Abstract
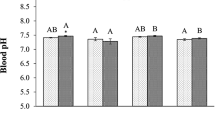
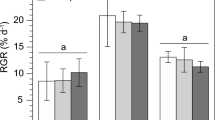
Nitric oxide (NO) is a non-traditional regulator of the growth of plants and phytoplankton. Here, the growth of five marine phytoplankton species, Platymonas helgolandica var. tsingtaoensis, Platymonas subcordiformis, Skeletonema costatum, Gymnodinium sp., and Prorocentrum donghaiense, was monitored, and carbonate system parameters in the culture media were determined after adding different concentrations of NO and sodium nitroprusside (SNP, NO donor) solutions. The two dietary algae (P. helgolandica var. tsingtaoensis and P. subcordiformis) and three red tide algae (S. costatum, Gymnodinium sp., and P. donghaiense) showed different responses to the same NO concentration. The red tide algae were more sensitive to exogenous NO than the dietary algae. NO with a concentration of 1.4 × 10−6 mol L−1 had the optimal stimulatory effect on the growth of the microalgae and increased the cell density by 9.8–38.3%. SNP solution with a concentration of 100 μmol L−1 inhibited the growth of the two dietary algae, and the cell density decreased by 38.8–84.3%. The addition of 10 μmol L−1 SNP solution to the three red tide algae decreased the cell density by 95.3–99.9%. Low concentrations of SNP (0.1 μmol L−1 for the two dietary algae and 0.01 μmol L−1 for the red tide algae) slightly promoted the growth of microalgae. High concentrations of NO (100 μmol L−1 SNP) inhibited CO2 assimilation, whereas low concentrations of NO (0.01–1.0 μmol L−1 SNP) promoted CO2 assimilation, indicating that NO participates in the regulation of photosynthesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets of the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anifowose AJ, Sakugawa H (2017) Determination of daytime flux of nitric oxide Radical (NO) at an inland sea-atmospheric boundary in Japan. J Aquat Pollut Toxicol 1:1–6. https://doi.org/10.21767/2581-804X.100010
Beligni MV, Lamattina L (1999a) Nitric oxide protects against cellular damage produced by methylviologen herbicides in potato plants. Nitric Oxide 3:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1006/niox.1999.0222
Beligni MV, Lamattina L (1999b) Is nitric oxide toxic or protective? Trends Plant Sci 4:299–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(99)01451-X
Cai WJ, Wang YC (1998) The chemistry, fluxes, and sources of carbon dioxide in the estuarine waters of the Satilla and Altamaha Rivers, Georgia. Limnol Oceanogr 43(4):657–668. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1998.43.4.0657
Caporn SJM (1989) The effects of oxides of nitrogen and carbon dioxide enrichment on photosynthesis and growth of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). New Phytol 111:473–481. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-813.1989.tb00710.x
Chen K, Feng H, Zhang M, Wang X (2003) Nitric oxide alleviated oxidative damage in the green algae Chlorella Pyrenoisoda caused by UV-B radiation. Folia Microbiol 48:389–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931372
Chen J, Zhen Y, Mi T, Yu Z (2009) Detection of Prorocentrum donghaiense using sandwich hybridization integrated with nuclease protection assay. Acta Oceanol Sin 28(2):121–126
Chi Z, O’Fallon JV, Chen S (2011) Bicarbonate produced from carbon capture for algae culture. Trends Biotechnol 29:537–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.06.006
Collos Y (1997) A physiological basis for estimating inorganic carbon release during photosynthesis by natural phytoplankton. Ecol Model 96(1–3):0–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(96)00070-1
Dickson AG (1990) Standard potential of the reaction: AgCl(s) + 1/2H2(g) = Ag(s) + HCl(aq), and and the standard acidity constant of the ion HSO4− in synthetic sea water from 273.15 to 318.15 K. J Chem Thermodyn 2:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9614(90)90074-Z
Dickson AG, Millero FJA (1987) Comparison of the equilibrium constants for the dissociation of carbonic acid in seawater media. Deep-Sea Res 34:1733–1743. https://doi.org/10.1016/0198-0149(87)90021-5
Domingos P, Prado AM, Wong A, Gehring C, Feijo JA (2015) Nitric oxide: a multitasked signaling gas in plants. Mol Plant 8:506–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.06.006
Feng WH, Liu CY, Yang GP, Li PF (2011) The effect of exogenous NO and copper onthe antioxidant systems of marine algae. Period Ocean Univ China 4:69–74
Floryszak-Wieczorek J, Milczarek G, Arasimowicz M, Ciszewski A (2006) Do nitric oxide donors mimic endogenous NO-relatedresponse in plants? Planta 224:1363–1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-006-0321-1
Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M (1999) Methods of seawater analysis. Wiley, New York, pp 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527613984
Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine animals. Plenum Press, New York, pp 26–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-8714-9_3
Gupta KJ, Igamberdiev AU, Manjunatha G, Segu S, Moran JF, Neelawarne B, Bauwe H, Kaiser WM (2011) The emerging roles of nitric oxide (NO) in plant mitochondria. Plant Sci 181:520–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.03.018
Hill AC, Bennett JH (1970) Inhibition of apparent photosynthesis by nitrogen oxides. Atmos Environ 4:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/0004-6981(70)90078-8
Hu YB, Liu CY, Yang GP, Zhang HH (2015) The response of the carbonate system to a green algal bloom during the post-bloom period in the southern Yellow Sea. Cont Shelf Res 94:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2014.12.006
Kim D, Yama G, Oda T (2006) Nitric oxide synthase-like enzyme mediated nitric oxide generation by harmful red tide phytoplankton, Chattonella marina. J Plankton Res 28:613–620. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbi145
Kim D, Kang YS, Yoon L, Yamaguchi K, Matsuoka K, Lee KW, Choi KS, Oda T (2008) Detection of nitric oxide (NO) in marine phytoplankters. J Biosci Bioeng 105:414–417. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.105.414
Kopyra M, Gwóźdź EA (2003) Nitric oxide stimulates seed germination and counteracts the inhibitory effect of heavy metals and salinity on root growth of Lupinus luteus. Plant Physiol Bioch 41:1011–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2003.09.003
Kumar A, Castellano I, Patti FP, Palumbo A, Buia MC (2015) Nitric oxide in marine photosynthetic organisms. Nitric Oxide 47:34–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2015.03.001
Lantoine F, Brunet A, Bedioui F, Devynck J, Devynck MA (1995) Direct measurement of nitric oxide production in platelets: relationship with cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. Biochem Bioph Res Co 215:842–848. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1995.2540
Lehner C, Kerschbaum HH, Lütz-Meindl U (2009) Nitric oxide suppresses growth and development in the unicellular green alga Micrasterias denticulata. J Plant Physiol 2:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2008.02.012
Leshem YY, Wills RH, Ku VV-V (1998) Evidence for the function of the free radical gas-nitric oxide (NO·)—as an endogenous maturation and senescence regulating factor in higher plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 36:825–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0981-9428(99)80020-5
Li L, Moore PK (2007) An overview of the biological significance of endogenous gases: new roles for old molecules. Biochem Soc T 35:1138–1141. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0351138
Li PF, Liu CY, Liu HH, Zhang Q, Wang L (2013) Protective function of nitric oxide on marine phytoplankton under abiotic stresses. Nitric Oxide 33(9):88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2013.06.007
Lipton SA, Chol YB, Pan ZH, Lel SZ, Chen H-SV, Sucher NJ, Losclzo J, Singel DJ, Stalmer JS (1993) A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature 364:626–632. https://doi.org/10.1038/364626a0
Liu CY, Li PF, Ren CY, Huang HW, Zhang ZB (2008) Effects of nitric oxide and copper on marine algae growth. J Harbin Inst Technol 40:812–817
Liu CY, Fang S, Zhao M, Bai XJ, Han Y, Li PF (2010) Fluorescence dynamic monitoring of nitric oxide release process following administration of sodium nitroprusside and its effect on the growth of microalga. Asian J Ecotoxicol 5:362–367
Liu CY, Gao CX, Zhang HB, Chen S, Deng P, Yue XA, Guo XY (2014a) Production of dimethylsulfide and acrylic acid from dimethylsulfoniopropionate during growth of three marine microalgae. Chin J Oceanol Limn 6:1270–1279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-015-4029-6
Liu CY, Kieber DJ, Yang GP, Xue C, Wang L-L, Liu HH (2014b) Evidence for the mutual effects of dimethyl sulfoniopropionate and nitric oxide during the growth of marine microalgae. Nitric Oxide 42:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2014.09.003
Lushchak VI (2011) Adaptive response to oxidative stress: bacteria, fungi, plants and animals. Comp Biochem Phys C 153(2):175–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.10.004
