Abstract
Introduction
Post-radiation injury of patients with brain arteriovenous malformations (AVM) include blood–brain barrier breakdown (BBBB), edema, and necrosis. Prevalence, clinical relevance, and response to treatment are poorly known. We present a series of consecutive brain AVM treated with stereotactic radiosurgery describing the appearance of radiation injury and clinical complications.
Methods
Consecutive patients with annual clinical and radiological follow-up (median length 63 months). Edema and BBBB were classified in four groups (minimal, perilesional, moderate, or severe), and noted together with necrosis. Clinical symptoms of interest were intracranial hypertension, new neurological deficits, new seizures, and brain hemorrhages.
Results
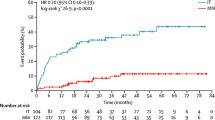
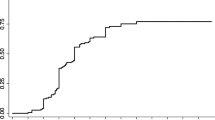
One hundred two cases, median age 34 years, 52 % male. Median irradiated volume 3.8 cc, dose to the margin of the nidus 18.5 Gy. Nineteen patients underwent a second radiosurgery. Only 42.2 % patients remained free from radiation injury. Edema was found in 43.1 %, blood–brain barrier breakdown in 20.6 %, necrosis in 6.9 %. Major injury (moderate or severe edema, moderate or severe BBBB, or necrosis) was found in 20 of 102 patients (19.6 %). AVM diameter >3 cm and second radiosurgery were independent predictors. Time to the worst imaging was 60 months. Patients with major radiation injury had a hazard ratio for appearance of focal deficits of 7.042 (p = 0.04), of intracranial hypertension 2.857 (p = 0.025), hemorrhage into occluded nidus 9.009 (p = 0.079), appearance of new seizures not significant.
Conclusions
Major radiation injury is frequent and increases the risk of neurological complications. Its late appearance implies that current follow-up protocols need to be extended in time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shin M, Maruyama K, Kurita H, Kawamoto S, Tago M, Terahara A, Morita A, Ueki K, Takakura K, Kirino T (2004) Analysis of nidus obliteration rates after gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations based on long-term follow-up data: the University of Tokyo experience. J Neurosurg 101:18–24
Schneider BF, Eberhard DA, Steiner LE (1997) Histopathology of arteriovenous malformations after gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 87:352–357
Huang PP, Kamiryo T, Nelson PK (2001) De novo aneurysm formation after stereotactic radiosurgery of a residual arteriovenous malformation: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1346–1348
Levegrün S, Hof H, Essig M, Schlegel W, Debus J (2004) Radiation-induced changes of brain tissue after radiosurgery in patients with arteriovenous malformations: correlation with dose distribution parameters. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:796–808
Parkhutik V, Lago A, Tembl JI, Vázquez JF, Aparici F, Mainar E, Vázquez V (2012) Postradiosurgery hemorrhage rates of arteriovenous malformations of the brain: influencing factors and evolution with time. Stroke 43:1247–1252
Lindquist C, Steiner L (1988) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of arteriovenous malformations. In: Lunsford LD (ed) Modern stereotactic neurosurgery. Hijhoff, Boston, pp 491–505
Atkinson RP, Awad IA, Batjer HH, Dowd CF, Furlan A, Giannotta SL, Gomez CR, Gress D, Hademenos G, Halbach V, Hemphill JC, Higashida RT, Hopkins LN, Horowitz MB, Johnston SC, Lawton MW, McDermott MW, Malek AM, Mohr JP, Qureshi AI, Riina H, Smith WS, Pile-Spellman J, Spetzler RF, Tomsick TA, Young WL (2001) Reporting terminology for brain arteriovenous malformation clinical and radiographic features for use in clinical trials. Stroke 32:1430–1442
Foroughi M, Kemeny AA, Lehecka M, Wons J, Kajdi L, Hatfield R, Marks S (2009) Operative intervention for delayed symptomatic radionecrotic masses developing following stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations—case analysis and literature review. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151:9–19
