Abstract
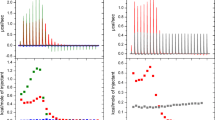
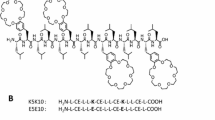
The biological activity of antimicrobial peptides is believed to be closely linked to their ability to perturb bacterial membranes. This makes it important to understand the basis of their membrane-binding properties. Here, we present a biophysical analysis of the interactions of the antimicrobial peptide Novicidin (Nc) with ether- and ester-linked C14 phospholipid vesicles below and above the lipid phase transition temperature (t p). These interactions are strongly dependent on whether the lipids contain ether or ester linkages. Nc is in random coil state in solution but undergoes a large increase in α-helicity in ether vesicles, and to a much smaller extent in ester vesicles, around the t p. This structure is lost at higher temperatures. Steady-state fluorescence and stopped-flow kinetics using fluorophore-labeled Nc reveal that Nc binds more strongly to ether vesicles than to ester vesicles below the t p, while there is no significant difference above the t p. This may reflect ether lipid interdigitation in the gel phase. Isothermal titration calorimetry reveals that partitioning of Nc into both lipids is exothermic and thus enthalpy driven. The higher enthalpy associated with binding to ether lipid may be linked to Nc’s higher propensity to form α-helical structure in this lipid. The large effect of the ether–ester interchange reveals that membrane–AMP interactions can be strongly modulated by charge-neutral head group changes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balakrishnan VS, Vad BS, Otzen DE (2013) Novicidin’s membrane permeabilizing activity is driven by membrane partitioning but not by helicity: a biophysical study of the impact of lipid charge and cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta 1834:996–1002
Bertelsen K, Vad B, Nielsen EH, Hansen SK, Skrydstrup T, Otzen DE, Vosegaard T, Nielsen NC (2011) Long-term-stable ether- lipid vs conventional ester- lipid bicelles in oriented solid-state nmr: altered structural information in studies of antimicrobial peptides. J Phys Chem B 115:1767–1774
Castanho MARB (2010) Membrane active peptides: methods and results on structure and function. IUL Biotechnology Series, San Diego
Dave PC, Billington E, Pan YL, Straus SK (2005) Interaction of alamethicin with ether-linked phospholipid bilayers: oriented circular dichroism, 31P solid-state NMR, and differential scanning calorimetry studies. Biophys J 89:2434–2442
Epand RM, Epand RF (2010) Biophysical analysis of membrane-targeting antimicrobial peptides: membrane properties and the design of peptides specifically targeting gram-negative bacteria. Centre for Agricultural Biosciences International, Oxford
Lakowicz JR (2004) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Matsuzaki K, Murase O, Fujii N, Miyajima K (1996) An antimicrobial peptide, magainin 2, induced rapid flip-flop of phospholipids coupled with pore formation and peptide translocation. Biochemistry 35:11361–11368
Mayer L, Hope M, Cullis P (1986) Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta 858:161–168
Mouritsen OG (2005) Life–as a matter of fat: the emerging science of lipidomics. Springer, Hidelberg
Mukherjee S, Chattopadhyay A (2005) Influence of ester and ether linkage in phospholipids on the environment and dynamics of the membrane interface: a wavelength-selective fluorescence approach. Langmuir 21:287–293
Nielsen SB, Otzen DE (2010) Impact of the antimicrobial peptide novicidin on membrane structure and integrity. J Colloid Interface Sci 345:248–256
O’Leary WM, Wilkinson S (1988) Microbial lipids. Academic Press, London, pp 117–202
Plasencia I, Cruz A, Casals C, Perez-Gil J (2001) Superficial disposition of the N-terminal region of the surfactant protein SP-C and the absence of specific SP-B-SP-C interactions in phospholipid bilayers. Biochem J 359:651–659