Mackerness SAH, John CF, Jordan B, Thomas B (2001) Early signaling components in ultraviolet-B responses: distinct roles for different reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide. FEBS Lett 489:237–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02103-2
Mallick N, Rai LC, Mohn FH, Soeder CJ (1999) Studies on nitric oxide (NO) formation by green alga Scenedesmus Obliquua and the diazotrophic cyanobacterium Anabaena doliolum. Chemosphere 39:1601–1610. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00058-2
Mallick N, Mohn FH, Soeder CJ (2000) Evidence sporting nitrite-dependent NO release by the green microalga Scenedesmus Obliquus. Plant Physiol 157:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(00)80133-9
Martens-Habbena W, Qin W, Horak REA, Urakawa H, Schauer AJ, Moffett JW, Armbrustb EV, Ingalls AE, Devol AH, Stahl DA (2015) The production of nitric oxide by marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea and inhibition of archaeal ammonia oxidation by a nitric oxide scavenger. Environ Microbiol 17:2261–2274. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12677
Mehrbach C, Culberson CH, Hawley JE, Pytkowicx RM (1973) Measurement of the apparent dissociation constants of carbonic acid in the seawater at atmospheric pressure. Limnol Oceanogr 18:897–907. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1973.18.6.0897
Misra AN, Vladkova R, Singh R, Misr M, Dobrikova AG, Apostolova EL (2014) Action and target sites of nitric oxide in chloroplasts. Nitric Oxide 39:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2014.04.003
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Breusegem FV (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. T Plant Sci 9:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009
Nagase H, Yoshihara K, Eguchi K, Okamoto Y, Murasaki S, Yamashita R, Hirata K, Miyamoto K (2001) Uptake pathway and continuous removal of nitric oxide from flue gas using microalgae. Biochem Eng J 7:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-703X(00)00122-4
Olasehinde EF, Takeda K, Sakugawa H (2009) Development of an analytical method for nitric oxide radical determination in natural waters. Anal Chem 81(16):6843–6850. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac901128y
Olasehinde EF, Takeda K, Sakugawa H (2010) Photochemical production and consumption mechanisms of nitric oxide in seawater. Environ Sci Technol 44:8403–8408. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101426x
Pierrot DE, Lewis E, Wallace DWR (2006) MS Excel program developed for CO2 system calculations. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, US Department of Energy. http://cdiac.ornl.gov/ftp/co2sys. Accessed 25 Nov 2019
Planchet E, Gupta KJ, Sonoda M, Kaiser WM (2005) Nitric oxide emission from tobacco leaves and cell suspensions: rate limiting factors and evidence for the involvement of mitochondrial electron transport. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 41(5):732–743. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313x.2005.02335.x
Qian HF, Chen W, Li JJ, Wang J, Zhou Z, Liu WP, Fu ZW (2009) The effect of exogenous nitric oxide on alleviating herbicide damage in Chlorella vulgaris. Aquatic Toxicol 92:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.02.008
Sakihama Y, Nakamura S, Yamasaki H (2002) Nitric oxide production mediated by nitrate reductase in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: an alternative NO production pathway in photosynthetic organism. Plant Cell Physiol 43:290–297. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcf034
Shi SY, Wang G, Wang YD, Zhang LG, Zhang LX (2005) Protective effect of nitric oxide against oxidative stress under ultraviolet-B radiation. Nitric Oxide 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2005.04.006
Singh AK, Sharma L, Mallick N (2004) Antioxidative role of nitric oxide on copper toxicity to a chlorophycean alga, Chlorella. Ecotox Environ Safe 59:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2003.10.009
Tang X, Chen J, Wang WH, Liu TW, Zhang J, Gao Y, Pei ZM, Zheng HL (2011) The changes of nitric oxide production during the growth of Microcystis aerugrinosa. Environ Pollut 159:3784–3792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.06.042
Tian Y, Yang GP, Liu CY, Li PF, Bange HW (2020) Photoproduction of nitric oxide in seawater. Ocean Sci 16:135–148. https://doi.org/10.5194/os-16-135-2020
Tischner R, Planchet E, Kaiser WM (2004) Mitochondrial electron transport as a source for nitric oxide in the unicellular green alga Chlorella sorokiniana. FEBS Lett 576:151–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2004.09.004
