Abstract
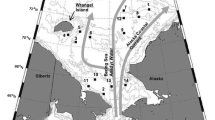
Sea ice algae can constitute an important carbon source for high-Antarctic euphausiids during winter. To quantify the importance of this ‘sympagic carbon’ during summer, the three most abundant Antarctic euphausiids, Euphausia superba, E. crystallorophias, and Thysanoessa macrura, collected off the Filchner Ice Shelf, were analyzed regarding their fatty acid (FA) and stable isotope compositions. Fingerprints of diatom- and dinoflagellate-associated FAs in the euphausiids indicated a mixed carbon source composition for all three species. Bulk and FA-specific carbon stable isotope compositions (δ13C) were used to quantify the contribution of sympagic carbon versus phytoplankton-produced carbon to the euphausiids’ carbon budget, suggesting a lower proportional contribution of sympagic carbon in E. superba (5–18%) compared to E. crystallorophias (16–36%) and T. macrura (15–36%). The latter two species probably received sympagic carbon through heterotrophic prey, a hitherto overlooked source of sympagic carbon for pelagic species. Euphausiids collected close to the surface indicated a higher importance of sympagic carbon to their carbon budget compared to individuals caught at greater depths. Our results imply that, in the southern Weddell Sea, ice algae play a significant, but possibly not critical role as a carbon source for the three euphausiids during summer. Their ability to utilize carbon of different origins implies a certain resilience to environmental change during summer. The winter period, however, remains the critical bottle neck of survival when Antarctic sea ice declines, because during this season of minimal pelagic productivity, ice algae standing stocks constitute the only dependable carbon source.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackley SF, Sullivan CW (1994) Physical controls on the development and characteristics of Antarctic sea ice biological communities—a review and synthesis. Deep Sea Res 41:1583–1604
Ackley SF, Buck KR, Taguchi S (1979) Standing crop of algae in the sea ice of the Weddell Sea region. Deep Sea Res 26:269–281
Ackman RG, Tocher CS, McLachlan J (1968) Marine phytoplankter fatty acids. J Fish Res Board Can 25:1603–1620
Arrigo KR (2014) Sea ice ecosystems. Annu Rev Mar Sci 6:439–467
Arrigo KR, van Dijken GL (2003) Phytoplankton dynamics within 37 Antarctic coastal polynya systems. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 108:3271
Arrigo KR, Robinson DH, Worthen DL, Dunbar RB, DiTullio GR, VanWoert M, Lizotte MP (1999) Phytoplankton community structure and the drawdown of nutrients and CO2 in the Southern Ocean. Science 283:365–367
Arrigo KR, van Dijken GL, Strong AL (2015) Environmental controls of marine productivity hot spots around Antarctica. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 120:5545–5565
Arts MT, Ackman RG, Holub BJ (2001) “Essential fatty acids” in aquatic ecosystems: a crucial link between diet and human health and evolution. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:122–137
Atkinson A, Siegel V, Pakhomov E, Rothery P (2004) Long-term decline in krill stock and increase in salps within the Southern Ocean. Nature 432:100
Atkinson A, Siegel V, Pakhomov EA, Rothery P, Loeb V, Ross RM, Quetin LB, Schmidt K, Fretwell P, Murphy EJ, Tarling GA (2008) Oceanic circumpolar habitats of Antarctic krill. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 362:1–23
Atkinson A, Siegel V, Pakhomov E, Jessopp M, Loeb V (2009) A re-appraisal of the total biomass and annual production of Antarctic krill. Deep Sea Res 56:727–740
Atkinson A, Hill SL, Pakhomov EA, Siegel V, Reiss CS, Loeb VJ, Steinberg DK et al (2019) Krill (Euphausia superba) distribution contracts southward during rapid regional warming. Nat Clim Change 9:90–91
