Abstract
Introduction
Neuroimaging in seizures associated with nonketotic hyperglycemia (NKH) is considered normal. We report magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) abnormalities in four patients with NKH and seizures.
Methods
We prospectively evaluated clinical and radiological abnormalities in four patients with NKH during the period March 2004 to December 2005.
Results
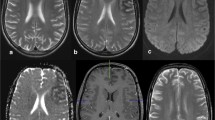
All patients presented with seizures, either simple or complex partial seizures or epilepsia partialis continua. Two of them had transient hemianopia. MRI showed subcortical T2 hypointensity in the occipital white matter and in or around the central sulcus (two patients each), T2 hyperintensity of the overlying cortex (two patients), focal overlying cortical enhancement (three patients) and bilateral striatal hyperintensity (one patient). Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) performed in three patients showed restricted diffusion. The ictal semiology and electroencephalographic (EEG) findings correlated with the MRI abnormalities. On clinical recovery, the subcortical T2 hypointensity and striatal hyperintensity reversed in all patients. The initial cortical change evolved to FLAIR hyperintensity suggestive of focal cortical gliosis. The radiological differential diagnosis considered initially included encephalitis, malignancy and hemorrhagic infarct rendering a diagnostic dilemma.
Conclusion
We identified subcortical T2 hypointensity rather than hyperintensity as a characteristic feature of seizures associated with NKH. Only very few similar reports exist in literature. Reversible bilateral striatal T2 hyperintensity in NKH has not been reported to the best of our knowledge.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schomer DL (1993) Focal status epilepticus and epilepsia partialis continua in adults and children. Epilepsia 34 [Suppl 1]:S29–S36
Senn P, Lovblad KO, Zutter D, et al (2003) Changes on diffusion-weighted MRI with focal motor status epilepticus: case report. Neuroradiology 45:246–249
Flacke S, Wullner U, Keller E, Hamzei F, Urbach H (2000) Reversible changes in echo planar perfusion and diffusion-weighted MRI in status epilepticus. Neuroradiology 42:92–95
Cokar O, Aydin B, Ozer F (2004) Non-ketotic hyperglycaemia presenting as epilepsia partialis continua. Seizure 13:264–269
Lammouchi T, Zoghlami F, Ben Slamia F, Grira M, Harzallah MS, Benammou S (2004) Epileptic seizures in non-ketotic hyperglycemia. Neurophysiol Clin 34:183–187
Seo DW, Na DG, Na DL, Moon SY, Hong SB (2003) Subcortical hypointensity in partial status epilepticus associated with nonketotic hyperglycemia. J Neuroimaging 13:259–263
Lavin PJ (2005) Hyperglycemic hemianopia: a reversible complication of non-ketotic hyperglycemia. Neurology 65:616–619
Wang CP, Hsieh PF, Chen CC, et al (2005) Hyperglycemia with occipital seizures: images and visual evoked potentials. Epilepsia 46:1140–1144
Maccario M, Messis CP, Vastola EF (1965) Focal seizures as a manifestation of hyperglycemia without ketoacidosis. A report of seven cases with review of the literature. Neurology 15:195–206
Cochin JP, Hannequin D, Delangre T, Guegan-Massardier E, Augustin P (1994) Continuous partial epilepsy disclosing diabetes mellitus. Rev Neurol (Paris) 150:239–241
Brazis PW, Lee AG, Graff-Radford N, Desai NP, Eggenberger ER (2000) Homonymous visual field defects in patients without corresponding structural lesions on neuroimaging. J Neuroophthalmol 20:92–96
Freedman KA, Polepalle S (2004) Transient homonymous hemianopia and positive visual phenomena in nonketotic hyperglycemic patients. Am J Ophthalmol 137:1122–1124
Ozer F, Mutlu A, Ozkayran T (2003) Reflex epilepsy and non-ketotic hyperglycemia. Epileptic Disord 5:165–168
Lee JH, Na DG, Choi KH, et al (2002) Subcortical low intensity on MR images of meningitis, viral encephalitis, and leptomeningeal metastasis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:535–542
Stricker T, Zuerrer M, Martin E, Boesch C (1991) MRI of two infants with tuberous sclerosis. Neuroradiology 33:175–177
Salamon N, Andres M, Chute DJ, et al (2006) Contralateral hemimicrencephaly and clinical-pathological correlations in children with hemimegalencephaly. Brain 129:352–365
Chabbert V, Ranjeva JP, Sevely A, Boetto S, Berry I, Manelfe C (1998) Diffusion- and magnetisation transfer-weighted MRI in childhood moya-moya. Neuroradiology 40:267–271
Chu K, Kang DW, Kim DE, Park SH, Roh JK (2002) Diffusion-weighted and gradient echo magnetic resonance findings of hemichorea-hemiballismus associated with diabetic hyperglycemia: a hyperviscosity syndrome? Arch Neurol 59:448–452
Placidi F, Floris R, Bozzao A, et al (2001) Ketotic hyperglycemia and epilepsia partialis continua. Neurology 57:534–537
Ida M, Mizunuma K, Hata Y, Tada S (1994) Subcortical low intensity in early cortical ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1387–1393
Benjelloun N, Renolleau S, Represa A, Ben-Ari Y, Charriaut-Marlangue C (1999) Inflammatory responses in the cerebral cortex after ischemia in the P7 neonatal rat. Stroke 30:1916–1924
Sabitha KM, Girija AS, Vargese KS (2001) Seizures in hyperglycemic patients. J Assoc Physicians India 49:723–726
Rangi PS, Partridge WJ, Newlands ES, Waldman AD (2005) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a possible late interaction between cytotoxic agents and general anaesthesia. Neuroradiology 47:586–590
Cotton F, Kamoun S, Rety-Jacob F, Tran-Minh VA, Nighoghossian N, Hermier M (2005) Acute hypertensive encephalopathy with widespread small-vessel disease at MRI in a diabetic patient: pathogenetic hypotheses. Neuroradiology 47:599–603
Finelli PF, DiMario FJ Jr (2003) Diagnostic approach in patients with symmetric imaging lesions of the deep gray nuclei. Neurologist 9:250–261
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghavendra, S., Ashalatha, R., Thomas, S.V. et al. Focal neuronal loss, reversible subcortical focal T2 hypointensity in seizures with a nonketotic hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Neuroradiology 49, 299–305 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0189-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0189-6