Abstract
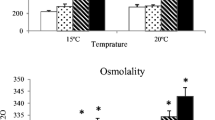
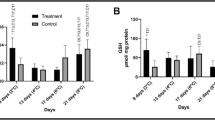
The Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis, originates from subtropical waters and displays great adaptability to environmental factors such as temperature. A comprehensive study on the effect of long-term temperature acclimation on xenobiotic metabolism, along with the assessment of other parameters related to physiological status, was designed to characterize the response of this species to temperature fluctuations within a realistic range. S. senegalensis juveniles were acclimated for a period of 60 days to two different ambient temperatures, 15 and 20 °C. Several hepatic, gill, muscular and plasmatic parameters were measured over time at the two temperatures. The lower temperature triggered, over time, the synthesis of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P450-related enzymes (e.g. 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase (EROD), carboxylesterases, and the conjugating enzyme uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase and, more significantly, EROD activity in gills. The antioxidant enzyme activities: catalase and glutathione reductase in liver were positively correlated to temperature. Plasmatic parameters (glucose, lactate, triglycerides and osmolality) were consistent with a good physiological status of the experimental fish. The expression of heat shock proteins in muscle did not significantly change in the two temperature groups. The results evidenced that the subtropical species S. senegalensis also uses the temperature compensation strategy to different degrees for most biotransformation enzymes; this response was more intense and faster in gills than in liver. This compensatory strategy did not apply to antioxidant enzymes and GST. The present findings highlight the need to consider the thermal history of the fish when using S. senegalensis as a sentinel in a biomarker-based pollution monitoring study. The fish plasticity on its strategy of physiological adaptation to temperature changes could contribute to explain the success in the geographical expansion of this species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamson A, Brandt I, Brunstrom B, Sundt RC, Jorgensen EH (2008) Monitoring contaminants from oil production at sea by measuring gill EROD activity in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Environ Pollut 153:169–175
Arellano-Aguilar O, Montero Montoya R, Macías García C (2009) Endogenous functions and expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes in teleost fish: a review. Rev Fish Sci 17:541–556
Arjona FJ, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Vargas-Chacoff L, del Rio MPM, Flik G, Mancera JM, Klaren PHM (2010) Acclimation of Solea senegalensis to different ambient temperatures: implications for thyroidal status and osmoregulation. Mar Biol 157:1325–1335
Beauvais SL, Cole KJ, Atchison GJ, Coffey M (2002) Factors affecting brain cholinesterase activity in bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus). Water Air Soil Pollut 135:249–264
Bonga SEW (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Botte ES, Smith-Keune C, Jerry DR (2013) Temperature: a prolonged confounding factor on cholinesterase activity in the tropical reef fish Acanthochromis polyacanthus. Aquat Toxicol 140:337–339
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carpenter HM, Fredrickson LS, Williams DE, Buhler DR, Curtis LR (1990) The effect of thermal-acclimation on the activity of arylhydrocarbon hydroxylase in rainbow-trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp Biochem Physiol C Comp Pharmacol 97:127–132
Castro C, Perez-Jimenez A, Guerreiro I, Peres H, Castro-Cunha M, Oliva-Teles A (2012) Effects of temperature and dietary protein level on hepatic oxidative status of Senegalese sole juveniles (Solea senegalensis). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 163:372–378
Collier AC, Tingle MD, Keelan JA, Paxton JW, Mitchell MD (2000) A highly sensitive fluorescent microplate method for the determination of UDP-glucuronosyl transferase activity in tissues and placental cell lines. Drug Metab Dispos 28:1184–1186
Costa PM, Caeiro S, Vale C, DelValls TA, Costa MH (2012) Can the integration of multiple biomarkers and sediment geochemistry aid solving the complexity of sediment risk assessment? A case study with a benthic fish. Environ Pollut 161:107–120
Costas B, Aragao C, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Vargas-Chacoff L, Arjona FJ, Mancera JM, Dinis MT, Conceicao LEC (2012) Different environmental temperatures affect amino acid metabolism in the eurytherm teleost Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis Kaup, 1858) as indicated by changes in plasma metabolites. Amino Acids 43:327–335
Dinis MT, Ribeiro L, Soares F, Sarasquete C (1999) A review on the cultivation potential of Solea senegalensis in Spain and in Portugal. Aquaculture 176:27–38