Bartsch A (1989) Die Eisalgenflora des Weddelmeeres (Antarktis): Artenzusammensetzung und Biomasse sowie Ökophysiologie ausgewählter Arten = Sea ice algae of the Weddell Sea (Antarctica): species composition, biomass, and ecophysiology of selected species. Rep Polar Res 63:1–110
Beaugrand G, Luczak C, Edwards M (2009) Rapid biogeographical plankton shifts in the North Atlantic Ocean. Glob Change Biol 15:1790–1803
Bernard KS, Gunther LA, Mahaffey SH, Qualls KM, Sugla M, Saenz BT, Cossio AM, Walsh J, Reiss CS (2018) The contribution of ice algae to the winter energy budget of juvenile Antarctic krill in years with contrasting sea ice conditions. ICES J Mar Sci 76:206–216
Bottino NR (1974) The fatty acids of Antarctic phytoplankton and euphausiids. Fatty acid exchange among trophic levels of the Ross Sea. Mar Biol 27:197–204
Boysen-Ennen E, Piatkowski U (1988) Meso-and macrozooplankton communities in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Polar Biol 9:17–35
Boysen-Ennen E, Hagen W, Hubold G, Piatkowski U (1991) Zooplankton biomass in the ice-covered Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Mar Biol 111:227–235
Brierley AS, Fernandes PG, Brandon MA, Armstrong F, Millard NW, McPhail SD, Stevenson P, Pebody M, Perrett J, Squires M, Bone DG (2002) Antarctic krill under sea ice: elevated abundance in a narrow band just south of ice edge. Science 295:1890–1892
Brown M, Jeffrey S, Volkman J, Dunstan G (1997) Nutritional properties of microalgae for mariculture. Aquaculture 151:315–331
Budge SM, Springer AM, Iverson SJ, Sheffield G (2007) Fatty acid biomarkers reveal niche separation in an Arctic benthic food web. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 336:305–309
Budge SM, Wooller MJ, Springer AM, Iverson SJ, McRoy CP, Divoky GJ (2008) Tracing carbon flow in an arctic marine food web using fatty acid-stable isotope analysis. Oecologia 157:117–129
Budge SM, Wang SW, Hollmén TE, Wooller MJ (2011) Carbon isotopic fractionation in eider adipose tissue varies with fatty acid structure: implications for trophic studies. J Exp Biol 214:3790–3800
CCAMLR (2011) Scheme of international scientific observation: scientific observers manual. CCAMLR, Hobart
CCAMLR (2016) Krill fisheries: www.ccamlr.org/en/fisheries/krill-fisheries. Accessed Dec 2013
Clarke A (1980) The biochemical composition of krill, Euphausia superba Dana, from South Georgia. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 43:221–236
Comiso JC, Maynard NG, Smith WO Jr, Sullivan CW (1990) Satellite ocean color studies of Antarctic ice edges in summer and autumn. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 95:9481–9496
Core Team R (2015) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Cripps GC, Watkins JL, Hill HJ, Atkinson A (1999) Fatty acid content of Antarctic krill Euphausia superba at South Georgia related to regional populations and variations in diet. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 181:177–188
Dalsgaard J, John MS, Kattner G, Müller-Navarra D, Hagen W (2003) Fatty acid trophic markers in the pelagic marine environment. Adv Mar Biol 46:225–340
Daly KL (1990) Overwintering development, growth, and feeding of larval Euphausia superba in the Antarctic marginal ice zone. Limnol Oceanogr 35:1564–1576
Darelius E, Fer I, Nicholls KW (2016) Observed vulnerability of Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf to wind-driven inflow of warm deep water. Nat Commun 7:12300
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S (1978) Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:495–506
DeWitt HH, Hopkins TL (1977) Aspects of the diet of the Antarctic silverfish, Pleuragramma antarcticum. In: Llano Houston GA (ed) Adaptations within Antarctic ecosystems. Gulf Publ Co, Hoston, pp 557–568
Dieckmann G, Lange M, Ackley S, Jennings J Jr (1991) The nutrient status in sea ice of the Weddell Sea during winter: effects of sea ice texture and algae. Polar Biol 11:449–456
