Abstract
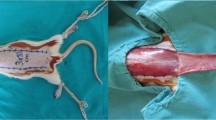
Thymoquinone (TQ) is a plant extract that has been shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, angiogenic, antimicrobial, and anticarcinogenic effects. The aim of this study is to research how the use of TQ affects flap viability. 42 rats were placed into 6 groups, with 7 rats in each. A 3 × 10 cm McFarlane flap model was used on the test animals. The sham group had used neither surgical nor TQ treatment. The control group had surgery but no treatment afterwards. The preoperative TQ group was given oral doses of 2 mg/kg. TQ for 10 days preoperatively with no treatment after the surgical procedure. The postoperative TQ group received oral doses of 2 mg/kg TQ for 10 days after the surgical process. The preoperative + postoperative (pre + postoperative) TQ group was given oral doses of 2 mg/kg TQ for 10 days both preoperatively and postoperatively. Finally, the dimethylsulfoxide group received 10 mg/kg dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) for 10 days both preoperatively and postoperatively. Ten days after surgery the findings were evaluated. The average rates of necrosis were found to be 29.7 % in the control group, 19.18 % in the preoperative TQ group, 13.05 % in the postoperative TQ group, 8.42 % in the pre + postoperative TQ group, and 29.03 % in the DMSO group. The experimental groups had better area measurement, histopathological, and electron microscopic results than the control group (All; p < 0.05). We believe that, because of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and angiogenic properties, thymoquinone is an agent that can prevent ischemia–reperfusion damage and, therefore, prevent necrosis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkharfy KM, Al-Daghri NM, Al-Attas OS, Alokail MS (2011) The protective effect of thymoquinone against sepsis syndrome morbidity and mortality in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 11:250–254
Arnold PB, Merritt W, Rodeheaver GT, Campbell CA, Morgan RF, Drake DB (2009) Effects of perivascular Botulinum Toxin-A application on vascular smooth muscle and flap viability in the rat. Ann Plast Surg 62(5):463–467
Aycan IO, Tufek A, Tokgoz O, Evliyaoğlu O, Fırat U, Kavak GO, Turgut H, Yüksel MU (2014) Thymoquinone treatment against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Int J Surg 12:213–218
Badary OA, Taha RA, Gamal El-Dın AM, Abdel-Wahab MH (2003) Thymoquinone is a potent superoxide anion scavenger. Drug ChemToxicol 26(2):87–98
Bai T, Yang Y, Wu YL, Jiang S, Lee JJ, Lian LH, Nan JX (2014) Thymoquinone alleviates thioacetamide induced hepatic fibrosis and inflammation by activating LKB1-AMPK signaling pathway in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 19:351–357
Barral SM, Araujo ID, Vidigal PV, Mayrink CA, Araujo AD, Costa PR (2011) Effects of sildenafil on the viability of random skin flaps. Acta Cir Bras 26(4):314–319
El-Dakhakhny M, Madi NJ, Lembert N, Ammon HPT (2002) Nigella sativa oil, nigellone and derived thymoquinone inhibit synthesis of 5-lipoxygenase products in polymorphonuclear leukocytes from rats. J Ethnopharmacol 81:161–164
Fujihara Y, Koyama H, Nishiyama N, Eguchi T, Takato T (2005) Gene transfer of bFGF to recipient bed improves survival of ischemic skin flap. Br J Plast Surg 58:511–517
Gali-Muhtasib H, Diab-Assaf M, Boltze C, Al-Hmaıra J, Hartig R, Roessner A, Schneıder-Stock R (2004) Thymoquinone extracted from black seed triggers apoptotic cell death in human colorectal cancer cells via a p53-dependent mechanism. Int J Oncol 25:857–866
Halawani E (2009) Antibacterial activity of thymoquinone and thymohydroquinone of Nigella sativaL. and their interaction with some antibiotics. Adv. Biol Res 3:148–152
Hart K, Baur D, Hodam J, Lesoon-Wood L, Parham M, Keith K, Vazquez R, Ager E, Pizarro J (2006) Short and long-term effects of sildenafil on skin flap survival in rats. Laryngoscope 116(4):522–528
Hosnuter M, Babuccu O, Kargi E, Altinyazar C (2003) Dual preconditioning: effects of pharmacological plus ischemic preconditioning on skin flap survival. Ann Plast Surg 50(4):398–402
Hosseinzadeh H, Parvardeh S (2004) Anticonvulsant effects of thymoquinone, the major constituent of Nigella sativa seeds, in mice. Phytomedicine 11(1):56–64
