Abstract
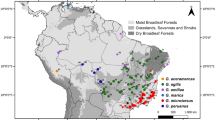
Pleistocene eustatic changes in sea level are often invoked to explain genetic divergence among marine organisms. However, molecular phylogenies have revealed relatively few examples of speciation events dating to the Pleistocene. We present a species-level hypothesis of the timing of evolution for the Pomacentrus coelestis species complex (Pomacentridae), based on the nuclear S7 intron and the mitochondrial Cytb gene, and reconstruct ancestral range distributions across the timetree. Ancestral range reconstruction suggests the complex originated in the Coral Triangle and East Indian Ocean, with subsequent range expansion outward from this region. We suggest that land barriers to dispersal (e.g., Indo-Pacific barrier) may be responsible for the divergence between Indian (P. alleni, P. similis, P. caeruleopunctatus, and P. caeruleus) and Pacific (P. micronesicus, P. auriventris, and P. coelestis) species groups, and subsequent isolation by Pleistocene sea-level fluctuations in certain areas of the Coral Triangle (glacial refugia) may play an important role in the diversification of this species complex. Additionally, our analyses show cryptic lineages within P. micronesicus and highlight the need for comprehensive sampling within and among species to reveal recent speciation events.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen GR (1991) Damselfishes of the World. Mergus Publishers, Melle
Allen GR (2002) Description of two new species of damselfishes (Pomacentridae: Pomacentrus) from Madagascar. Aqua 6:45–52
Allen GR (2008) Conservation hotspots of biodiversity and endemism for Indo-Pacific coral reef fishes. Aquat Conser Mar Freshw Ecosyst 18:541–556
Allen GR, Erdmann MV (2006) Cirrhilabrus cenderawasih, a new wrasse (Pisces: Labridae) from Papua, Indonesia. Aqua J Ichthyol Aquat Biol 11:125–131
Allen GR, Erdmann MV (2012) Reef Fishes of the East Indies. Tropical Reef Research, Perth
Barber PH, Bellwood DR (2005) Biodiversity hotspots: evolutionary origins of biodiversity in wrasses (Halichoeres: Labridae) in the Indo-Pacific and new World tropics. Mol Phylogenet Evol 35:235–253
Bellwood DR, Wainwright PC (2002) The history and biogeography of fishes on coral reefs. In: Sale PF (ed) Coral Reef Fishes: Dynamics and Diversity on a Complex Ecosystem. Academic Press, New York
Bellwood DR, Klanten S, Cowman PF, Pratchett MS, Konow N, van Herwerden L (2010) Evolutionary history of the butterflyfishes (f: Chaetodontidae) and the rise of coral feeding fishes. J Evol Biol 23:335–349
Benzie JAH (1999) Major genetic differences between crown-of-thorns starfish (Acanthaster planci ) populations in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Evolution 53:1782–1795
Briggs JC, Bowen BW (2012) A realignment of marine biogeographic provinces with particular reference to fish distributions. J Biogeogr 39:12–30
Carpenter KE, Springer VG (2005) The center of the center of marine shore fish biodiversity: the Philippine Islands. Environ Biol Fish 72:467–480
Carpenter KE, Barber PH, Crandall ED, Ablan-Lagman MCA, Mahardika GN, Ambariyanto et al (2011) Comparative phylogeography of the Coral Triangle and implications for marine management. J Mar Biol 2011:1–14
Chappell J (1981) Relative and average sea level changes, and endo-, epi-, and exogenic processes on the Earth. In: Allison I (ed) Sea level, ice, and climatic change. International Association of Hydrological Sciences, vol 131. International Association of Hydrological Science, United Kingdom
Choat JH, Klanten OS, van Herwerden L, Robertson DR, Clements KD (2012) Patterns and processes in the evolutionary history of parrotfishes (Family Labridae). Biol J Linn Soc 107:529–557
Chow S, Hazama K (1998) Universal PCR primers for S7 ribosomal protein gene introns in fish. Mol Ecol 7:1247–1263
Coates AG, Obando JA (1996) The geologic evolution of the Central American isthmus. In Jackson J, Budd AF, Coates AG (eds) Evolution and environment in tropical America, University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Cowman PF, Bellwood DR (2011) Coral reefs as drivers of cladogenesis: expanding coral reefs, cryptic extinction events, and the development of biodiversity hotspots. J Evol Biol 24:2543–2562