Donnelly J, Sutton TT, Torres JJ (2006) Distribution and abundance of micronekton and macrozooplankton in the NW Weddell Sea: relation to a spring ice-edge bloom. Polar Biol 29:280–293
Driscoll RM, Reiss CS, Hentschel BT (2015) Temperature-dependent growth of Thysanoessa macrura: inter-annual and spatial variability around Elephant Island, Antarctica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 529:49–61
El-Sayed SZ, Taguchi S (1981) Primary production and standing crop of phytoplankton along the ice-edge in the Weddell Sea. Deep Sea Res A Oceanogr Res Pap 28:1017–1032
Ericson JA, Hellessey N, Nichols PD, Kawaguchi S, Nicol S, Hoem N, Virtue P (2018) Seasonal and interannual variations in the fatty acid composition of adult Euphausia superba Dana, 1850 (Euphausiacea) samples derived from the Scotia Sea krill fishery. J Crust Biol 38:662–672
Fahrbach E, Rohardt G, Krause G (1992) The Antarctic coatal current in the southeastern Weddell Sea. Can J Fish Aquat 57:178–191
Falkowski PG, Barber RT, Smetacek V (1998) Biogeochemical controls and feedbacks on ocean primary production. Science 281:200–206
Falk-Petersen S, Sargent JR, Henderson J, Hegseth EN, Hop H, Okolodkov YB (1998) Lipids and fatty acids in ice algae and phytoplankton from the Marginal Ice Zone in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol 20:41–47
Falk-Petersen S, Sargent JR, Lønne OJ, Timofeev S (1999) Functional biodiversity of lipids in Antarctic zooplankton: Calanoides acutus, Calanus propinquus, Thysanoessa macrura and Euphausia crystallorophias. Polar Biol 21:37–47
Falk-Petersen S, Hagen W, Kattner G, Clarke A, Sargent J (2000) Lipids, trophic relationships, and biodiversity in Arctic and Antarctic krill. Can J Fish Aquat 57:178–191
Flores H, Atkinson A, Kawaguchi S, Krafft BA, Milinevsky G, Nicol S, Reiss C, Tarling GA, Werner R, Rebolledo EB, Cirelli V (2012a) Impact of climate change on Antarctic krill. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 458:1–19
Flores H, van Franeker JA, Siegel V, Haraldsson M, Strass V, Meesters EH, Bathmann U, Wolff WJ (2012b) The association of Antarctic krill Euphausia superba with the under-ice habitat. PLoS One 7:e31775
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Foldvik A, Gammelsrød T, Østerhus S, Fahrbach E, Rohardt G, Schröder M, Nicholls KW, Padman L, Woodgate RA (2004) Ice shelf water overflow and bottom water formation in the southern Weddell Sea. J Geophys Res 109:C02015
Foster TD, Carmack EC (1976) Frontal zone mixing and Antarctic Bottom Water formation in the southern Weddell Sea. Deep Sea Res Oceanogr Abstr 23:301–317
Fransson A, Chierici M, Yager PL, Smith WO (2011) Antarctic sea ice carbon dioxide system and controls. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 116:C12035
Frazer TK (1996) Stable isotope composition (δ13C and δ15N) of larval krill, Euphausia superba, and two of its potential food sources in winter. J Plankton Res 18:1413–1426
Fry B, Sherr EB (1984) δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Contrib Mar Sci 27:13–47
Garrison DL (1991) Antarctic sea ice biota. Am Zool 31:17–34
Garrison DL, Buck KR (1989) The biota of Antarctic pack ice in the Weddell Sea and Antarctic Peninsula regions. Polar Biol 10:211–219
Gigliotti JC, Davenport MP, Beamer SK, Tou JC, Jaczynski J (2011) Extraction and characterisation of lipids from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba). Food Chem 125:1028–1036
Godlewska M, Klusek Z (1987) Vertical distribution and diurnal migrations of krill-Euphausia superba Dana-from hydroacoustical observations, SIBEX, December 1983/January 1984. Polar Biol 8:17–22
Graeve M (1993) Umsatz und Verteilung von Lipiden in arktischen marinen Organismen unter besonderer Berücksichtigung unterer trophischer Stufen = Turnover and distribution of lipids in Arctic marine organisms with regard to lower trophic levels. Rep Polar Res 124:1–141