Kaseb AO, Chinnakannu K, Chen D, Sivanandam A, Tejwani S, Menon M, Dou QP, Reddy GP (2007) Androgen receptor and E2F-1 targeted thymoquinone therapy for hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res 67:7782–7788
Kayser MR (1999) Surgical Flaps. SRPS 9(2):1–65
Kerem H, Akdemir O, Ates U, Uyanikgil Y (2014) Demirel Sezer E, Bilkay U, Turgut M, Sozmen E, Songur E. The effect of melatonin on a dorsal skin flap model. J Invest Surg 27(2):57–64
Kerrigan CL (1983) Skin flap failure: pathophysiology. Plast Reconstr Surg 72(6):766–777
Kerrigan CL, Daniel RK (1983) Monitoring acute skin-flap failure. Plast Reconstr Surg 71:519–524
Kerrigan CL, Daniel RK (1984) Skin flap research: a candid view. Ann Plast Surg 13:383–387
Khiabani KT, Kerrigan CL (2002) Differing flow patterns between ischemically challenged flap skin and flap skeletal muscle: implications for salvageregiments. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:220–227
Kouidhi B, Zmantar T, Jrah H, Souiden Y, Chaieb K, Mahdouani K, Bakhrouf A (2011) Antibacterial and resistance-modifying activities of thymoquinone against oral pathogens. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 10:29–35
Mahgoub AA (2003) Thymoquinone protects against experimental colitis in rats. Toxicol Lett 143:133–143
Mohamed A, Shoker A, Bendjelloul F, Mare A, Alzrigh M, Benghuzzi H, Desin T (2003) Improvement of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) by thymoquinone; an oxidative stress inhibitor. Biomed Sci Instrum 39:440–445
Pang CY, Neligan PC, Forrest CR, Nakatsuka T, Sasaki GH (1986) Hemodynamics and vascular sensitivity to circulating norepinephrine in normal skin and delayed and acute random skin flaps in the pig. Plast Reconstr Surg 78(1):75–84
Qi W, Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Kim SJ, Manchester LC, Cabrera J, Sainz RM, Mayo JC (1999) Melatonin reduces lipid peroxidation and tissue edema in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci 44:2257–2262
Ragheb A, Attia A, Eldin WS, Elbarbry F, Gazarin S, Shoker A (2009) The protective effect of thymoquinone, an anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, against renal injury: a review. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 20(5):741–752
Reinisch JF (1974) The pathophysiology of skin flap circulation. The delay phenomenon. Plast Reconstr Surg 54(5):585–598
Roepke M, Diestel A, Bajbouj K, Walluscheck D, Schonfeld P, Roessner A, Schneıder-Stock R, Galı-Muhtasıb H (2007) Lack of p53 augments thymoquinone-induced apoptosis and caspase activation in human osteosarcoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther 6(2):160–169
Sayed MD (1980) Traditional medicine in health care. J Ethnopharmacol 2:19–22
Selcuk CT, Durgun M, Tekin R, Yolbas L, Bozkurt M, Akcay C, Alabalk U, Basarali MK (2013) Evaluation of the effect of thymoquinone treatment on wound healing in a rat burn model. J Burn Care Res 34(5):274–281
Shoieb AM, Elgayyar M, Dudrick PS, Bell JL, Tithof PK (2003) In vitro inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis in cancer cell lines by thymoquinone. Int J Oncol 22:107–113
Stein HJ, Fayman MS, Oosthuizen MM, Hinder RA (1989) Verapamil improves survival of rat hyperemic island skin flaps. Surgery 106(4):617–622
Tekeoglu I, Dogan A, Ediz L, Budancamanak M, Demirel A (2007) Effects of thymoquinone (volatile oil of black cumin) on rheumatoid arthritis in rat models. Phytother Res 21:895–897
Vedder NB (2006) Flap physiology. In: Mathes plastic surgery, 2nd edn, vol 1. Saunders Elsevier, Philadelphia:; p 483-506
Vourtsis SA, Spyriounis PK, Agrogiannis GD, Ionac M, Papalois AE (2012) VEGF application on rat skin flap survival. J Invest Surg 25(1):14–19
Wolfort SF, Angel MF, Knight KR, Amiss LR, Morgan RF (1992) The beneficial effect of dextran on anastomotic patency and flap survival in a strongly thrombogenic model. J Reconstr Microsurg 8:375–378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocak, O.F., Bozan, N., Oksuz, M. et al. The Effect of the Active Ingredient Thymoquinone on Flap Viability in Random Pattern Flaps in Rats. J Membrane Biol 249, 513–522 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-016-9893-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-016-9893-2