Abstract
Purpose
Tacrolimus is a commonly used immunosuppressant in solid organ transplantation recipients, but it is characterized by a narrow therapeutic range and large inter-individual variability. The purpose of this study was to establish a population pharmacokinetic (PK) model of tacrolimus and evaluate the influence of clinical covariates, including the genetic polymorphisms of the cytochrome P450 3A5 gene (CYP3A5) and gene encoding P-glycoprotein (ABCB1), on the PK parameters in adult Korean kidney transplant recipients.
Methods
Clinical data were collected retrospectively for 400 days after the initiation of a tacrolimus-based immunosuppression therapy. Data from 2,788 trough blood samples obtained from 80 subjects were used to perform a population PK analysis with a nonlinear mixed-effect model (NONMEM).
Results
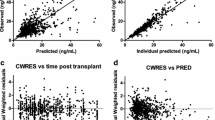
The estimated population mean values of clearance (CL/F) and volume of distribution (V/F) were 22.9 L/h and 716 L, respectively, and the k a was fixed to 4.5 h-1. The CYP3A5 genotype, hematocrit level, and post-operative days were identified as the main covariates that influence CL/F, and body weight was found to have a significant effect on V/F. Other covariates, including ABCB1 genotype, corticosteroid dosage, sex, and other clinical data, did not contribute to the pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus.
Conclusions
This tacrolimus population PK model will be a valuable tool in developing rational guidelines and provides a basis for individualized therapy after kidney transplantation in clinical settings of Korea.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jusko WJ, Piekoszewski W, Klintmalm GB, Shaefer MS, Hebert MF, Piergies AA, Lee CC, Schechter P, Mekki QA (1995) Pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in liver transplant patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 57(3):281–290
Venkataramanan R, Swaminathan A, Prasad T, Jain A, Zuckerman S, Warty V, McMichael J, Lever J, Burckart G, Starzl T (1995) Clinical pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus. Clin Pharmacokinet 29(6):404–430
Kershner RP, Fitzsimmons WE (1996) Relationship of FK506 whole blood concentrations and efficacy and toxicity after liver and kidney transplantation. Transplantation 62(7):920–926
Scott LJ, McKeage K, Keam SJ, Plosker GL (2003) Tacrolimus - A further update of its use in the management of organ transplantation. Drugs 63(12):1247–1297
Staatz CE, Tett SE (2004) Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tacrolimus in solid organ transplantation. Clin Pharmacokinet 43(10):623–653
Hesselink DA, van Gelder T, van Schaik RH (2005) The pharmacogenetics of calcineurin inhibitors: one step closer toward individualized immunosuppression? Pharmacogenomics 6(4):323–337
Koch I, Weil R, Wolbold R, Brockmoller J, Hustert E, Burk O, Nuessler A, Neuhaus P, Eichelbaum M, Zanger U, Wojnowski L (2002) Interindividual variability and tissue-specificity in the expression of cytochrome P450 3A mRNA. Drug Metab Dispos 30(10):1108–1114
Chowbay B, Cumaraswamy S, Cheung YB, Zhou Q, Lee EJ (2003) Genetic polymorphisms in MDR1 and CYP3A4 genes in Asians and the influence of MDR1 haplotypes on cyclosporin disposition in heart transplant recipients. Pharmacogenetics 13(2):89–95
Hustert E, Haberl M, Burk O, Wolbold R, He YQ, Klein K, Nuessler AC, Neuhaus P, Klattig J, Eiselt R, Koch I, Zibat A, Brockmoller J, Halpert JR, Zanger UM, Wojnowski L (2001) The genetic determinants of the CYP3A5 polymorphism. Pharmacogenetics 11(9):773–779
Lamba JK, Lin YS, Schuetz EG, Thummel KE (2002) Genetic contribution to variable human CYP3A-mediated metabolism. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54(10):1271–1294