Graeve M, Kattner G, Hagen W (1994) Diet-induced changes in the fatty acid composition of Arctic herbivorous copepods: experimental evidence of trophic markers. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 182:97–110
Graeve M, Kattner G, Piepenburg D (1997) Lipids in Arctic benthos: does the fatty acid and alcohol composition reflect feeding and trophic interactions? Polar Biol 18:53–61
Hagen W, Kattner G (1998) Lipid metabolism of the Antarctic euphausiid Thysanoessa macrura and its ecological implications. Limnol Oceanogr 43:1894–1901
Hardge K, Peeken I, Neuhaus S, Lange BA, Stock A, Stoeck T, Weinisch L, Metfies K (2017) The importance of sea ice for exchange of habitat-specific protist communities in the Central Arctic Ocean. J Mar Syst 165:124–138
Hecky RE, Hesslein RH (1995) Contributions of benthic algae to lake food webs as revealed by stable isotope analysis. J N Am Benthol Soc 14:631–653
Hellmer HH, Kauker F, Timmermann R, Determann J, Rae J (2012) Twenty-first-century warming of a large Antarctic ice-shelf cavity by a redirected coastal current. Nature 485:225–228
Hellmer HH, Kauker F, Timmermann R, Hattermann T (2017) The fate of the southern Weddell Sea continental shelf in a warming climate. J Clim 30:4337–4350
Hopkins TL (1985) Food web of an Antarctic midwater ecosystem. Mar Biol 89:197–212
Hopkins TL, Torres JJ (1989) Midwater food web in the vicinity of a marginal ice zone in the western Weddell Sea. Deep Sea Res A Oceanogr Res Pap 36:543–560
Horner R (2017) Taxonomy of sea ice microalgae. In: Horner R (ed) Sea ice biota. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 147–157
Jia Z, Swadling KM, Meiners KM, Kawaguchi S, Virtue P (2016) The zooplankton food web under East Antarctic pack ice—a stable isotope study. Deep Sea Res II Top Stud Oceanogr 131:189–202
Ju SJ, Harvey HR (2004) Lipids as markers of nutritional condition and diet in the Antarctic krill Euphausia superba and Euphausia crystallorophias during austral winter. Deep Sea Res II Top Stud Oceanogr 51:2199–2214
Kalinowski J (1978) Vertical migration of krill in the region of South Georgia, February–March 1976. Pol Arch Hydrobiol 25:573–583
Kattner G, Hagen W (1998) Lipid metabolism of the Antarctic euphausiid Euphausia crystallorophias and its ecological implications. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 170:203–213
Kaufmann RS, Smith KL Jr, Baldwin RJ, Glatts RC, Robison BH, Reisenbichler KR (1995) Effects of seasonal pack ice on the distribution of macrozooplankton and micronekton in the northwestern Weddell Sea. Mar Biol 124:387–397
Kittel W, Stepnik R (1983) Distribution of Euphausia crystallorophias, E. frigida, E. triacantha and Thysanoessa macrura (Crustacea, Euphausiacea) in the southern Drake Passage and Bransfield Strait in February and March 1981. Pol Polar Res 4:7–19
Knust R, Schröder M (2014) The Expedition PS82 of the research vessel POLARSTERN to the southern Weddell Sea in 2013/2014. Rep Polar Res 680:1–155
Ko AR, Yang EJ, Kim MS, Ju SJ (2016) Trophodynamics of euphausiids in the Amundsen Sea during the austral summer by fatty acid and stable isotopic signatures. Deep Sea Res II Top Stud Oceanogr 123:78–85
Kohlbach D, Graeve M, Lange BA, David C, Peeken I, Flores H (2016) The importance of ice algae-produced carbon in the central Arctic Ocean ecosystem: food web relationships revealed by lipid and stable isotope analyses. Limnol Oceanogr 61:2027–2044
Kohlbach D, Lange BA, Schaafsma FL, David C, Vortkamp M, Graeve M, van Franeker JA, Krumpen T, Flores H (2017) Ice algae-produced carbon is critical for overwintering of Antarctic krill Euphausia superba. Front Mar Sci 4:310
Kohlbach D, Graeve M, Lange BA, David C, Schaafsma FL, van Franeker JA, Vortkamp M, Brandt A, Flores H (2018) Dependency of Antarctic zooplankton species on ice algae-produced carbon suggests a sea ice-driven pelagic ecosystem during winter. Glob Change Biol 24:4667–4681
Kohnen H (1982) Die Filchner-Schelfeis-Expedition 1980/1981 = The Filchner Ice-Shelf-Expedition. Rep Polar Res 1:1–50
