Abstract
Purpose
Minnelide is an experimental antineoplastic agent that is currently the subject of a phase 1 clinical trial for the treatment of pancreatic and gastrointestinal malignancies. In this study, we documented two cases of reversible acute cerebellar toxicity (REACT) associated with Minnelide and compared its radiological manifestations with other cerebellotoxic agents.
Methods
Both patients had histories of progressive metastatic cancer and participated in a phase 1 clinical trial with Minnelide. They had an MRI examination including T2WI, FLAIR and SWI, axial and coronal DWI, and ADC map on admission and follow up.
Results
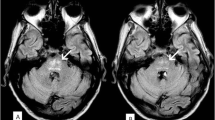
In each patient, the initial MRI demonstrated increased signal on FLAIR and restricted diffusion in the cerebellar cortex without involvement of deep cerebellar nuclei or supratentorial areas. The presenting symptoms and the majority of imaging findings resolved on follow up MRI.
Conclusion
To our knowledge, Minnelide has shown an uncommon radiologic pattern of isolated cerebellar cortical involvement compared to other causes of cerebellar toxicity. Since this is a new medication, physicians’ familiarity with the presenting symptoms and its temporal association with the imaging findings is important.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PRES:
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome
- REACT:
-
Reversible acute cerebellar toxicity
References
Chugh R, Sangwan V, Patil SP et al (2012) A preclinical evaluation of Minnelide as a therapeutic agent against pancreatic cancer. Sci Transl Med 4:156ra139
McKinney AM, Kieffer SA, Paylor RT, SantaCruz KS, Kendi A, Lucato L (2009) Acute toxic leukoencephalopathy: potential for reversibility clinically and on MRI with diffusion-weighted and FLAIR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 193:192–206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanipour Roshan, S., Spano, A.D., McKinney, A.M. et al. Potentially reversible acute cerebellar toxicity associated with Minnelide. Neuroradiology 59, 419–421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1809-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1809-z