Kuehl P, Zhang J, Lin Y, Lamba J, Assem M, Schuetz J, Watkins PB, Daly A, Wrighton SA, Hall SD, Maurel P, Relling M, Brimer C, Yasuda K, Venkataramanan R, Strom S, Thummel K, Boguski MS, Schuetz E (2001) Sequence diversity in CYP3A promoters and characterization of the genetic basis of polymorphic CYP3A5 expression. Nat Genet 27(4):383–391
Goto M, Masuda S, Kiuchi T, Ogura Y, Oike F, Okuda M, Tanaka K, Inui K (2004) CYP3A5*1-carrying graft liver reduces the concentration/oral dose ratio of tacrolimus in recipients of living-donor liver transplantation. Pharmacogenetics 14(7):471–478
Haufroid V, Mourad M, Van Kerckhove V, Wawrzyniak J, De Meyer M, Eddour DC, Malaise J, Lison D, Squifflet JP, Wallemacq P (2004) The effect of CYP3A5 and MDR1 (ABCB1) polymorphisms on cyclosporine and tacrolimus dose requirements and trough blood levels in stable renal transplant patients. Pharmacogenetics 14(3):147–154
Mourad M, Wallemacq P, De Meyer M, Brandt D, Van Kerkhove V, Malaise J, Chaib Eddour D, Lison D, Haufroid V (2006) The influence of genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 3A5 and ABCB1 on starting dose- and weight-standardized tacrolimus trough concentrations after kidney transplantation in relation to renal function. Clin Chem Lab Med 44(10):1192–1198
Thervet E, Anglicheau D, King B, Schlageter MH, Cassinat B, Beaune P, Legendre C, Daly AK (2003) Impact of cytochrome p450 3A5 genetic polymorphism on tacrolimus doses and concentration-to-dose ratio in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 76(8):1233–1235
Roy JN, Barama A, Poirier C, Vinet B, Roger M (2006) Cyp3A4, Cyp3A5, and MDR-1 genetic influences on tacrolimus pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients. Pharmacogenet Genomics 16(9):659–665
Hesselink DA, van Schaik RH, van Agteren M, de Fijter JW, Hartmann A, Zeier M, Budde K, Kuypers DR, Pisarski P, Le Meur Y, Mamelok RD, van Gelder T (2008) CYP3A5 genotype is not associated with a higher risk of acute rejection in tacrolimus-treated renal transplant recipients. Pharmacogenet Genomics 18(4):339–348
MacPhee IA, Fredericks S, Tai T, Syrris P, Carter ND, Johnston A, Goldberg L, Holt DW (2004) The influence of pharmacogenetics on the time to achieve target tacrolimus concentrations after kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 4(6):914–919
Marzolini C, Paus E, Buclin T, Kim RB (2004) Polymorphisms in human MDR1 (P-glycoprotein): Recent advances and clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacol Ther 75(1):13–33
Haufroid V, Wallemacq P, VanKerckhove V, Elens L, De Meyer M, Eddour DC, Malaise J, Lison D, Mourad M (2006) CYP3A5 and ABCB1 polymorphisms and tacrolimus pharmacokinetics in renal transplant candidates: guidelines from an experimental study. Am J Transplant 6(11):2706–2713
Hesselink DA, van Schaik RH, van der Heiden IP, van der Werf M, Gregoor PJ, Lindemans J, Weimar W, van Gelder T (2003) Genetic polymorphisms of the CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and MDR-1 genes and pharmacokinetics of the calcineurin inhibitors cyclosporine and tacrolimus. Clin Pharmacol Ther 74(3):245–254
Mai I, Perloff ES, Bauer S, Goldammer M, Johne A, Filler G, Budde K, Roots I (2004) MDR1 haplotypes derived from exons 21 and 26 do not affect the steady-state pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in renal transplant patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 58(5):548–553
Park SY, Kang YS, Jeong MS, Yoon HK, Han KO (2008) Frequencies of CYP3A5 genotypes and haplotypes in a Korean population. J Clin Pharm Ther 33(1):61–65
Kim YO, Kim MK, Woo YJ, Lee MC, Kim JH, Park KW, Kim EY, Roh YI, Kim CJ (2006) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the multidrug resistance 1 gene in Korean epileptics. Seizure 15(1):67–72