Kühl S, Schneppenheim R (1986) Electrophoretic investigation of genetic variation in two krill species Euphausia superba and E. crystallorophias (Euphausiidae). Polar Biol 6:17–23
Lascara CM, Hofmann EE, Ross RM, Quetin LB (1999) Seasonal variability in the distribution of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, west of the Antarctic Peninsula. Deep Sea Res I Oceanogr Res Pap 46:951–984
Laws RM (1985) The ecology of the Southern Ocean. Am Sci 73:26–40
Lizotte MP (2001) The contributions of sea ice algae to Antarctic marine primary production. Am Zool 41:57–73
Loose B, Schlosser P, Perovich D, Ringelberg D, Ho DT, Takahashi T, Richter-Menge J, Reynolds CM, McGillis WR, Tison J-L (2010) Gas diffusion through columnar laboratory sea ice: implications for mixed-layer ventilation of CO2 in the seasonal ice zone. Tellus Ser B 63:23–29
Mackey AP, Atkinson A, Hill SL, Ward P, Cunningham NJ, Johnston NM, Murphy EJ (2012) Antarctic macrozooplankton of the southwest Atlantic sector and Bellingshausen Sea: baseline historical distributions (Discovery Investigations, 1928–1935) related to temperature and food, with projections for subsequent ocean warming. Deep Sea Res II Top Stud Oceanogr 59:130–146
Marr JWS (1962) The natural history and geography of the Antarctic krill (Euphasia superba Dana). Discov Rep. XXXII. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 33–464
Marschall HP (1988) The overwintering strategy of Antarctic krill under the pack-ice of the Weddell Sea. Polar Biol 9:129–135
McBride MM, Dalpadado P, Drinkwater KF, Godø OR, Hobday AJ, Hollowed AB, Kristiansen T, Murphy EJ, Ressler PH, Subbey S (2014) Krill, climate, and contrasting future scenarios for Arctic and Antarctic fisheries. ICES J Mar Sci 71:1934–1955
McConville MJ (2017) Chemical composition and biochemistry of sea ice microalgae. In: Horner RA (ed) Sea ice biota. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 105–129
Meiners K, Vancoppenolle M, Thanassekos S, Dieckmann GS, Thomas D, Tison JL, Arrigo KR, Garrison D, McMinn A, Lannuzel D (2012) Chlorophyll a in Antarctic sea ice from historical ice core data. Geophys Res Lett 39:L21602
Miller DGM, Hampton I (1989) Biology and ecology of the Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana): a review. BIOMASS Sci Ser 9:1–166
Minagawa M, Wada E (1984) Stepwise enrichment of δ15N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between δ15N and animal age. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1135–1140
Mintenbeck K, Brey T, Jacob U, Knust R, Struck U (2008) How to account for the lipid effect on carbon stable-isotope ratio (δ13C): sample treatment effects and model bias. J Fish Biol 72:815–830
Nachtsheim DA, Ryan S, Schröder M, Jensen L, Oosthuizen WC, Bester MN, Hagen W, Bornemann H (2019) Foraging behaviour of Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddellii) in connection to oceanographic conditions in the southern Weddell Sea. Prog Oceanogr 173:165–179
Nemoto T, Nasu K (1958) Thysanoessa macrura as a food of baleen whales in the Antarctic. Sci Rep Whales Res Inst 13:193–199
Nicholls KW, Østerhus S, Makinson K, Gammelsrød T, Fahrbach E (2009) Ice-ocean processes over the continental shelf of the southern Weddell Sea, Antarctica: a review. Rev Geophys 47:RG3003
Nichols DS, Nichols PD, Sullivan CW (1993) Fatty acid, sterol and hydrocarbon composition of Antarctic sea ice diatom communities during the spring bloom in McMurdo Sound. Antarct Sci 5:271–278
Nicol S (2006) Krill, currents, and sea ice: Euphausia superba and its changing environment. Bioscience 56:111–120
Norkko A, Thrush S, Cummings V, Gibbs M, Andrew N, Norkko J et al (2007) Trophic structure of coastal Antarctic food webs associated with changes in sea ice and food supply. Ecology 88:2810–2820
Núñez-Riboni I, Fahrbach E (2009) Seasonal variability of the Antarctic Coastal Current and its driving mechanisms in the Weddell Sea. Deep Sea Res I Oceanogr Res Pap 56:1927–1941