Ganz JC, Reda WA, Abdelkarim K (2010) Adverse radiation effects after gamma knife surgery in relation to dose and volume. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 152:803–815
Hayhurst C, Monsalves E, van Prooijen M, Cusimano M, Tsao M, Menard C, Kulkarni AV, Schwartz M, Zadeh G (2012) Pretreatment predictors of adverse radiation effects after radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:803–808
Herbert C, Moiseenko V, Mckenzie M, Redekop G, Hsu F, Gete E, Gill B, Lee R, Luchka K, Haw C, Lee A, Toyota B, Martin M (2012) Factors predictive of symptomatic radiation injury after linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery for intracerebral arteriovenous malformations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:872–877
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Maitz AH, Lunsford LD (1998) Analysis of neurological sequelae from radiosurgery of arteriovenous malformations: how location affects outcome. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 40:273–278
Buis DR, Meijer OW, van den Berg R, Lagerwaard FJ, Bot JC, Slotman BJ, Vandertop WP (2010) Clinical outcome after repeated radiosurgery for brain arteriovenous malformations. Radiother Oncol 95:250–256
Yamamoto M, Hara M, Ide M, Ono Y, Jimbo M, Saito I (1998) Radiation-related adverse effects observed on neuro-imaging several years after radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Surg Neurol 49:385–397
Izawa M, Hayashi M, Chernov M, Nakaya K, Ochiai T, Murata N, Takasu Y, Kubo O, Hori T, Takakura K (2005) Long-term complications after gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):34–37
van der Berg R, Buis DR, Lagerwaard FJ, Nijeholt GJ Là, Vandertop WP (2008) Extensive white matter changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain arteriovenous malformations: a prognostic sign for obliteration? Neurosurg 63:1064–1069
Nataf F, Ghossoub M, Missir O, Beuvon F, Varlet P, Merienne L, Schlienger M, Roux FX (2001) Parenchymal changes after radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Clinical and MRI data. Neurochirurgie 47:355–368
Parkhutik V, Lago A, Tembl JI, Sahuquillo P, Freire-Alvarez E (2010) Who controls arteriovenous malformations of the brain without surgery in Spain? Rev Neurol 50:128
Pan DH, Guo WY, Chung WY, Shiau CY, Chang YC, Wang LW (2000) Gamma knife radiosurgery as a single treatment modality for large cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):113–119
Skjøth-Rasmussen J, Roed H, Ohlhues L, Jespersen B, Juhler M (2010) Complications following linear accelerator based stereotactic radiation for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:542–547
Lindqvist M, Karlsson B, Guo WY, Kihlstrom L, Lippitz B, Yamamoto M (2000) Angiographic long-term follow-up data for arteriovenous malformations previously proven to be obliterated after gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurg 46:803–808
Shin M, Kawahara N, Maruyama K, Tago M, Ueki K, Kirino T (2005) Risk of hemorrhage from an arteriovenous malformation confirmed to have been obliterated on angiography after stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 102:842–846
Finitsis S, Anxionnat R, Bracard S, Lebedinsky A, Marchal C, Picard L (2005) Symptomatic radionecrosis after AVM stereotactic radiosurgery. Study of 16 consecutive patients. Interv Neuroradiol 11:25–33
Lynn M, Friedman WA (2007) Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of a radiosurgical complication: technical case report. Neurosurg 60:E579
Shuto T, Matsunaga S, Suenaga J (2011) Surgical treatment for late complications following gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 89:96–102
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Dr. Larrea from the Virgen del Consuelo Hospital (Valencia, Spain), who performed the radiosurgeries.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parkhutik, V., Lago, A., Aparici, F. et al. Late clinical and radiological complications of stereotactical radiosurgery of arteriovenous malformations of the brain. Neuroradiology 55, 405–412 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1115-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1115-8