Craig MT, Eble JA, Bowen BW, Robertson DR (2007) High genetic connectivity across the Indian and Pacific Oceans in the reef fish Myripristis berndti (Holocentridae). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 334:245–254
Drew J, Barber PH (2009) Sequential cladogenesis of the reef fish Pomacentrus moluccensis (Pomacentridae) supports the peripheral origin of marine biodiversity in the Indo-Australian archipelago. Mol Phylogenet Evol 53:335–339
Drew J, Allen G, Kaufman L, Barber PH (2008) Endemism and regional colour and genetic differences in five putatively cosmopolitan reef fishes. Conserv Biol 22:965–975
Drew JA, Allen GR, Erdmann MV (2010) Congruence between mitochondrial genes and color morphs in a coral reef fish: population variability in the Indo-Pacific damselfish Chrysiptera rex (Snyder, 1909). Coral Reefs 29:439–444
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol Biol 7:214
Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A (2012) Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol 29:1969–1973
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Fessler JL, Westneat MW (2007) Molecular phylogenetics of the butterflyfishes (Chaetodontidae): taxonomy and biogeography of a global coral reef fish family. Mol Phylogenet Evol 45:50–68
Gaither MR, Rocha LA (2013) Origins of species richness in the Indo-Malay-Philippine biodiversity hotspot: evidence for the centre of overlap hypothesis. J Biogeogr 40:1638–1648
Goetze E (2011) Population differentiation in the open sea: insights from the pelagic copepod Pleuromamma xiphias. Integr Comp Biol 51:580–597
Kennett JP, Keller G, Srinivasan MS (1985) Miocene planktonic foraminiferal biogeography and paleogeographic development of the Indo-Pacific region. Geol Soc Mem 163:197–236
Knowlton N (2000) Molecular genetic analyses of species boundaries in the sea. Hydrobiologia 420:73–90
Leray M, Beldade R, Holbrook SJ, Schmitt RJ, Planes S, Bernardi G (2010) Allopatric divergence and speciation in coral reef fish: the three-spot Dascyllus, Dascyllus trimaculatus, species complex. Evolution 64:1218–1230
Liu SYV, Dai CF, Allen GR, Erdmann MV (2012) Phylogeography of the neon damselfish Pomacentrus coelestis indicates a cryptic species and different species origins in the West Pacific Ocean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 458:155–167
Liu SYV, Ho HCH, Dai CF (2013) A new species of Pomacentrus (Actinopterygii: Pomacentridae) from Micronesia, with comments on its phylogenetic relationships. Zool Stud 52:6–13
Matzke NJ (2013) BioGeoBEARS: BioGeography with Bayesian (and likelihood) evolutionary analyses in R scripts. Dissertation, University of California, Berkeley
McCafferty S, Bermingham E, Quenouille B, Planes S, Hoelzer G, Asoh K (2002) Historical biogeography and molecular systematics of the Indo-Pacific genus Dascyllus (Teleostei: Pomacentridae). Mol Ecol 11:1377–1392
McMillan WO, Palumbi SR (1995) Concordant evolutionary patterns among Indo-West Pacific butterflyfishes. Proc R Soc B-Biol Sci 260:229–236
Messmer V, van Herwerden L, Munday PL, Jones GP (2005) Phylogeography of colour polymorphism in the coral reef fish Pseudochromis fuscus, from Papua New Guinea and the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 24:392–402
Mora C, Sale PF (2002) Are populations of coral reef fish open or closed? Trends Ecol Evol 17:422–428
Naish T, Powell R, Levy R, Wilson G, Scherer R, Talarico F, Krissek L, Niessen F, Pompilio M, Wilson T et al (2009) Obliquity-paced Pliocene West Antarctic ice sheet oscillations. Nature 458:322–328
Palumbi SR (1994) Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, and marine speciation. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 25:547–572
Palumbi SR (1996) What can molecular genetics contribute to marine biogeography? An urchin’s tale. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 203:75–92
Posada D (2008) JModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:123–1256
Potts DC (1983) Evolutionary disequilibrium among Indo-Pacific corals. Bull Mar Sci 33:619–632
Randall JE (1998) Zoogeography of shore fishes of the Indo-Pacific region. Zool Stud 37:227–268
R Development Team (2012) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.r-project.org