Durieux EDH, Farver TB, Fitzgerald PS, Eder KJ, Ostrach DJ (2011) Natural factors to consider when using acetylcholinesterase activity as neurotoxicity biomarker in young-of-year striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Fish Physiol Biochem 37:21–29
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Feidantsis K, Pörtner HO, Lazou A, Kostoglou B, Michaelidis B (2009) Metabolic and molecular stress responses of the gilthead seabream Sparus aurata during long-term exposure to increasing temperatures. Mar Biol 156:797–809
Feidantsis K, Antonopoulou E, Lazou A, Portner HO, Michaelidis B (2013) Seasonal variations of cellular stress response of the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). J Comp Physiol B 183:625–639
Fitzsimmons PN, Lien GJ, Nichols JW (2007) A compilation of in vitro rate and affinity values for xenobiotic biotransformation in fish, measured under physiological conditions. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 145:485–506
Fonseca VF, Franca S, Serafim A, Company R, Lopes B, Bebianno MJ, Cabral HN (2011a) Multi-biomarker responses to estuarine habitat contamination in three fish species: Dicentrarchus labrax, Solea senegalensis and Pomatoschistus microps. Aquat Toxicol 102:216–227
Fonseca VF, Franca S, Vasconcelos RP, Serafim A, Company R, Lopes B, Bebianno MJ, Cabral HN (2011b) Short-term variability of multiple biomarker response in fish from estuaries: influence of environmental dynamics. Mar Environ Res 72:172–178
Gonçalves C, Martins M, Costa MH, Caeiro S, Costa PM (2013) Ecological risk assessment of impacted estuarine areas: integrating histological and biochemical endpoints in wild Senegalese sole. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 95:202–211
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-Transferases. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Jorgensen EH, Wolkers J (1999) Effect of temperature on the P4501A response in winter- and summer-acclimated Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) after oral benzo a pyrene exposure. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56:1370–1375
Koenig S, Solé M (2012) Natural variability of hepatic biomarkers in Mediterranean deep-sea organisms. Mar Environ Res 79:122–131
Koenig S, Guillen K, Solé M (2013) Comparative xenobiotic metabolism capacities and pesticide sensitivity in adults of Solea solea and Solea senegalensis. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 157:329–336
Kyprianou T-D, Pörtner H, Anestis A, Kostoglou B, Feidantsis K, Michaelidis B (2010) Metabolic and molecular stress responses of gilthead seam bream Sparus aurata during exposure to low ambient temperature: an analysis of mechanisms underlying the winter syndrome. J Comp Physiol B 180:1005–1018
Lange U, Saborowski R, Siebers D, Buchholz F, Karbe L (1998) Temperature as a key factor determining the regional variability of the xenobiotic-inducible ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity in the liver of dab (Limanda limanda). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:328–338
López-Galindo C, Vargas-Chacoff L, Nebot E, Casanueva JF, Rubio D, Solé M, Mancera JM (2010a) Biomarker responses in Solea senegalensis exposed to sodium hypochlorite used as antifouling. Chemosphere 78:885–893
López-Galindo C, Vargas-Chacoff L, Nebot E, Casanueva JF, Rubio D, Solé M, Mancera JM (2010b) Sublethal effects of the organic antifoulant Mexel (R) 432 on osmoregulation and xenobiotic detoxification in the flatfish Solea senegalensis. Chemosphere 79:78–85
Mastropaolo W, Yourno J (1981) An ultraviolet spectrophotometric assay for alpha-naphthyl acetate and alpha-naphthyl butyrate esterases. Anal Biochem 115:188–193
McCormick SD (2001) Endocrine control of osmoregulation in teleost fish. Am Zool 41:781–794
Oliva M, de Canales MLG, Gravato C, Guilhermino L, Perales JA (2010) Biochemical effects and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in senegal sole (Solea senegalensis) from a Huelva estuary (SW Spain). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1842–1851
Oliva M, Vicente JJ, Gravato C, Guilhermino L, Galindo-Riano MD (2012) Oxidative stress biomarkers in Senegal sole, Solea senegalensis, to assess the impact of heavy metal pollution in a Huelva estuary (SW Spain): seasonal and spatial variation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 75:151–162
Olsvik PA, Vikesa V, Lie KK, Hevroy EM (2013) Transcriptional responses to temperature and low oxygen stress in Atlantic salmon studied with next-generation sequencing technology. BMC Genomics 14(1):817
Pörtner HO (2002) Climate variations and the physiological basis of temperature dependent biogeography: systemic to molecular hierarchy of thermal tolerance in animals. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 132:739–761