Yi SY, Hong KS, Lim HS, Chung JY, Oh DS, Kim JR, Jung HR, Cho JY, Yu KS, Jang IJ, Shin SG (2004) A variant 2677A allele of the MDR1 gene affects fexofenadine disposition. Clin Pharmacol Ther 76(5):418–427
Antignac M, Barrou B, Farinotti R, Lechat P, Urien S (2007) Population pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of tacrolimus in kidney transplant patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 64(6):750–757
Antignac M, Hulot JS, Boleslawski E, Hannoun L, Touitou Y, Farinotti R, Lechat P, Urien S (2005) Population pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in full liver transplant patients: modelling of the post-operative clearance. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 61(5–6):409–416
Fukatsu S, Yano I, Igarashi T, Hashida T, Takayanagi K, Saito H, Uemoto S, Kiuchi T, Tanaka K, Inui K (2001) Population pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in adult recipients receiving living-donor liver transplantation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 57(6–7):479–484
Beysens AJ, Wijnen RM, Beuman GH, van der Heyden J, Kootstra G, van As H (1991) FK 506: monitoring in plasma or in whole blood? Transplant Proc 23(6):2745–2747
Li D, Lu W, Zhu JY, Gao J, Lou YQ, Zhang GL (2007) Population pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus and CYP3A5, MDR1 and IL-10 polymorphisms in adult liver transplant patients. J Clin Pharm Ther 32(5):505–515
Sam WJ, Tham LS, Holmes MJ, Aw M, Quak SH, Lee KH, Lim SG, Prabhakaran K, Chan SY, Ho PC (2006) Population pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in whole blood and plasma in asian liver transplant patients. Clin Pharmacokinet 45(1):59–75
Staatz CE, Willis C, Taylor PJ, Lynch SV, Tett SE (2003) Toward better outcomes with tacrolimus therapy: population pharmacokinetics and individualized dosage prediction in adult liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 9(2):130–137
Staatz CE, Willis C, Taylor PJ, Tett SE (2002) Population pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in adult kidney transplant recipients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 72(6):660–669
Benkali K, Premaud A, Picard N, Rerolle JP, Toupance O, Hoizey G, Turcant A, Villemain F, Le Meur Y, Marquet P, Rousseau A (2009) Tacrolimus population pharmacokinetic-pharmacogenetic analysis and Bayesian estimation in renal transplant recipients. Clin Pharmacokinet 48(12):805–816
McCune JS, Hawke RL, LeCluyse EL, Gillenwater HH, Hamilton G, Ritchie J, Lindley C (2000) In vivo and in vitro induction of human cytochrome P4503A4 by dexamethasone. Clin Pharmacol Ther 68(4):356–366
Kagaya H, Miura M, Satoh S, Inoue K, Saito M, Inoue T, Habuchi T, Suzuki T (2008) No pharmacokinetic interactions between mycophenolic acid and tacrolimus in renal transplant recipients. J Clin Pharm Ther 33(2):193–201
Jorgensen K, Povlsen J, Madsen S, Madsen M, Hansen H, Pedersen A, Heinsvig EM, Poulsen J (2002) C2 (2-h) levels are not superior to trough levels as estimates of the area under the curve in tacrolimus-treated renal-transplant patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17(8):1487–1490
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No.2011-0000354).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nayoung Han and Hwi-yeol Yun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, N., Yun, Hy., Hong, Jy. et al. Prediction of the tacrolimus population pharmacokinetic parameters according to CYP3A5 genotype and clinical factors using NONMEM in adult kidney transplant recipients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69, 53–63 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-012-1296-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-012-1296-4