Renema W, Bellwood DR, Braga JC, Bromfield K, Hall R, Johnson KG, Lunt P, Meyer CP, McMonagle LB, Morley RJ, O’Dea A, Tood JA, Wesselingh FP, Wilson MEJ, Pandolfi JM (2008) Hopping hotspots: global shifts in marine biodiversity. Science 321:654–657
Ridgway T, Sampayo EM (2005) Population genetic status of the western Indian Ocean; What do we know? West Indian Ocean J Mar Sci 4:1–9
Rocha LA, Bowen BW (2008) Speciation in coral-reef fishes. J Fish Biol 72:1101–1121
Rohling EJ, Braun K, Grant K, Kucera M, Robers AP, Siddall M, Trommer G (2010) Comparison between Holocene and Marine Isotope Stage-11 sea-level histories. Earth Planet Sci Lett 291:97–105
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Hohna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard M, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542
Santini F, Nguyen MTT, Sorenson L, Waltzek TB, Lynch Alfaro JW, Eastman JM, Alfaro ME (2013a) Do habitat shifts drive diversification in teleost fishes? An example from the pufferfishes (Tetraodontidae). J Evol Biol 26:1003–1018
Santini F, Sorenson L, Alfaro ME (2013b) A new multi-locus timescale reveals the evolutionary basis of diversity patterns of triggerfishes and filefishes (Balistidae, Monacanthidae; Tetraodontiformes). Mol Phylogenet Evol 69:165–176
Santini F, Sorenson L, Marcroft T, Dornburg A, Alfaro ME (2013c) A multilocus molecular phylogeny of boxfishes (Aracanidae, Ostraciidae; Tetraodontiformes). Mol Phylogenet Evol 66:153–160
Satapoomin U (2002) In: Comparative study of reef fish fauna in Thai waters: the Gulf of Thailand versus the Andaman Sea. Technical Paper Phuket Marine Biological Center
Schultz JK, Pyle RL, DeMartini E, Bowen BW (2007) Genetic connectivity among color morphs and Pacific archipelagos for the flame angelfish, Centropyge loriculus. Mar Biol 151:167–175
Siddall M, Rohling EJ, Almogi-Labin A, Hemleben C, Meischner D, Schmelzer I, Smeed DA (2003) Sea-level fluctuations during the last glacial cycle. Nature 423:853–858
Sorenson L, Santini F, Carnevale G, Alfaro ME (2013) A multi-locus timetree of surgeonfishes (Acanthuridae, Percomorpha), with revised family taxonomy. Mol Phylogenet Evol 68:150–160
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Steinke D, Zemlak TS, Hebert PDN (2009) Barcoding Nemo: DNA-based identifications for the ornamental fish trade. Plos One:e6300
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Taylor MS, Hellberg ME (2005) Marine radiations at small geographic scales: speciation in neotropical reef gobies (Elacatinus). Evolution 59:374–385
Vogler C, Benzie J, Barber PH, Erdmann MV, Ambariyanto, Sheppard C, Tenggardjaja K, Gérard K, Wörheide G (2012) Phylogeography of the crown-of-thorns starfish in the Indian Ocean. Plos One:e43499
Voris HK (2000) Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia: shorelines, river systems and time durations. J Biogeogr 27:1153–1167
Wallace CC, Paulay G, Hoeksema BW, Bellwood DR, Hutchings PA, Barber PH, Erdmann M, Wolstenholme J (2002) Nature and origins of unique high diversity reef faunas in the Bay of Tomini, Central Sulawesi: the ultimate “centre of diversity”? P Ninth Int Coral Reef Symp 1:185–192
Woodland DJ (1983) Zoogeography of the Siganidae (Pisces): an interpretation of distribution and richness patterns. Bull Mar Sci 33:713–717
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Andrew Bentley (University of Kansas Biodiversity Institute) and Ofer Gon (South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity) for providing tissue samples of Pomacentrus caeruleopunctatus (SAIAB 80854 and SAIAB 77347, respectively), and Bruno Frederich for sharing samples of Pomacentrus caeruleus from Madagascar. This study was supported by a grant from the National Science Council of Taiwan ROC (NSC99-2811-M-002-151) to C.F.D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Taylor.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorenson, L., Allen, G.R., Erdmann, M.V. et al. Pleistocene diversification of the Pomacentrus coelestis species complex (Pisces: Pomacentridae): historical biogeography and species boundaries. Mar Biol 161, 2495–2507 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2521-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2521-8