Pörtner HO, Lucassen M, Storch D (2005) Metabolic biochemistry: its role in thermal tolerance and in the capacities of physiological and ecological function. In: Farrell AP, Steffensen JF (eds) The physiology of polar fishes. Fish physiology, Vol 22. Elsevier Inc, Amsterdam, p 79. doi:10.1016/S1546-5098(04)22003-9
Regoli F, Giuliani ME (2014) Oxidative pathways of chemical toxicity and oxidative stress biomarkers in marine organisms. Mar Environ Res 93:106–117
Regoli F, Giuliani ME, Benedetti M, Arukwe A (2011) Molecular and biochemical biomarkers in environmental monitoring: a comparison of biotransformation and antioxidant defense systems in multiple tissues. Aquat Toxicol 105:56–66
Sabatés A, Martin P, Lloret J, Raya V (2006) Sea warming and fish distribution: the case of the small pelagic fish, Sardinella aurita, in the western Mediterranean. Glob Chang Biol 12:2209–2219
Salat J, Pascual J (2002) The oceanographic and meteorological station at l’Estartit (NW Mediterranean). In: Tracking long-term hydrological change in the Mediterranean Sea. CIESM Workshop Series, 16:29–32. Monaco
Sánchez-Nogué B, Varó I, Solé M (2013) Comparative analysis of selected biomarkers and pesticide sensitivity in juveniles of Solea solea and Solea senegalensis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3480–3488
Siscar R, Palanques A, Torreblanca A, Solé M (2013) Metal concentrations and detoxification mechanisms in Solea solea and Solea senegalensis from NW mediterranean fishing grounds. Mar Pollut Bull 77:90–99
Sleiderink HM, Beyer J, Scholtens E, Goksoyr A, Nieuwenhuize J, Vanliere JM, Everaarts JM, Boon JP (1995) Influence of temperature and polyaromatic contaminants on CYP1A levels in north-sea dab (Limandalimanda). Aquat Toxicol 32:189–209
Smith EM, Wilson JY (2010) Assessment of cytochrome P450 fluorometric substrates with rainbow trout and killifish exposed to dexamethasone, pregnenolone-16 alpha-carbonitrile, rifampicin, and beta-naphthoflavone. Aquat Toxicol 97:324–333
Solé M, Vega S, Varó I (2012) Characterization of type “B” esterases and hepatic CYP450 isoenzymes in Senegalese sole for their further application in monitoring studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:72–79
Somero GN (2010) The physiology of climate change: how potentials for acclimatization and genetic adaptation will determine ‘winners’ and ‘losers’. J Exp Biol 213:912–920
Somero GN (2012) The physiology of global change: linking patterns to mechanisms. Annu Rev Mar Sci 4:39–61
Tomanek L, Somero GN (1999) Evolutionary and acclimation-induced variation in the heat-shock responses of congeneric marine snails (genus Tegula) from different thermal habitats: implications for limits of thermotolerance and biogeography. J Exp Biol 202:2925–2936
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Varó I, Navarro JC, Nunes B, Guilhermino L (2007) Effects of dichlorvos aquaculture treatments on selected biomarkers of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) fingerlings. Aquaculture 266:87–96
Vassault A (1983) Lactate dehydrogenase. In: Bergmeyer MO (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, enzymes: oxidoreductases, transferases. Academic Press, New York, pp 118–126
Vinagre C, Fonseca V, Cabral H, Costa MJ (2006) Habitat suitability index models for the juvenile soles, Solea solea and Solea senegalensis, in the Tagus estuary: defining variables for species management. Fish Res 82:140–149
Vinagre C, Narciso L, Pimentel M, Cabral HN, Costa MJ, Rosa R (2013) Contrasting impacts of climate change across seasons: effects on flatfish cohorts. Reg Environ Change 13:853–859
West JL, Bailey JR, Almeida-Val VMF, Val AL, Sidell BD, Driedzic WR (1999) Activity levels of enzymes of energy metabolism in heart and red muscle are higher in north-temperate-zone than in Amazonian teleosts. Can J Zool 77:690–696
Wheelock CE, Phillips BM, Anderson BS, Miller JL, Miller MJ, Hammock BD (2008) Applications of carboxylesterase activity in environmental monitoring and toxicity identification evaluations (TIEs). Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 195:117–178
Zenetos A, Gofas S, Morri C, Rosso A et al (2012) Alien species in the Mediterranean Sea by 2012. A contribution to the application of European Union’s Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD). Part 2. Introduction trends and pathways. Mediterr Mar Sci 13:328–352
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the Ministry of Science and Innovation of Spain (ref: CTM2010-16611). S. Piñeiro and L. Cabrera from the SCSIE University of Valencia are acknowledged for the fish maintenance and the students K. Guillén, S. Brau and A. Martínez for their help in sample processing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B. Wallace.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solé, M., Varó, I., González-Mira, A. et al. Xenobiotic metabolism modulation after long-term temperature acclimation in juveniles of Solea senegalensis . Mar Biol 162, 401–412 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2588-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2588-2