O’Brien DP (1987) Direct observations of the behavior of Euphausia superba and Euphausia crystallorophias (Crustacea: Euphausiacea) under pack ice during the Antarctic spring of 1985. J Crustac Biol 7:437–448
Pakhomov E, Perissinotto R (1996) Antarctic neritic krill Euphausia crystallorophias: spatio-temporal distribution, growth and grazing rates. Deep Sea Res I Oceanogr Res Pap 43:59–87
Pakhomov EA, Perissinotto R (1997) Spawning success and grazing impact of Euphausia crystallorophias in the Antarctic shelf region. In: Battaglia B, Valencia J, Walton DWH (eds) Antarctic communities: species, structure and survival. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 187–192
Parnell A, Inger R (2016) Stable isotope mixing models in R with SIMMR. Retrieved from https://cran.rproject.org/web/packages/simmr/vignettes/simmr.html
Parnell AC, Phillips DL, Bearhop S, Semmens BX, Ward EJ, Moore JW, Jackson AL, Grey J, Kelly DJ, Inger R (2013) Bayesian stable isotope mixing models. Environmetrics 24:387–399
Paul D, Skrzypek G, Forizs I (2007) Normalization of measured stable isotopic compositions to isotope reference scales-a review. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 21:3006–3014
Phleger CF, Nichols PD, Virtue P (1998) Lipids and trophodynamics of Antarctic zooplankton. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 120:311–323
Piñones A, Fedorov AV (2016) Projected changes of Antarctic krill habitat by the end of the 21st century. Geophys Res Lett 43:8580–8589
Post DM (2002) Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 83:703–718
Rau GH, Mearns AJ, Young DR, Olson RJ, Schafer HA, Kaplan IR (1983) Animal 13C/12C correlates with trophic level in pelagic food webs. Ecology 64:1314–1318
Ritz DA (1994) Social aggregation in pelagic invertebrates. Adv Mar Biol 30:156–216
Roe HSJ, Shale DM (1979) A new multiple rectangular midwater trawl (RMT 1 + 8 M) and some modifications to the Institute of Oceanographic Sciences’ RMT 1 + 8. Mar Biol 50:283–288
Rosier SHR, Hofstede C, Brisbourne AM, Hattermann T, Nicholls KW, Davis PE, Anker PG, Hillenbrand CD, Smith AM, Corr HF (2018) A new bathymetry for the southeastern Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf: implications for modern oceanographic processes and glacial history. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 123:4610–4623
Ross RM, Quetin LB, Newberger T, Shaw CT, Jones JL, Oakes SA, Moore KJ (2014) Trends, cycles, interannual variability for three pelagic species west of the Antarctic Peninsula 1993–2008. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 515:11–32
Ryan S, Hattermann T, Darelius E, Schröder M (2017) Seasonal cycle of hydrography on the eastern shelf of the Filchner Trough, Weddell Sea, Antarctica. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 122:6437–6453
Schmidt K, Atkinson A (2016) Feeding and food processing in Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana). In: Siegel V (ed) Biology and ecology of Antarctic Krill. Springer, Cham, pp 175–224
Schmidt K, Atkinson A, Stübing D, McClelland JW, Montoya JP, Voss M (2003) Trophic relationships among Southern Ocean copepods and krill: some uses and limitations of a stable isotope approach. Limnol Oceanogr 48:277–289
Schmidt, K, Brown, TA, Belt, ST, Ireland, LC, Taylor, KWR, Thorpe, SD, Ward, P, Atkinson A (2018) Do pelagic grazers benefit from sea ice? Insights from the Antarctic sea ice proxy IPSO25. Biogeosciences:1987–2006
Schnack-Schiel SB, Mujica A (1994) The zooplankton of the Antarctic Peninsula region. In: El-Sayed S (ed) Southern Ocean ecology: The BIOMASS Perspective. Cambridge University Press, UK, pp 79–92
Scott CL, Falk-Petersen S, Sargent JR, Hop H, Lønne OJ, Poltermann M (1999) Lipids and trophic interactions of ice fauna and pelagic zooplankton in the marginal ice zone of the Barents Sea. Polar Biol 21:65–70