Prenner EJ, Lewis RNAH, Kondejewski LH, Hodges RS, McElhaney RN (1999) Differential scanning calorimetric study of the effect of the antimicrobial peptide gramicidin S on the thermotropic phase behavior of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylglycerol lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1417:211–223
Ratledge C, Wilkinson SG (eds) (1988) An overview of microbial lipids. In: Microbial lipids, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 3–22
Schibli DJ, Epand RF, Vogel HJ, Epand RM (2002) Tryptophan-rich antimicrobial peptides: comparative properties and membrane interactions. Biochem Cell Biol 80:667–677
Seto GWJ, Marwaha S, Kobewka DM, Lewis RNAH, Separovic F, McElhaney RN (2007) Interactions of the Australian tree frog antimicrobial peptides aurein 1.2, citropin 1.1 and maculatin 1.1 with lipid model membranes: differential scanning calorimetric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:2787–2800
Shai Y (1999) Mechanism of the binding, insertion and destabilization of phospholipid bilayer membranes by alpha-helical antimicrobial and cell nonselective membrane-lytic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1462:55–70
Skerlavaj B, Benincasa M, Risso A, Zanetti M, Gennaro R (1999) SMAP-29: a potent antibacterial and antifungal peptide from sheep leukocytes. FEBS Lett 463:58–62
Slater JL, Huang CH (1988) Interdigitated bilayer membranes. Progr Lipid Res 27:325–359
Smith R, Thomas DE, Atkins AR, Separovic F, Cornell BA (1990) Solid state 13C NMR studies of the effects of sodium ions on the gramicidin a ion channel. Biochim Biophys Acta 1026:161–166
Vad BS, Thomsen LA, Bertelsen K, Franzmann M, Pedersen JM, Nielsen SB, Vosegaard T, Valnickova Z, Skrydstrup TS, Enghild JJ, Wimmer R, Nielsen NC, Otzen DE (2010a) Divorcing folding from function: how acylation affects membrane-perturbing properties of an anti-microbial peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1804:806–820
Vad B, Thomsen LA, Bertelsen K, Franzmann M, Pedersen JM, Nielsen SB, Vosegaard T, Valnickova Z, Skrydstrup T, Enghild JJ (2010b) Divorcing folding from function: how acylation affects the membrane-perturbing properties of an antimicrobial peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1804:806–820
Vad BS, Bertelsen K, Johansen CH, Pedersen JM, Skrydstrup T, Nielsen NC, Otzen DE (2010c) Pardaxin permeabilizes vesicles more efficiently by pore formation than by disruption. Biophys J 98:576
Wang G (2010) Antimicrobial peptides: discovery design and novel therapeutic strategies. Centre for Agricultural Biosciences International, Oxford
White SH, Wimley WC (1999) Membrane protein folding and stability: physical principles. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 28:319–365
Wilkinson SG (1988) Gram-negative bacteria. In: Ratledge C, Wilkinson SG (eds) Microbial Lipids, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 299–488
Zhu WL, Lan H, Park IS, Kim JI, Jin HZ, Hahm KS, Shin SY (2006) Design and mechanism of action of a novel bacteria-selective antimicrobial peptide from the cell-penetrating peptide Pep-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349:769–774
Zhu WL, Nan YH, Hahm K, Shin SY (2007) Cell selectivity of an antimicrobial peptide melittin diastereomer with D-amino acid in the leucine zipper sequence. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:1090–1094
Acknowledgments
Brian S. Vad and Daniel E. Otzen are supported by the Danish Research Foundation (in SPIN). Vijay S. Balakrishnan is supported by the Danish Research Training Council and Novozymes A/S. We are very grateful to Anne Søndergaard and Jan Skov Pedersen for deconvoluting CD spectra using the programme WLSQ_CD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vad, B.S., Balakrishnan, V.S., Nielsen, S.B. et al. Phospholipid Ether Linkages Significantly Modulate the Membrane Affinity of the Antimicrobial Peptide Novicidin. J Membrane Biol 248, 487–496 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9792-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-015-9792-y