity: complications and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 111(7):2223–2229
Ozkan O, Coskunfirat OK, Ozgentas HE (2004) An ideal and versatile material for soft-tissue coverage: experiences with most modifications of the anterolateral thigh flap. J Reconstr Microsurg 20(5):377–383
Luo S, Raffoul W, Luo J et al (1999) Anterolateral thigh flap: a review of 168 cases. Microsurgery 19(5):232–238
Muramatsu K, Shigetomi M, Ihara K, Kawai S, Doi K (2001) Vascular complication in free tissue transfer to the leg. Microsurgery 21(8):362–365
Louton RB, Harley RA, Hagerty RC (1989) A fasciocutaneous transposition flap for coverage of defects of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71(7):988–994
Ozkan O, Coskunfirat OK, Ozgentas HE (2004) The use of free anterolateral thigh flap for reconstructing soft tissue defects of the lower extremities. Ann Plast Surg 53(5):455–461
Yildirim S, Gideroglu K, Akoz T (2003) Anterolateral thigh flap: ideal free flap choice for lower extremity soft-tissue reconstruction. J Reconstr Microsurg 19(4):225–233
Bonanni F, Rhodes M, Lucke JF (1993) The futility of predictive scoring of mangled lower extremities. J Trauma 34(1):99–104
Bosse MJ, MacKenzie EJ, Kellam JF et al (2002) An analysis of outcomes of reconstruction or amputation after leg-threatening injuries. N Engl J Med 347(24):1924–1931
Perttunen JR, Nieminen H, Tukiainen E, Kuokkanen H, Asko-Seljavaara S, Komi PV (2000) Asymmetry of gait after free flap reconstruction of severe tibial fractures with extensive soft-tissue damage. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 34(3):237–243
Archer KR, Castillo RC, Mackenzie EJ, Bosse MJ (2006) Physical disability after severe lower-extremity injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 87(8):1153–1155
McCarthy ML, MacKenzie EJ, Edwin D, Bosse MJ, Castillo RC, Starr A (2003) Psychological distress associated with severe lower-limb injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A(9):1689–1697
Conflict of interest
Dr. Sen has the following consulting and disclosures a consultant for Stryker Orthopedics and has consulted for Smith and Nephew as well. He has also recently received research funding from Synthes USA. However, regarding this paper, he has no conflicts with this paper.
Ethical standards
For this type of article formal consent from an ethics committee is not required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aho, J.M., Sen, M.K. & Saint-Cyr, M. Free and pedicle flaps in lower extremity trauma. Eur J Plast Surg 38, 171–182 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-014-1056-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-014-1056-z