Abstract
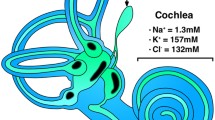
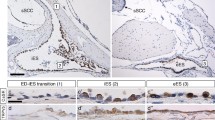
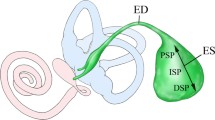
Intravenous application of catecholamines produces a depression in the endolymphatic sac direct current potential (ESP) and increases endolymphatic pressure via the β-adrenergic receptor (AR) in guinea pigs, suggesting that catecholamines play a role in the endolymphatic system. However, the localization of ARs in the endolymphatic sac (ES) is still undetermined. The presence of ARs in the rat ES was investigated by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction using laser capture microdissection (LCM) and immunohistochemical analysis. Expression of α1A-, α1B-, α2A-, α2B-, β1-, β2- and β3-ARs was observed in LCM samples of ES epithelia. Immunohistochemical analysis using specific antibodies showed immunofluorescence of β2- and β3-ARs in epithelial cells of the ES intermediate portion, and no specific staining results were obtained for α1-, α2A-, α2B- and β1-ARs. The presence of β2-AR with no clear immunostaining of β1-AR in ES epithelial cells is in accordance with previous electrophysiological and pharmacological results, which suggests that β2-AR mediates the action of catecholamines on the ESP. The presence of β3-AR in the ES epithelial cells and its absence in the stria vascularis implies that β3-AR plays a specific role in the ES.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama K, Miyashita T, Matsubara A, Mori T, Inamoto R, Nishiyama A, Mori N (2008a) A new approach for selective rat endolymphatic sac epithelium collection to obtain pure specific RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:611–614
Akiyama K, Miyashita T, Mori T, Inamoto R, Mori N (2008b) Expression of thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl cotransporter in the rat endolymphatic sac. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 371:649–653
Coman OA, Paunescu H, Ghita I, Coman L, Badararu A, Fulga I (2009) Beta 3 adrenergic receptors: molecular, histological, functional and pharmacological approaches. Rom J Morphol Embryol 50:169–179
Couloigner V, Teixeira M, Sterkers O, Rask-Andersen H, Ferrary E (2004) The endolymphatic sac: its roles in the inner ear [in French]. Med Sci (Paris) 20:304–310
Dahlmann A, von During M (1995) The endolymphatic duct and sac of the rat: a histological, ultrastructural, and immunocytochemical investigation. Cell Tissue Res 282:277–289
Emorine LJ, Marullo S, Briend-Sutren MM, Patey G, Tate K, Delavier-Klutchko C, Strosberg AD (1989) Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science 245:1118–1121
Fauser C, Schimanski S, Wangemann P (2004) Localization of beta1-adrenergic receptors in the cochlea and the vestibular labyrinth. J Membr Biol 201:25–32
Gauthier C, Rozec B, Manoury B, Balligand JL (2011) Beta-3 adrenoceptors as new therapeutic targets for cardiovascular pathologies. Curr Heart Fail Rep 8:184–192
Guild S (1927) Observations upon the structure and normal contents of the ductus and saccus endolymphaticus in the guinea-pig (Cavia cobaya). Am J Anat 39:1–56
Hoshikawa H, Furuta H, Mori N, Sakai S (1994) Absorption activity and barrier properties in the endolymphatic sac. Ultrastructural and morphometric analysis. Acta Otolaryngol 114:40–47
Inamoto R, Miyashita T, Akiyama K, Mori T, Mori N (2009) Endolymphatic sac is involved in the regulation of hydrostatic pressure of cochlear endolymph. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R1610–R1614
Kimura RS (1967) Experimental blockage of the endolymphatic duct and sac and its effect on the inner ear of the guinea pig. A study on endolymphatic hydrops. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 76:664–687
Lo WW, Daniels DL, Chakeres DW, Linthicum FH Jr, Ulmer JL, Mark LP, Swartz JD (1997) The endolymphatic duct and sac. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:881–887
Matsubara A, Miyashita T, Mori T, Akiyama K, Inamoto R, Mori N (2012) The mRNA of claudins is expressed in the endolymphatic sac epithelia. Auris Nasus Larynx 39:361–364
Miyashita T, Tatsumi H, Hayakawa K, Mori N, Sokabe M (2007) Large Na+ influx and high Na+, K+-ATPase activity in mitochondria-rich epithelial cells of the inner ear endolymphatic sac. Pflugers Arch 453:905–913
Mori N, Uozumi N (1991) Evidence that beta 2-receptors mediate action of catecholamines on endolymphatic sac DC potential. Am J Physiol 260:R911–R915
Mori N, Uozumi N, Sakai S (1990) Catecholamines depress endolymphatic sac direct current potential in guinea pigs. Am J Physiol 259:R921–R924
Myslivecek J, Novakova M, Palkovits M, Krizanova O, Kvetnansky R (2006) Distribution of mRNA and binding sites of adrenoceptors and muscarinic receptors in the rat heart. Life Sci 79:112–120
Sakikawa Y, Wall C 3rd, Kimura RS (1999) Vestibular responses of normal and hydropic ears of the guinea pig to middle ear pressure application. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:271–276
Takumida M, Harada Y, Bagger-Sjoback D, Rask-Andersen H (1991) Modulation of the endolymphatic sac function. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 481:129–134
Tonndorf J (1976) Endolymphatic hydrops: mechanical causes of hearing loss. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 212:293–299
Wangemann P, Liu J, Shimozono M, Scofield MA (1999) Beta1-adrenergic receptors but not beta2-adrenergic or vasopressin receptors regulate K+ secretion in vestibular dark cells of the inner ear. J Membr Biol 170:67–77
Wangemann P, Liu J, Shimozono M, Schimanski S, Scofield MA (2000) K+ secretion in strial marginal cells is stimulated via beta1-adrenergic receptors but not via beta2-adrenergic or vasopressin receptors. J Membr Biol 175:191–202
Zhang Y, Kolli T, Hivley R, Jaber L, Zhao FI, Yan J, Herness S (2010) Characterization of the expression pattern of adrenergic receptors in rat taste buds. Neuroscience 169:1421–1437
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-aid for Scientific Research (22591883 to N.M.). The authors thank Ms. Y. Iwakura for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsubara, A., Miyashita, T., Inamoto, R. et al. Presence of Adrenergic Receptors in Rat Endolymphatic Sac Epithelial Cells. J Membrane Biol 246, 109–114 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9508-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-012-9508-5