Uhida A, Jagendorf AT, Hibino T, Takabe T (2002) Effects of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide on both salt and heat stress tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 163:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00159-0
Wang J, Zhang Y, Li H, Cao J (2013a) Competitive interaction between diatom Skeletonema costatum and dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense in laboratory culture. J Plankton Res 35(2):367–378. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbs098
Wang X, Xu Y, Zhong Y, Jing B (2013b) P30: effects of nitric oxide on photosynthesis rate of phaeodactylum tricornutum. Nitric Oxide 31:S25–S26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2013.02.032
Wendehenne D, Pugin A, Klessig D, Durner J (2001) Nitric oxide: comparative synthesis and signaling in animal and plant cells T. Plant Sci 6(177):183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(01)01893-3
Wilhelm C, Büchel C, Fisahn J, Goss R, Jakob T, Laroche J, Lavaud J, Lohr M, Riebesell U, Stehfest K, Valentin K, Kroth PG (2006) The regulation of carbon and nutrient assimilation in diatoms is significantly different from green algae. Protist 2:91–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protis.2006.02.003
Wink DA, Mitchell JB (1998) Chemical biology of nitric oxide: insights into regulatory, cytotoxic and cytoprotective mechanisms of nitric oxide. Free Radical Biol Med 25:434–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00092-6
Xiao Y, Liu Y, Wang G (2012) Involvement of nitric oxide in the mechanism of biochemical alterations induced by simulated microgravity in Microcystis aeruginosa. Adv Space Res 49:850–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2011.11.003
Xing L, Zhang ZB, Liu CY, Wu ZZ, Lin C (2005) Amperometric detection of nitric oxide with microsensor in the medium of seawater and its applications. Sensors 5:537–545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s5120537
Yamasaki H (2000) Nitrite-dependent nitric oxide production pathway: implications for involvement of active nitrogen species in photoinhibition in vivo. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 355:1477–1488. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2000.0708
Zafiriou OC, McFarland M (1981) Nitric oxide from nitrite photolysis in the central equatorial Pacific. J Geophys Res 86:3173–3182. https://doi.org/10.1029/JC086iC04p03173
Zafiriou OC, True MB (1979) Nitrite photolysis in seawater by sunlight. Mar Chem 8:9–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(79)90029-X
Zhang ZB, Xing L, Jiang LQ, Wang YC, Ren CY, Cai WJ (2003) The electrochemical determination of nitric oxide in seawater media with microelectrodes. Sensors 3:304–313. https://doi.org/10.3390/s30800304
Zhang ZB, Lin C, Liu C, Xing L, Wu ZZ, Sun F (2005) Study on patterns and chemical features of NO effect on marine phytoplankton growth. Sci China 48(4):376–384. https://doi.org/10.1360/03yb0166
Zhang ZB, Liu CY, Wu ZZ, Xing L, Li PF (2006a) Detection of nitric oxide in culture media and studies on nitric oxide formation by marine microalgae. Med Sci Monitor 12:75–85
Zhang ZB, Wu ZZ, Liu CY, Xing L (2006b) The study on the effect of NO on the growth of Chaetoceros curvisetus. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 24:413–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842858
Zhang ZB, Xing L, Wu ZZ, Liu CY, Lin C, Liu LS (2006c) Discovery of nitric oxide in marine ecological system and the chemical characteristics of nitric oxide. Sci China 5:475–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-006-2017-6
Acknowledgements
This word was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41676065 and 40706040) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFA0601301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by ZM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by LP and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest for this submission, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Ethical approval
No animals were used in this study.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: R. Bi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, PF., Zhao, M., Liu, CY. et al. Effects of nitric oxide on the growth of marine microalgae and carbonate chemistry parameters. Mar Biol 169, 1 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-021-03988-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-021-03988-8