Siegel V (2005) Distribution and population dynamics of Euphausia superba: summary of recent findings. Polar Biol 29:1–22
Smetacek V, Scharek R, Nöthig EM (1990) Seasonal and regional variation in the pelagial and its relationship to the life history cycle of krill. In: Kerry KR, Hempel G (eds) Antarctic ecosystems. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 103–114
Smith WO Jr, Sakshaug E (2013) Polar phytoplankton. In: Smith WO Jr (ed) Polar oceanography. Academic Press, New York, pp 477–525
Søreide JE, Hop H, Carroll ML, Falk-Petersen S, Hegseth EN (2006) Seasonal food web structures and sympagic-pelagic coupling in the European Arctic revealed by stable isotopes and a two-source food web model. Prog Oceanogr 71:59–87
Spreen G, Kaleschke L, Heygster G (2008) Sea ice remote sensing using AMSR‐E 89‐GHz channels. J Geophys Res (Oceans) 113: C02S03
Steinberg DK, Ruck KE, Gleiber MR, Garzio LM, Cope JS, Bernard KS, Stammerjohn SE, Schofield OM, Quetin LB, Ross RM (2015) Long-term (1993–2013) changes in macrozooplankton off the Western Antarctic Peninsula. Deep Sea Res I Oceanogr Res Pap 101:54–70
Taki K, Hayashi T, Naganobu M (2005) Characteristics of seasonal variation in diurnal vertical migration and aggregation of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) in the Scotia Sea, using Japanese fishery data. CCAMLR Sci 12:163–172
Thomas PG, Green K (1988) Distribution of Euphausia crystallorophias within Prydz Bay and its importance to the inshore marine ecosystem. Polar Biol 8:327–331
Torstensson A, Dinasquet J, Chierici M, Fransson A, Riemann L, Wulff A (2015) Physicochemical control of bacterial and protist community composition and diversity in Antarctic sea ice. Environ Microbiol 17:3869–3881
Trathan PN, Hill SL (2016) The importance of krill predation in the Southern Ocean. In: Siegel V (ed) Biology and ecology of Antarctic Krill. Springer, Cham, pp 321–350
Viso A-C, Marty J-C (1993) Fatty acids from 28 marine microalgae. Phytochemistry 34:1521–1533
Volkman J, Jeffrey S, Nichols P, Rogers G, Garland C (1989) Fatty acid and lipid composition of 10 species of microalgae used in mariculture. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 128:219–240
Wang SW, Budge SM, Iken K, Gradinger RR, Springer AM, Wooller MJ (2015) Importance of sympagic production to Bering Sea zooplankton as revealed from fatty acid-carbon stable isotope analyses. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 518:31–50
Acknowledgements
We thank the captain Stefan Schwarze and the crew of the RV ‘Polarstern’ expedition PS82 for their excellent support with work at sea. We thank Theresa Geißler, Julia Dürschlag and Dieter Janssen for their help with the laboratory analyses at the Alfred Wegener Institute, Germany. Furthermore, we acknowledge the support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC); Benjamin A. Lange: D. Kohlbach and B. A. Lange received a NSERC Visiting Fellowship in Canadian Laboratories. Comments and suggestions by two anonymous reviewers helped to improve the original version of the manuscript. This study is part of the Helmholtz Association Young Investigators Group Iceflux: Ice-ecosystem carbon flux in polar oceans (VH-NG-800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest (financial/non-financial).
Ethical approval
All international, national, and institutional guidelines for sampling of organisms for the study have been followed.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: N. Aberle-Malzahn.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reviewed by undisclosed experts.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohlbach, D., Lange, B.A., Graeve, M. et al. Varying dependency of Antarctic euphausiids on ice algae- and phytoplankton-derived carbon sources during summer. Mar Biol 166, 79 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-019-3527-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-019-3527-z